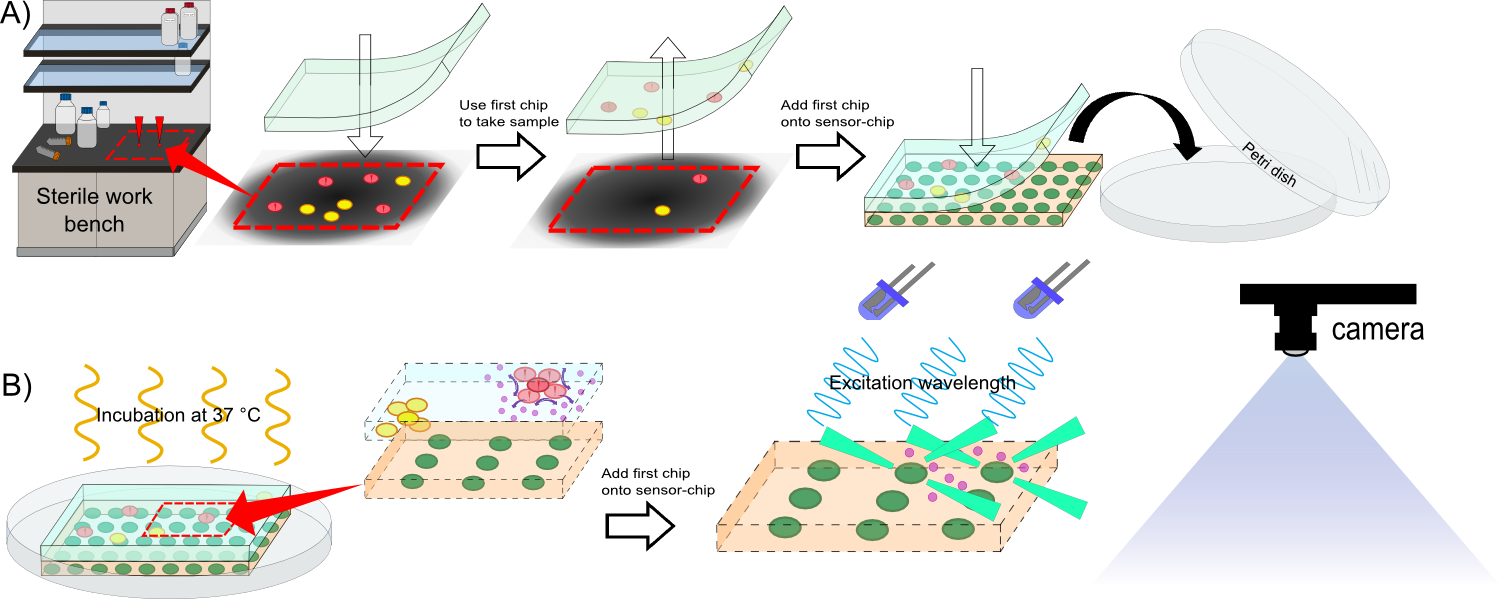
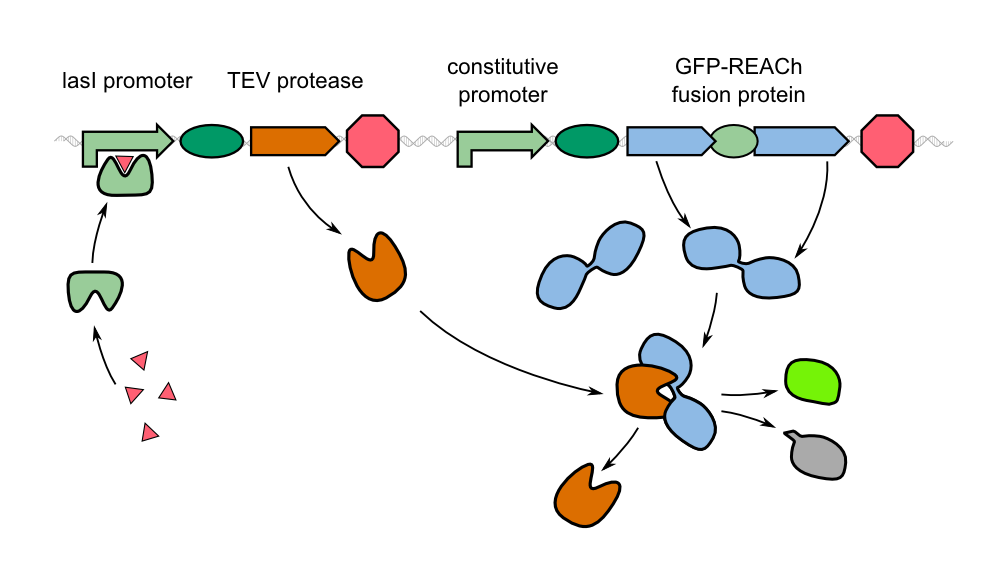
Team:Aachen/Project/2D Biosensor
From 2014.igem.org
Aschechtel (Talk | contribs) (→Achievements) |
Aschechtel (Talk | contribs) (→Achievements) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
| - | === | + | === Medium === |
At the beginning we had no own device and had to work with the equipment of the lab: a Molecular Imager® Gel Doc<sup>TM</sup> XR+ from BIO-RAD. The Gel Doc<sup>TM</sup> uses uv light and has only two filter. Because of this it was not ideal for our project. | At the beginning we had no own device and had to work with the equipment of the lab: a Molecular Imager® Gel Doc<sup>TM</sup> XR+ from BIO-RAD. The Gel Doc<sup>TM</sup> uses uv light and has only two filter. Because of this it was not ideal for our project. | ||
LB medium has under uv light a hight fluorescence. The background fluorescence was to high to see a signal of our cells so we used minimal media (NA, M9, Hartman) to minimize the background. This worked fine for the first tries but the cells don't grow well in the minimal media. | LB medium has under uv light a hight fluorescence. The background fluorescence was to high to see a signal of our cells so we used minimal media (NA, M9, Hartman) to minimize the background. This worked fine for the first tries but the cells don't grow well in the minimal media. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
For longer storage up to 5 days in the fridge (+ 4°C) TB medium can be used. It has a smal background flourescence in WatsOn. | For longer storage up to 5 days in the fridge (+ 4°C) TB medium can be used. It has a smal background flourescence in WatsOn. | ||
| - | === | + | === Agar concentration === |
For the sensor chip an agarose concentration of 1.5% is used. | For the sensor chip an agarose concentration of 1.5% is used. | ||
We first tryed agar. When the agar conzentration is lower than 1.5% the chip is not stable and brakes fast. When the agar conzentration is higher than 1.5% the medium gets solid befor pooring it into chip form. | We first tryed agar. When the agar conzentration is lower than 1.5% the chip is not stable and brakes fast. When the agar conzentration is higher than 1.5% the medium gets solid befor pooring it into chip form. | ||
In the end we choose agarose instead of agar because the agarose is better linked and so the difusion is not so high. | In the end we choose agarose instead of agar because the agarose is better linked and so the difusion is not so high. | ||
| + | === Induction === | ||
| + | For the induction of the used constructs we use IPTG or 3-oxo-C12 HSL. | ||
| + | The sensor cells with K1319042 can ditect a IPTG concentration of 1 mM. | ||
| + | The sensor cells with K131026 can ditect a HSL concentration of 500 µg/ml | ||
--> | --> | ||
{{Team:Aachen/Footer}} | {{Team:Aachen/Footer}} | ||
Revision as of 10:01, 14 October 2014
|
|
|
|
 "
"