Team:Paris Saclay/Project/Odor-free ecoli
From 2014.igem.org
(→Odor-free E.coli chassis) |
(→The Principle of the construction) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==The Principle of the construction== | ==The Principle of the construction== | ||
| - | In the lab, we already had a strain in which the tnaA was replaced by a kanamycin resistance, but this strain was too modified to be used for our project. So we switched the tnaA sequence with the kanamycin resistance in our bacterium by phage transduction. After the recombination, we used a flipase to delete the kanamycin resistance. The remaining bacterium doesn't smell at all. | + | In the lab, we already had a strain in which the tnaA was replaced by a kanamycin resistance, but this strain was too modified to be used for our project. So we switched the tnaA sequence with the kanamycin resistance in our bacterium by phage transduction. Transduction is the transfer of bacterial DNA from one bacterium (the donor) to another (the recipient) by a bacteriophage P1. |
| + | |||
| + | After the recombination, we used a flipase to delete the kanamycin resistance. The remaining bacterium doesn't smell at all. | ||
[[File:Paris Saclay Odor Free coli.jpg|500px|center]] | [[File:Paris Saclay Odor Free coli.jpg|500px|center]] | ||
{{Team:Paris_Saclay/default_footer}} | {{Team:Paris_Saclay/default_footer}} | ||
Revision as of 17:50, 7 October 2014

Contents |
Countdown
This page is under Romain's responsibility
- Deadline: 08/oct.
- Completed text.
- Deadline: 12/oct
- Final review Philipe.
Odor-free E.coli chassis
Introduction
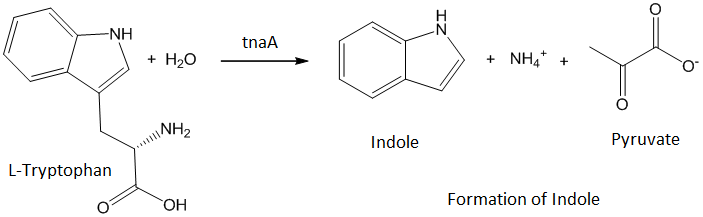
Escherichia coli stinks because of the tnaA gene which produces an enzyme that transforms the L-tryptophan into indole, responsible for the stench. If we want our lemon to smell like one, we have to delete this gene.
The Principle of the construction
In the lab, we already had a strain in which the tnaA was replaced by a kanamycin resistance, but this strain was too modified to be used for our project. So we switched the tnaA sequence with the kanamycin resistance in our bacterium by phage transduction. Transduction is the transfer of bacterial DNA from one bacterium (the donor) to another (the recipient) by a bacteriophage P1.
After the recombination, we used a flipase to delete the kanamycin resistance. The remaining bacterium doesn't smell at all.
 "
"