|
|
| Line 8: |
Line 8: |
| | | | |
| | = BioBrickBox = | | = BioBrickBox = |
| - | In 2012, the iGEM-team LMU-Munich began the task to develop essential Biobricks, like vectors, promoters, reporters and affinity tags, especially suited for the use in B. subtilis in order to establish a new chassis in the E. coli dominated world of iGEM. Even after the finale of the iGEM competition in 2012, the project was pursued further since its importance for synthetic biology and resulted in a publication in the Journal of Biological Engineering about this so called Bacillus BioBrick Box (B4) | + | In 2012, the iGEM-team LMU-Munich began the task to develop essential BioBricks, like vectors, promoters, reporters and affinity tags, especially suited for the use in ''Bacillus subtilis'' in order to establish a new chassis in the ''Escherichia coli''-dominated world of iGEM. Even after the finals of the iGEM competition in 2012, the project was pursued further since its importance for synthetic biology and resulted in a publication in the Journal of Biological Engineering about this so called [http://www.jbioleng.org/content/7/1/29 ''Bacillus'' BioBrick Box]. |
| | | | |
| - | This year, our team aims to enhance this Bacillus BioBrick Box by adding new parts, like different colored fluorescent proteins or a whole new cloning strategy. | + | This year, our team aims to enhance the ''Bacillus'' BioBrick Box by adding new parts, like different colored fluorescent proteins or a whole new cloning strategy. |
| | | | |
| | <html> | | <html> |
| Line 30: |
Line 30: |
| | <article class="ac-small"> | | <article class="ac-small"> |
| | </html> | | </html> |
| - | The upp gene from Bacillus subtilis W168 encodes for a Uracilphosphoribosyl transferase (UPRTase). | + | The ''upp'' gene from Bacillus subtilis W168 encodes for a Uracilphosphoribosyl transferase (UPRTase). |
| | Its key reaction in uracil salvage is the reaction of a uracil molecule with a 5'-phosphoribosyl-a-1- pyrophosphate (PRPP) molecule, resulting in the formation of UMP. | | Its key reaction in uracil salvage is the reaction of a uracil molecule with a 5'-phosphoribosyl-a-1- pyrophosphate (PRPP) molecule, resulting in the formation of UMP. |
| - | A second locus, the pyrR Gene, encoding a second UPRTase has been identified. However it has been shown, that the UPRTase derived from pyrR locus has an influence on overall UPRTase activity < 1 %. (J Martinussen, P Glaser, P S Andersen and H H Saxild J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177(1):271. ) | + | A second locus, the pyrR Gene, encoding a second UPRTase has been identified. However it has been shown, that the UPRTase derived from pyrR locus has an influence on overall UPRTase activity of < 1 %. (J Martinussen, P Glaser, P S Andersen and H H Saxild J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177(1):271. ) |
| - | This makes the upp gene derived UPRTase the only physiologically relevant catalyst for UPRTase activity. | + | This makes the ''upp''-derived UPRTase the only physiologically relevant catalyst for UPRTase activity. |
| | Exposure to the pyrimidine analogue 5-Fluorouracil UPRTase results in production of 5-fluoro-dUMP, a very potent inhibitor of the thymidylate synthase (Neuhard, J. (1983) Utilization of preformed pyrimidine bases and nucleosides. In Metabolism of Nucleotides, Nucleosides and Nucleobases in Microorganisms. Munch- Petersen, A. (eds). New York: Academic Press, pp. 95– 148. ). As a result 5-FU is toxic to the Bacillus subtilis W168 strain. | | Exposure to the pyrimidine analogue 5-Fluorouracil UPRTase results in production of 5-fluoro-dUMP, a very potent inhibitor of the thymidylate synthase (Neuhard, J. (1983) Utilization of preformed pyrimidine bases and nucleosides. In Metabolism of Nucleotides, Nucleosides and Nucleobases in Microorganisms. Munch- Petersen, A. (eds). New York: Academic Press, pp. 95– 148. ). As a result 5-FU is toxic to the Bacillus subtilis W168 strain. |
