Before we get started:
Every system needs a fail-safe, and ours is no exception. While designing our previous components, it occurred to us that we need a contingency plan in case our Control and Cleanse sections failed, or were overwhelmed. At this point, our patient would probably require external help, in the form of a dentist check-up.
This problem is, however, more complex than you might think. For example, many people are unaware of the extent of their tooth decay until they start to feel severe pain – at which point it is too late for preventive measures! Many people also live in areas far from dental coverage, and a visit to the dentist becomes a significant investment in time and expense.
Most importantly, for people needing Long-Term-Care, or disabled persons, who are a significant target user of HOPE (see [Project Overview] for more information), timely dental checkups become even more of a challenge because it is up to the caretaker to discover and report the decay.
For this reason, we have decided to develop a system to detect tooth decay as it is happening, and to send out a warning message to HOPE’s user.
So how did we do it?
Right now you probably know the main microbial target of our project, S. mutans. However, aside from S. mutans, there exists numerous bacteria that also play a role in tooth decay. One of them is a closely related species in the same genus: Streptococcus sobrinus.
So what makes S. sobrinus so special? For starters, it is a very good indicator for tooth decay – even more so than S. mutans, its main cause! Also, like S. mutans, it is present in almost everyone’s mouth, meaning it is safe to use and safe to insert. Lastly, a peculiar trait for S. sobrinus is that its population rises sharply right before tooth decay is about to occur. Therefore, if we inserted a modified S. sobrinus, and allowed it to manufacture a distinct signaling product, we can detect when tooth decay is about to happen by the sudden flood of that product.
But what will that product be? A fluorescent protein is very visible, but natural low levels of S. sobrinus in your mouth would mean a perpetual colored glow on your teeth, which can be embarrassing and unsightly. Something that’s more pleasant, just as effective, but not quite as conspicuous is a smell, and specifically the smell of banana, caused by isoamyl acetate.
Isoamyl acetate is produced from many possible pathways, but a convenient three-step mechanism uses L-Leucine as the raw material, and involves Saccharomyces cerevisiae, otherwise known as the Baker’s yeast or the Brewer’s yeast. In this case, we stand on the shoulders of past teams, as the [2006 MIT iGEM team] has already biobricked the three enzymes. Because of this, we simply constructed the three enzymes together into a full circuit.
Aside from that, we added two terminators in front of the main enzymes, in order to act as a threshold (Please see [Control: Target] for more information on the use of terminators as thresholds). The significance of this addition is that it prevents a constitutive expression of the banana odor, and thus makes it less detectable and annoying to users. Only when tooth decay is about to happen and the amount of S. sobrinus multiplies hugely do users start to detect the characteristic banana odor.

Putting it to the test!
Part introduction
(1) Branched-chain amino acid transaminase (banana 1): Branched-chain amino acid transaminase is a branched-chain amino acid transaminase derived from BAT2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BAT2 catalyzes the first step in isoamyl alcohol biosynthesis: conversion of leucine to α-ketoisocaproate via enzymatic reaction.
(2) Ketoisocaproate decarboxylase (banana 2): Ketoisocaproate decarboxylase is a branched-chain amino acid transaminase derived from THI3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. THI3 catalyzes the second step in isoamyl alcohol biosynthesis: conversion of α-ketoisocaproate to 3-methylbutanal via enzymatic reaction.α-ketoisocaproate can be converted to isoamyl alcohol which is a precursor to isoamyl acetate (banana odor).
(3) Alcohol acetyltransferase I (banana 3): Alcohol acetyltransferase I is derived from ATF1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. ATF1 catalyzes the conversion of isoamyl alcohol to isoamyl acetate. Isoamyl acetate has a banana smell.
Future work
Banana odor biosynthetic system contains BAT2 gene (j45009) and THI3 genes (j45009) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of isoamyl alcohol, and ATF1 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of isoamyl acetate, which has a banana smell. BAT2 encodes a cytosolic branched-chain amino acid transaminase that catalyzes the conversion of leucine to α-ketoisocaproate. THI3 encodes an α-ketoisocaproate decarboxylase that catalyzes the conversion of α-ketoisocaproate to 3-methylbutanal. 3-methylbutanal is reduced to isoamyl alcohol by an NADH-dependent reaction by an alcohol dehydrogenase. ATF1 catalyzes the conversion of isoamyl alcohol to isoamyl acetate, which has a banana smell.
Conduct “blind smell tests” that is participants have to distinguish between cell cultures producing banana odor and the natural fecal odor of E. coli.
Analyze cultures with the banana odor biosynthetic system for isoamyl acetate production and measure levels of isoamyl acetate by gas chromatography (anticipated result).
GC analysis standard curve isoamyl acetate RT = 6.3 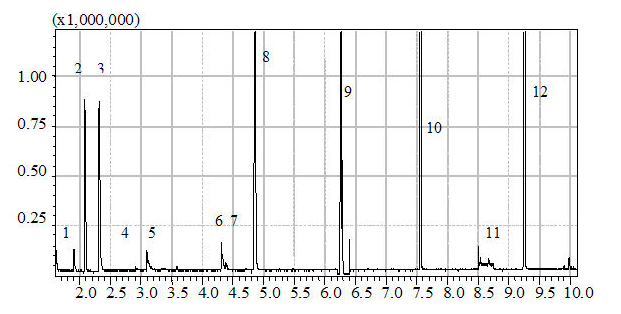 cited from virtual lab website which is free to copy and redistribute
cited from virtual lab website which is free to copy and redistribute
Measure isoamyl acetate concentration of cultures at different culture cell densities over growth time (anticipated result).
