Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec
From 2014.igem.org
| Line 163: | Line 163: | ||
<tr><td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/2a/Bielefeld_CeBiTec_2014-10-17_Haken.png" width="50px"></td><td>Construction of an <a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Project/rMFC/Mediators" target="_blank">electrophilic <i>E.coli</i> strain</a></td></tr> | <tr><td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/2a/Bielefeld_CeBiTec_2014-10-17_Haken.png" width="50px"></td><td>Construction of an <a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Project/rMFC/Mediators" target="_blank">electrophilic <i>E.coli</i> strain</a></td></tr> | ||
<tr><td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/2a/Bielefeld_CeBiTec_2014-10-17_Haken.png" width="50px"></td><td>Successful <a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Results/Pathway" target="_blank">isobutanol production</a></td></tr> | <tr><td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/2a/Bielefeld_CeBiTec_2014-10-17_Haken.png" width="50px"></td><td>Successful <a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Results/Pathway" target="_blank">isobutanol production</a></td></tr> | ||
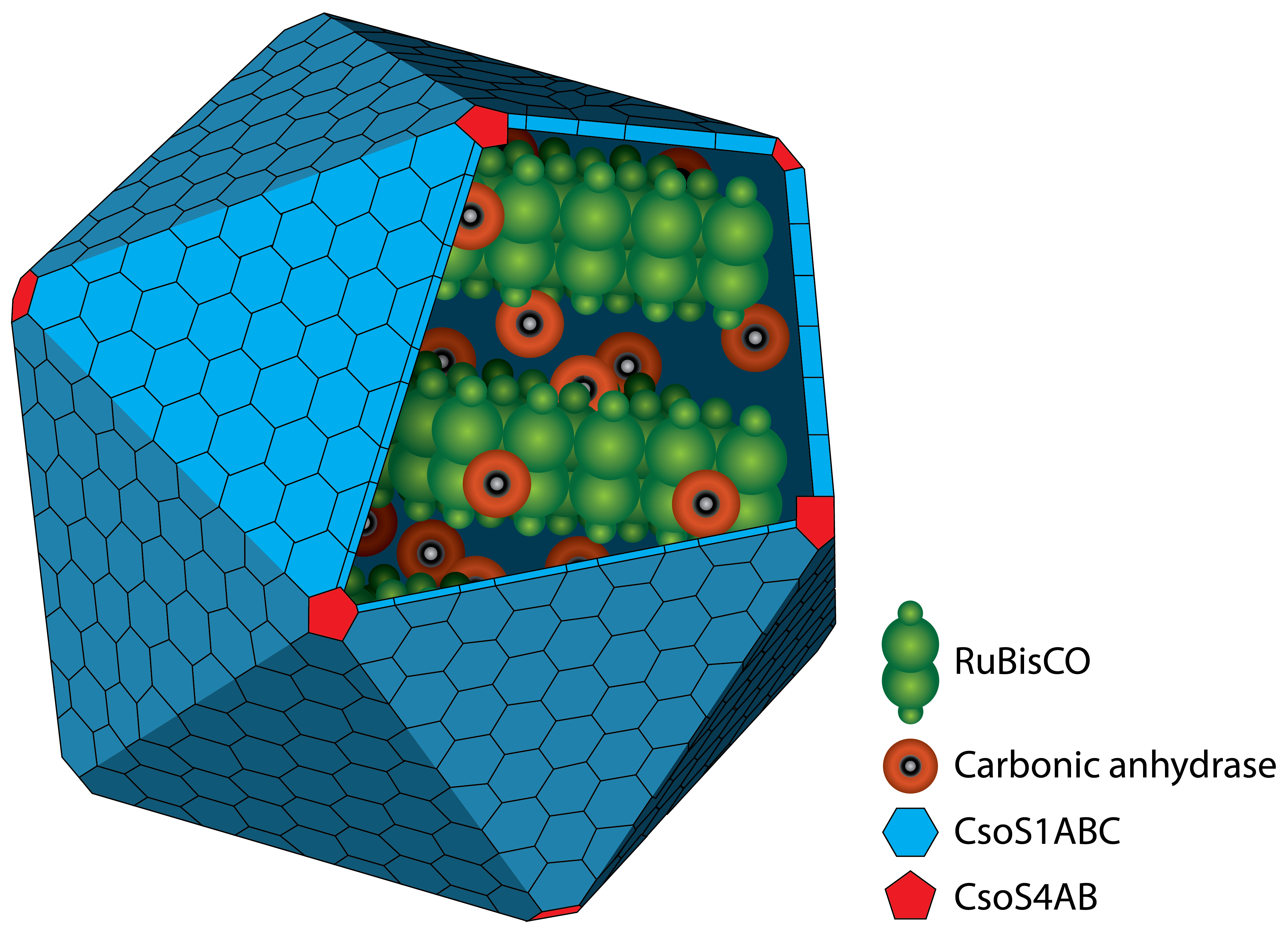
| - | <tr><td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/2a/Bielefeld_CeBiTec_2014-10-17_Haken.png" width="50px"></td><td>Construction of a functional microcompartment, the carboxysome</td></tr> | + | <tr><td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/2a/Bielefeld_CeBiTec_2014-10-17_Haken.png" width="50px"></td><td>Construction of a functional microcompartment, the <a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-CeBiTec/Results/CO2-fixation/Carboxysome" target="_blank">carboxysome</a></td></tr> |
<tr><td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/2a/Bielefeld_CeBiTec_2014-10-17_Haken.png" width="50px"></td><td>Genome integration of OprF</td></tr> | <tr><td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/2a/Bielefeld_CeBiTec_2014-10-17_Haken.png" width="50px"></td><td>Genome integration of OprF</td></tr> | ||
<tr><td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/2a/Bielefeld_CeBiTec_2014-10-17_Haken.png" width="50px"></td><td>Functional <i>in-vitro</i> assay of RuBisCo</td></tr> | <tr><td><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/2a/Bielefeld_CeBiTec_2014-10-17_Haken.png" width="50px"></td><td>Functional <i>in-vitro</i> assay of RuBisCo</td></tr> | ||
Revision as of 03:54, 18 October 2014
Welcome to our project
Our project
The supply with electricity is facing three major problems: the storage of electricity, the increasing amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide and the development of alternative energy sources. Therefore we want to implement a proof of concept for the production of the biofuel isobutanol from carbon dioxide. A bacterial microcompartment originated from cyanobacteria, called carboxysome, is used to realize the fixation of carbon dioxide in Escherichia coli. Within this microcompartment the carbon dioxide fixation is enabled under aerobic conditions. The needed energy for this process is provided by electricity. The electrons are transferred with a mediator into the cells and its uptake is empowered by different modifications of E. coli, like over-expression of the fumarate reductase. This concept is realized in a self-constructed bioreactor. Finally the production of isobutanol is established by hetereologous expression of various enzymes from different species.
Achievements
 | Design and construction of a rMFC |
 | Design and construction of a flow cell reactor |
 | Construction of an electrophilic E.coli strain |
 | Successful isobutanol production |
 | Construction of a functional microcompartment, the carboxysome |
 | Genome integration of OprF |
 | Functional in-vitro assay of RuBisCo |
 | Development of an antibiotic-free selection system |
 | Several human practice projects |
 | SYNENERGENE cooperation |
 | Help another team |
 "
"