| | B. subtilis 5FU-resistant (5FUR) mutants selected on low drug concentration (10 mM 5FU) are UPRTase-defective. (Nygaard, P. (1993) Purine and pyrimidine salvage pathways. In Bacillus Subtilis and Other Gram-Positive Bacteria: Biochemistry, Physiology, and Molecular Genetics. Sonenshein, A.L., Hoch, J.A. and Losick, R., (eds). Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology, pp. 359–378. ) | | B. subtilis 5FU-resistant (5FUR) mutants selected on low drug concentration (10 mM 5FU) are UPRTase-defective. (Nygaard, P. (1993) Purine and pyrimidine salvage pathways. In Bacillus Subtilis and Other Gram-Positive Bacteria: Biochemistry, Physiology, and Molecular Genetics. Sonenshein, A.L., Hoch, J.A. and Losick, R., (eds). Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology, pp. 359–378. ) |
| - | This has made upp a go to choice for negative selection in combination with an B. subtilis W168 ?upp strain. So far it has been used to make clean in-frame deletions and point mutations. (A new mutation delivery system for genome-scale approaches in Bacillus subtilis Céline Fabret,† S. Dusko Ehrlich and Philippe Noirot* Génétique Microbienne, INRA, Domaine de Vilvert, 78352 Jouy en Josas Cedex, France. ) | + | This has made ''upp'' a go to choice for negative selection in combination with an B. subtilis W168 Δ''upp'' strain. So far it has been used to make clean in-frame deletions and point mutations. (A new mutation delivery system for genome-scale approaches in Bacillus subtilis Céline Fabret,† S. Dusko Ehrlich and Philippe Noirot* Génétique Microbienne, INRA, Domaine de Vilvert, 78352 Jouy en Josas Cedex, France. ) |
| | | | |
| - | However to our knowledge no application using upp for clean insertions has been established so far. | + | However, to our knowledge, no application using ''upp'' for clean insertions has been established so far. |
| | | | |
| - | The I-SceI Restricition endonuclease has a highly specific recognition sequence of 18 nucleotides. No such sequence is present in the W168 strain. It creates a double strand break at targetet location, which leads to an increased rate of repair at the specific site. By this the rate of homologous recombination has already been indreased by an factor of 100x. (Establishment of a Markerless Mutation Delivery System in Bacillus subtilis Stimulated by a Double-Strand Break in the Chromosome Ting Shi1,2,3,4., Guanglu Wang1,2,3,4., Zhiwen Wang1,2,3,4*, Jing Fu1,2,3,4, Tao Chen1,2,3,4, Xueming Zhao1,2,3,4 ) | + | The I-SceI Restricition endonuclease has a highly specific recognition sequence of 18 nucleotides. No such sequence is present in the W168 strain. It creates a double strand break at targeted location, which leads to an increased rate of repair at the specific site. By this, the rate of homologous recombination is increased by an factor of 100x. (Establishment of a Markerless Mutation Delivery System in Bacillus subtilis Stimulated by a Double-Strand Break in the Chromosome Ting Shi1,2,3,4., Guanglu Wang1,2,3,4., Zhiwen Wang1,2,3,4*, Jing Fu1,2,3,4, Tao Chen1,2,3,4, Xueming Zhao1,2,3,4 ) |
| | <html> | | <html> |
| | </article> | | </article> |
| Line 49: |
Line 49: |
| | <article class="ac-small"> | | <article class="ac-small"> |
| | </html> | | </html> |
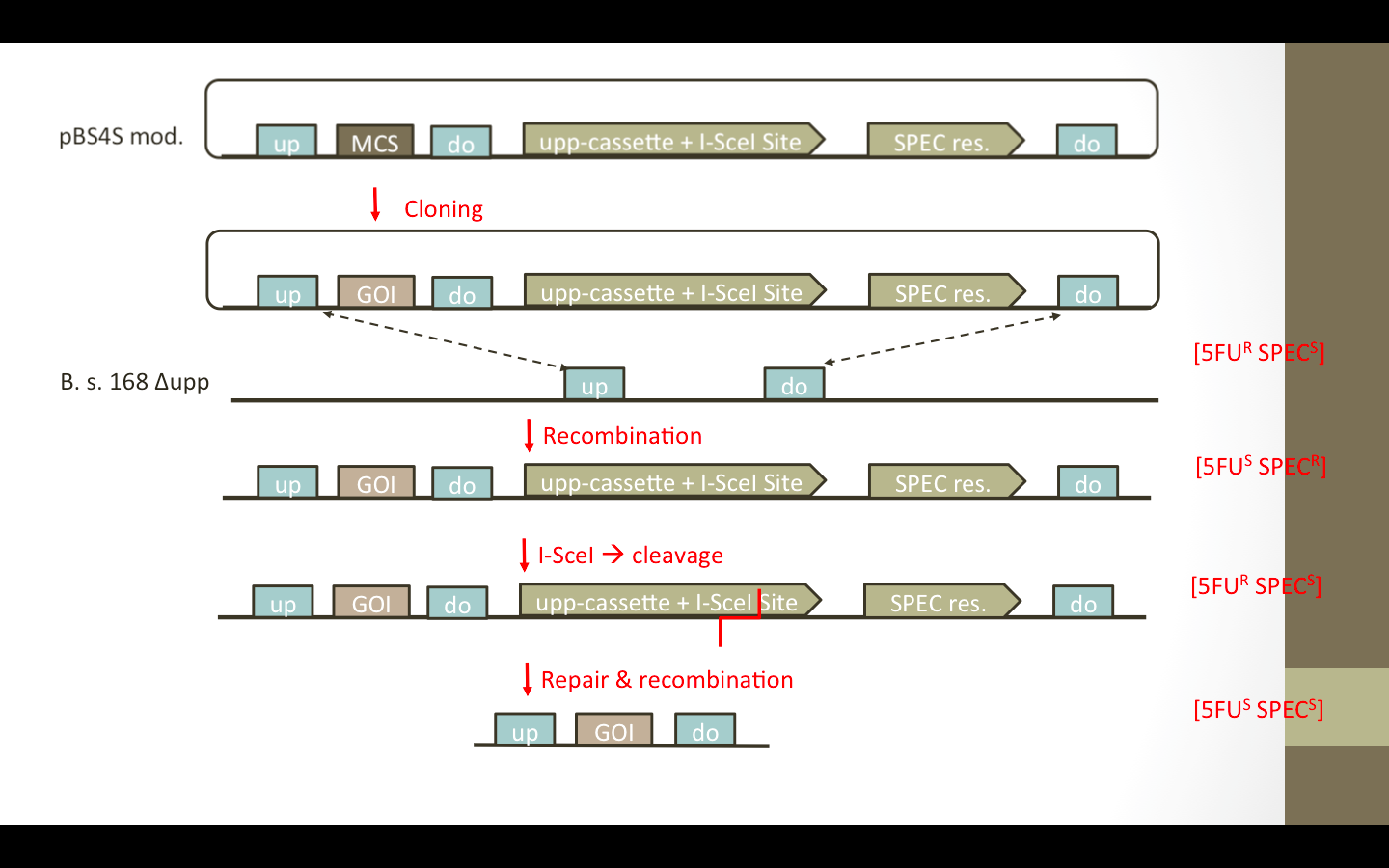
