Team:Paris Saclay/Modeling/oxygen diffusion
From 2014.igem.org
(→Graphical visualization) |
(→Oxygen Diffusion) |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
By replacing $(2)$ in $(1)$, we obtain the following '''equation of diffusion''' : | By replacing $(2)$ in $(1)$, we obtain the following '''equation of diffusion''' : | ||
| - | \[ \forall t, \forall x, \bigg( \frac{\partial}{\partial t} - D \frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2} \bigg) n(x,t) = \sigma (x,t) \qquad (3) \] | + | \[ \forall t>0, \forall x, \bigg( \frac{\partial}{\partial t} - D \frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2} \bigg) n(x,t) = \sigma (x,t) \qquad (3) \] |
As our lemon is exposed to the ambient air, we stay in steady state where the source $ \sigma (x,t) $ is equal to $N_0$ the quantity of $O_2$ in the air. | As our lemon is exposed to the ambient air, we stay in steady state where the source $ \sigma (x,t) $ is equal to $N_0$ the quantity of $O_2$ in the air. | ||
Revision as of 17:46, 9 October 2014

Contents |
Oxygen Diffusion
Countdown
This page is under Eugene's responsibility
- Deadline: 08/oct.
- Final text
- Deadline: 12/oct
- Final review by Claire.
Oxygen Diffusion
To realise our artwork, we use an agarose gel to obtain the shape of a lemon. To push the resemblance to the extreme, we wish to have a crust in the edge of the lemon when we separate it. In fact, we build bacteria who produce yellow/green color in presence of oxygen. Thus we must evaluate the penetration of the oxygen in the gel !
Oxygen penetrates into the gel by diffusion phenomenon that we will study below. We first use the following phenomenological law suggested by Adolphe Fick in 1855:
In an homogeneous and isotropic environment, containing particles distributed inhomogeneously, appears spontaneously a volumetric flow density vector particle $\overrightarrow{J}(M,t) $. In any point $M$ in space, this vector is proportional to the gradient of the particle density $n(M,t)$. Mathematically, this relationship takes the form: \[ \overrightarrow{J}(M,t) = - D \times \nabla n(M,t) \qquad (1) \] where $D$ is the diffusion coefficient and $\nabla$ is the gradient vector.
In equation from Fick's law above, we need to know the parameter $D$. We then searched in scientific literature and the article [1] describes a method to get it. Referring to this article, the diffusion coefficient of oxygen in agarose is $ D = 0{,}256 \times 10^{-8} m^2 s^{-1} $.
The phenomenon we are facing is quite difficult to tackle if taken as a whole and we must emit a number of intuitively acceptables hypothesis:
