Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Project/CO2-fixation/Carboxysome
From 2014.igem.org
(Created page with "{{Template:Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/igem.css}} {{Template:Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/main.css}} {{Template:Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Banner_team.css}} {{Template:Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Ba...")
Newer edit →
Revision as of 15:01, 14 October 2014
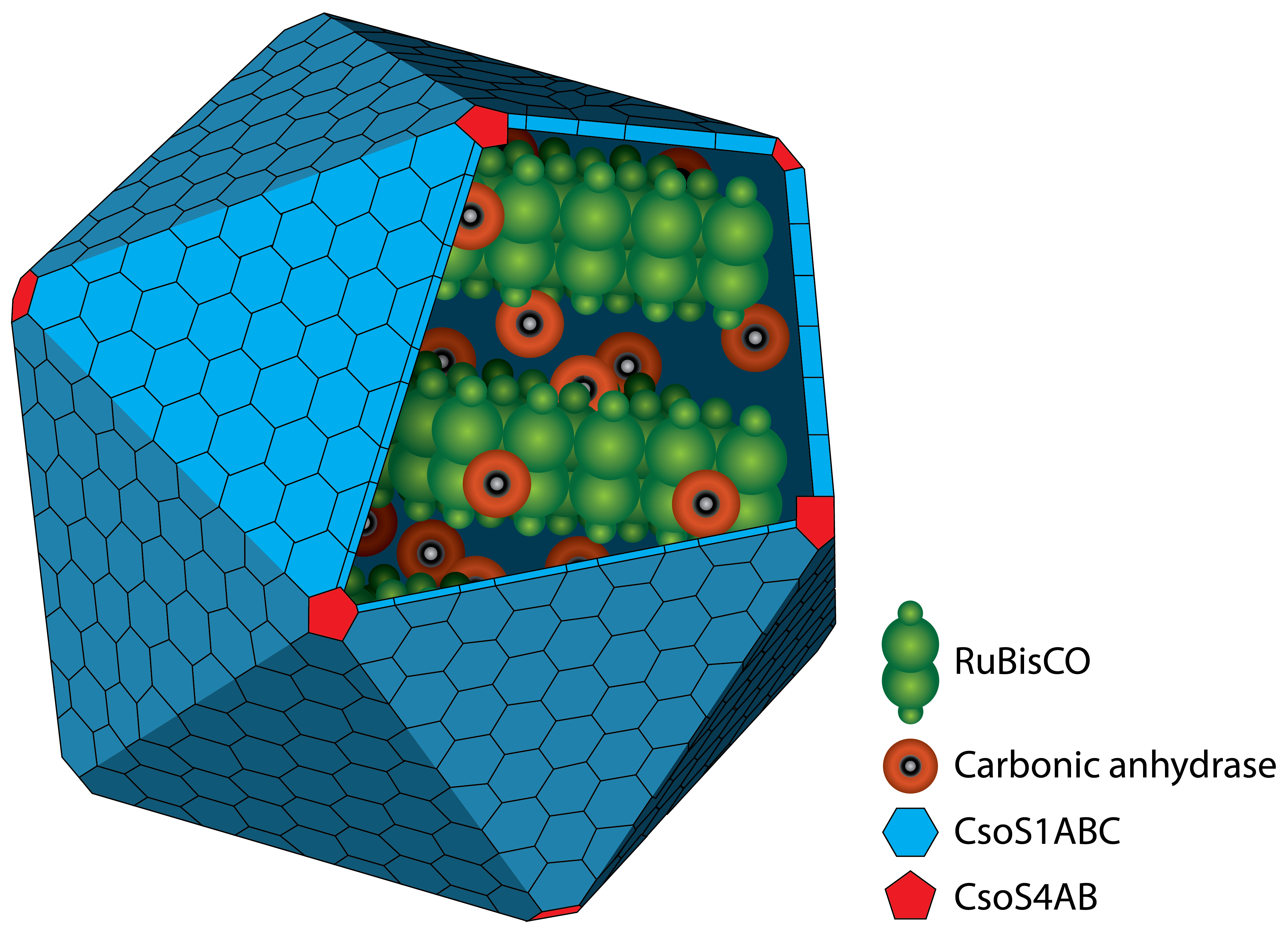
Carboxysome
A carboxysome is an intracellular microcompartiment with a protein shell. The protein shell consists of two different types of proteins. Pentamers are used for the vertices of the icosaeder and hexamers for the facets. In the interior there are two different enzymes. On the one hand there is the RuBisCO which catalyses the reaction like described above. On the other hand there is the carbonic anhydrase which converts hydrogen carbonate (HCO3-) to carbon dioxide. The resulting carbon dioxide is the substrate for the RuBisCO.
The advantage of the microcompartiment is that the concentration of carbon dioxide inside can be much higher than outside which increases the efficiency of the RuBisCO.
There are two different types of carboxysomes which are classified by the habitat of the organism. It is found in all cyanobacteria and some chemolitoautotrophic bacteria. A deletion mutant for a single gene of the cluster results in a conditionally lethal phenotype which requires high concentrations of carbon dioxide.
 "
"