| - | The Plan was to restructure the BioBrick compatible, integrative Bacillus subtilis vectors pBS1C, pBS2E and pBS4S in a fashion that leads to deletion of the antibiotic resistance after Insertion of a gene of interest has been made. | + | The Plan was to restructure the BioBrick compatible, integrative ''Bacillus subtilis'' vectors [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J179000 pSB1C], [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J179001 pSB2E] and [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J179002 pSB4S] in a fashion that leads to deletion of the antibiotic resistance after insertion of a gene of interest has been made. |
| - | Integration of those basic vectors is achieved via homologous recombination between the lacA/thrC/amyE locus and the corresponding up and down fragments on the vector. This leads to an insertion of the Gene of interest within the RCF25 compatible multiple cloning site and the resistance for positive selection (MLS/Spec/CAM). | + | Integration of those basic vectors is achieved via homologous recombination between the ''amyE''/''lacA''/''thrC'' locus and the corresponding up and down fragments on the vector. This leads to an insertion of the gene of interest within the RCF10 compatible multiple cloning site and the resistance for positive selection (CAM/MLS/Spec). |
| | | | |
| - | We wanted to add the upp-cassette, containing an I-SceIsite, as well as an additional up/down fragment to the vector. The desired vectors are presented in Fig. 1.. The upp-cassette will allow negative selection in 5FU media. The contained I-SceI site will be cut by the I-SceI restriction endonuclease encoded on helper plasmid pEBS-cop1. (Figure) | + | We wanted to add the ''upp''-cassette, containing an I-SceIsite, as well as an additional up/down fragment to the vector. The desired vectors are presented in Fig. 1. The ''upp''-cassette will allow negative selection in 5FU media. The contained I-SceI site will be cut by the I-SceI restriction endonuclease which is encoded on helper plasmid pEBS-cop1. (nochmal auf das paper verweisen) (Figure) |
| | | | |
| | Cloning Strategy | | Cloning Strategy |
| Line 86: |
Line 86: |
| | <article class="ac-small"> | | <article class="ac-small"> |
| | </html> | | </html> |
| - | Fluorescent Proteins are often derivates of the first described FP, GFP, which was isolated from the jellyfish ''Aequorea victoria''. This Protein is of typical barrel-shape, built from 11 ß-sheets and a cromophor in the middle of the barrel. This barrelstructure is typical for fluorescent proteins, wether they derive from GFP or not. Other colors than green where developed by changing single amino acids in the chromophore of GFP (e.g.: Yellow: YFP and Cyan: CFP) or by analyzing Fluorescent Proteins from other organisms, like ''Discosoma striata'', a coral, from which some of our red FPs, like dsREd derive. | + | Fluorescent Proteins are often derivates of the first described FP, GFP, which was isolated from the jellyfish ''Aequorea victoria''. This protein is of typical barrel-shape, built from 11 ß-sheets and a chromophor in the middle of the barrel. This barrel structure is typical for fluorescent proteins, whether they derive from GFP or not. Other colors than green where developed by changing single amino acids in the chromophore of GFP (e.g.: Yellow: YFP and Cyan: CFP) or by analyzing fluorescent proteins from other organisms, like ''Discosoma striata'', a coral, from which some of our red FPs, like dsRed derive. |
| - | FPs are an important tool in today’s research, for example in order to study gene expression or the location of specific proteins in a cell or a whole organism. This is the reason, why we tried to establish some different colors of FPs for use in B. subtilis by evaluating them for the Bacillus BioBrick Box (B4). | + | FPs are an important tool in today’s research, for example in order to study gene expression or the location of specific proteins in a cell or a whole organism. This is the reason, why we tried to establish some different colors of FPs for use in B. subtilis by evaluating them for the ''Bacillus'' BioBrick Box. |