- To simplify the problem, we consider that the diffusion of oxygen particle occurs only in one direction. So $\overrightarrow{J}(M,t) = J(x,t) \overrightarrow{e}_x $. This hypothesis is credible because we seek the maximum penetrance of oxygen. This is why we consider that the diffusion occurs in the line of greatest slope.
- Spatial variations in the density of particles are connected to spatial variations of the vector $\overrightarrow{J}(M,t)$ by the material's equation of conservation in presence of volume distribution of particle source $\sigma (x,t)$ (device which injects or subtracts the particles to the system) :
\[ \frac{\partial n}{\partial t} (x,t) = - \frac{\partial J}{\partial x} (x,t) + \sigma (x,t) \qquad (2) \]
By replacing $(2)$ in $(1)$, we obtain the following equation of diffusion : \[ \forall t>0, \forall x, \bigg( \frac{\partial}{\partial t} - D \frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2} \bigg) n(x,t) = \sigma (x,t) \qquad (3) \]
As our lemon is exposed to the ambient air, we stay in steady state where the source $ \sigma (x,t) $ is equal to $N_0$ the quantity of $O_2$ in the air.
To solve this equation, we use Fourier's analysis and it is known (classical solution of the heat equation) that
\[ \forall x, \forall t>0, n(x,t) = \frac{N_0}{\sqrt{4 \pi D t}} exp \bigg(- \frac{x^2}{4 D t} \bigg) + \int_{0}^{t} \underbrace{N_0 * exp \bigg(- \frac{|x|^2}{4 D \tau} \bigg)}_{= 0 \text{ by symmetry of the gaussian distribution }} \frac{d\tau}{\sqrt{4 \pi D \tau} } \]
Whence, \[ \boxed{ \forall x, \forall t>0, n(x,t) = \frac{N_0}{\sqrt{4 \pi D t}} exp \bigg(- \frac{x^2}{4 D t} \bigg) } \]
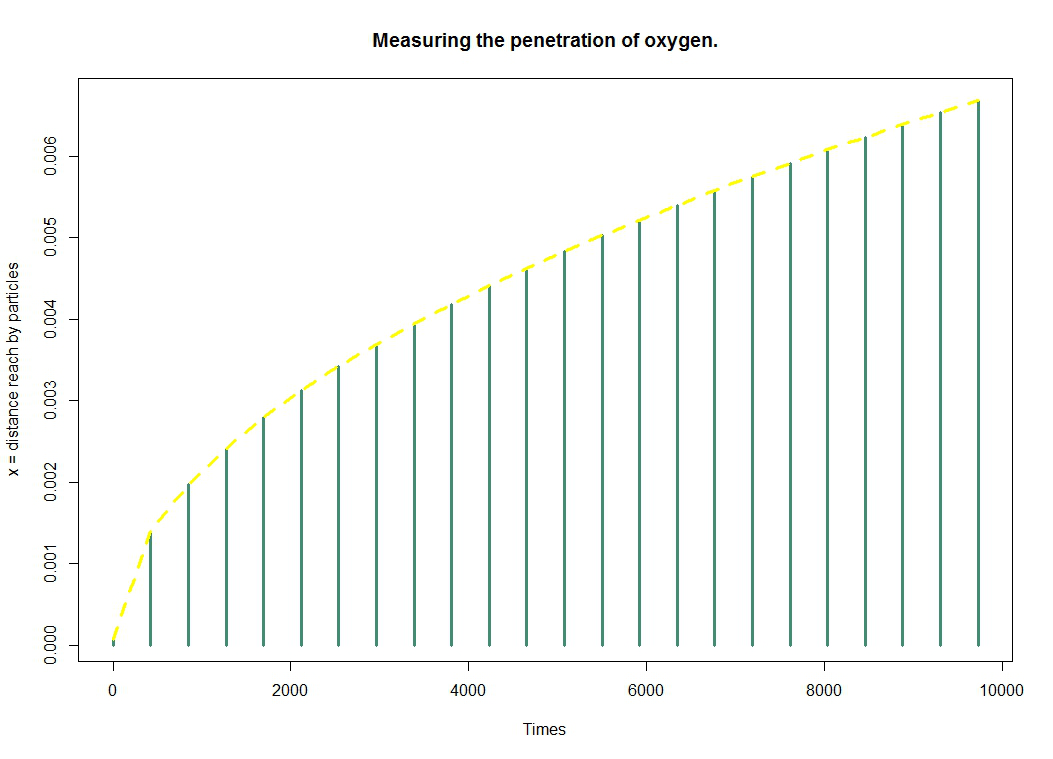
Thus we deduce easily that the average dispersion of the particles is given by the variance $\boxed{ \Delta x = \sqrt{2Dt} }$. Using this formula, we deduct that, for example, oxygen will penetrate $3 \times 10^{-3} m$ in $1956.522 s = 32.6082 $ minutes.
The charts below give us a very clear idea of penetrance evaluated over time.
Graphical visualization
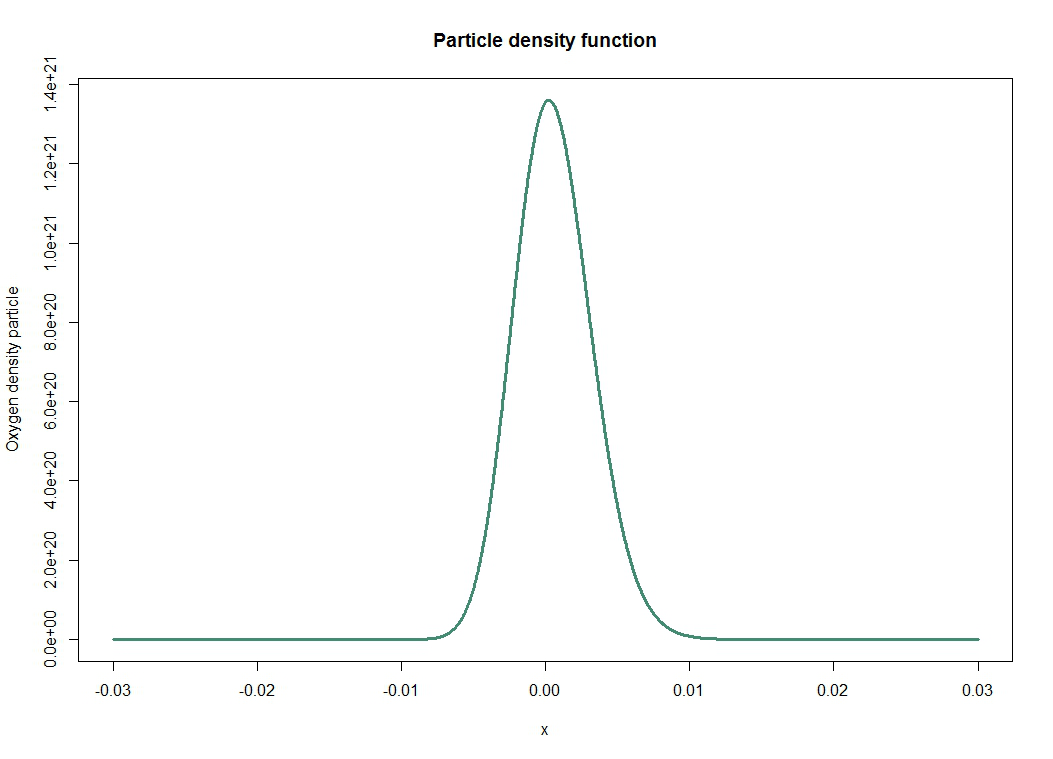
We represent in the first figure the solution of the diffusion equation that was previously established. This basically tells us the mean and the average dispersion of particles: it is a probability density given by
\[ \forall x, \forall t>0, n(x,t) = \frac{N_0}{\sqrt{4 \pi D t}} exp \bigg(- \frac{x^2}{4 D t} \bigg) \]
Remember that the purpose of this model is to provide information on the penetration of oxygen into the gel. The figure represents the distance reached by oxygen particles over time. We get it through the formula $ \Delta x = \sqrt{2Dt} $.
[1] A.C. Hulst, H.J.H. Hens, R.M. Buitelaar and J. Tramper, Determination of the effective diffusion coefficient of oxygen in gel materials in relation to gel concentration, Biotechnology Techniques Vol 3 No 3 199-204 (1989).
[2] Vincent Renvoizé, Physique PC-PC*, Cap Prepas, Pearson Education, 2010.
 "
"