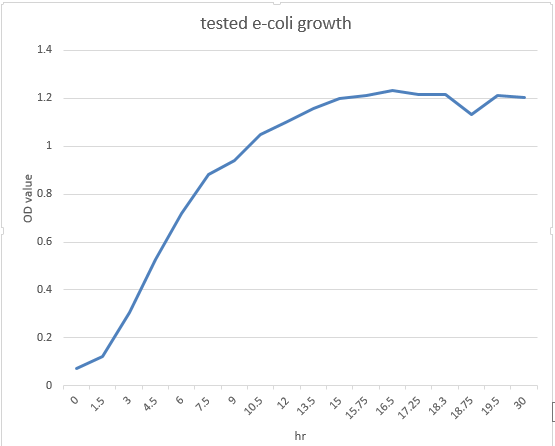
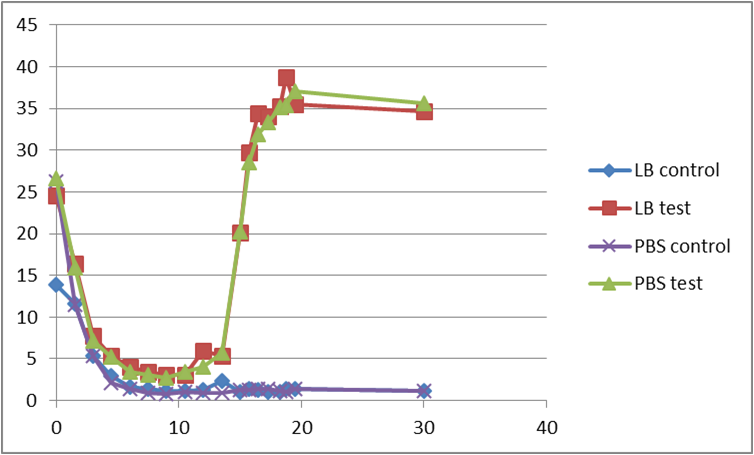
These are the e-coli growth curve and the INPNC display curve we tested in the attachment experiment.We expected the expression curve of banana odor biosynthetic system might assemble the tendency of them.
Our results
(1)

In the well of 4 and 6, after electrophoresis by using 1% gel, the DNA lengths are close to 2000 bp, and those are cut by using restriction enzyme EcoR1 and Spe1. The correct length of vector after cutting is 2043 bp, and the correct length of insert after cutting is 1161 bp.
When cut by restriction enzyme Xba1 and Pst1, the result in well 8 and 10 show that the DNA lengths are close to 2000 bp and 1500 bp. The correct length of vector after cutting is 2044 bp, and the correct length of insert after cutting is 1160 bp.
(2)
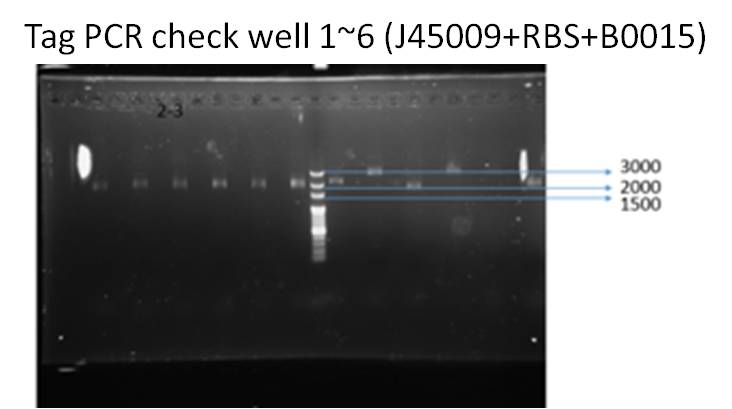
We ran taq PCR and got the result with correct DNA length (about 2000 bp), which means successfully ligation.
(3)
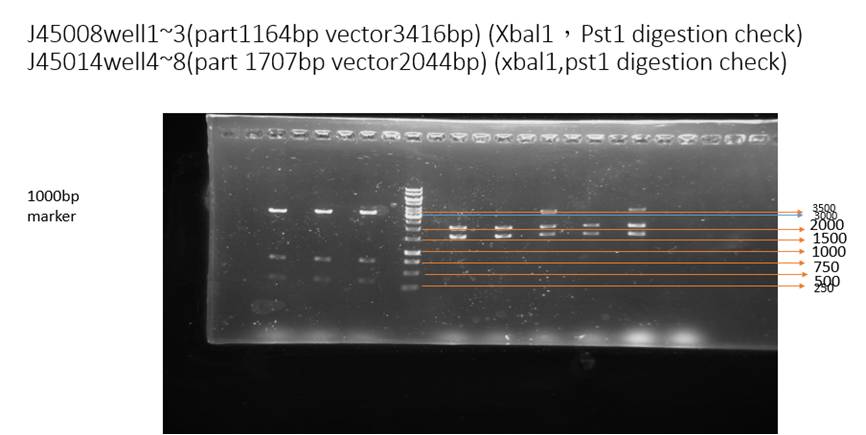
This figure is a digestion check of our part. Restriction enzyme Pst1 and Xba1 is added to cut BBa_J25008 (well1~3). The result shows the correct vector lengths (3416 bp). Besides, restriction enzyme Pst1 and Xba1 is added to cut BBa_J45014(well4~8), the results shows the correct vector lengths (about 2044 bp) and insert lengths (about 1707 bp).
 "
"