| | <html> | | <html> |
| | </article> | | </article> |
| Line 96: |
Line 96: |
| | <article class="ac-small"> | | <article class="ac-small"> |
| | </html> | | </html> |
| - | Seven different FPs (see chart below) where chosen and either obtained from the Registry or from the AG Mascher. | + | Seven different FPs (see chart below) where chosen and either obtained from the registry or from the AG Mascher. |
| - | The Biobrick E1010 (DsRed) was mutated via site directed mutagenesis by overlap extension PCR in order to delete two AgeI-Restriction sites and make the Biobrick compatible for the Freiburgstandard. | + | The Biobrick E1010 (DsRed) was mutated via site directed mutagenesis by overlap extension PCR in order to delete two AgeI-Restriction sites and make the Biobrick compatible for the Freiburg standard RFC25. |
| | | | |
| - | The Biobricks E1010 (DsRed) and K592100 (mTagBFP) where both provided with the necessary overhangs for the Freiburgstandard, the other FPs where already provided with the proper restriction sites | + | The BioBricks E1010 (DsRed) and K592100 (mTagBFP) where both provided with the necessary overhangs for the Freiburg standard, the other FPs where already provided with the proper restriction overhangs. |
| - | This seven FPs where fused with a His-Tag, each C- and N-terminal and cloned into the vector pBS0K-Pspac and transformed into B. subtilis.
| + | These seven FPs where fused with a His-Tag, each C- and N-terminal and cloned into the vector pBS0K-Pspac and transformed into ''B. subtilis''. |
| | | | |
| - | The intensity and spectrum of the fluorescence was measured by a TECAN Plate Reader, kindly provided by the AG Leonhardt | + | The intensity and spectrum of the fluorescence was measured by a TECAN Plate Reader, kindly provided by the AG Leonhardt from the LMU. |
| | <html> | | <html> |
| | </article> | | </article> |
| Line 112: |
Line 112: |
| | </html> | | </html> |
| | The mutagenesis of the Biobrick E1010 was successful and confirmed by sequencing, the thus created Biobrick is called BBa_K1351021. The fusion with the His tags were also successfully conducted and confirmed by sequencing. | | The mutagenesis of the Biobrick E1010 was successful and confirmed by sequencing, the thus created Biobrick is called BBa_K1351021. The fusion with the His tags were also successfully conducted and confirmed by sequencing. |
| - | The fusion into the vector pBS0K-Pspac was confirmed via Colony PCR and the transformation into'' B. subtilis'' was conducted successfully. | + | The ligation into the vector pBS0K-Pspac was confirmed via Colony PCR and the transformation into'' B. subtilis'' was conducted successfully. |
| - | The fluorescence of all of the proteins, however, proved to be not very good and often at the same level as the auto fluorescence of the Bacillus wild type. The examination of the cells under a microscope revealed, that the promoter is not suited for this experimental set up, since the gene expression is very heterogeneous and rather low. This problem will be solved by recloning the FPs into the vector pBS1C together with the Xylose-inducible promoter Pxyl. | + | The fluorescence of all of the proteins, however, proved to be not very good and often at the same level as the auto fluorescence of the ''B. subtilis'' wild type. The examination of the cells under a microscope revealed, that the promoter is not suited for this experimental set up, since the gene expression is very heterogeneous and rather low. This problem will be solved by recloning the FPs into the vector pBS1C together with the Xylose-inducible promoter Pxyl. |
| | <html> | | <html> |
| | </article> | | </article> |
 "
"