Team:Aachen/Project/2D Biosensor
From 2014.igem.org
(→Development & Optimization) |
(→Equipment and medium selection) |
||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
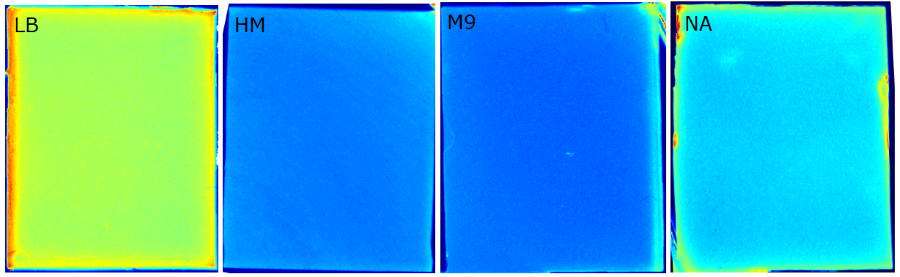
{{Team:Aachen/FigureFloat|Aachen_Chip_medium_geldoc.png|title=Differend medium in the Gel Doc™|subtitle=complex media exhibited high background fluorescence while less back- ground fluorescence was observed with the minimal media (HM, M9, NA).|right|width=500px}} | {{Team:Aachen/FigureFloat|Aachen_Chip_medium_geldoc.png|title=Differend medium in the Gel Doc™|subtitle=complex media exhibited high background fluorescence while less back- ground fluorescence was observed with the minimal media (HM, M9, NA).|right|width=500px}} | ||
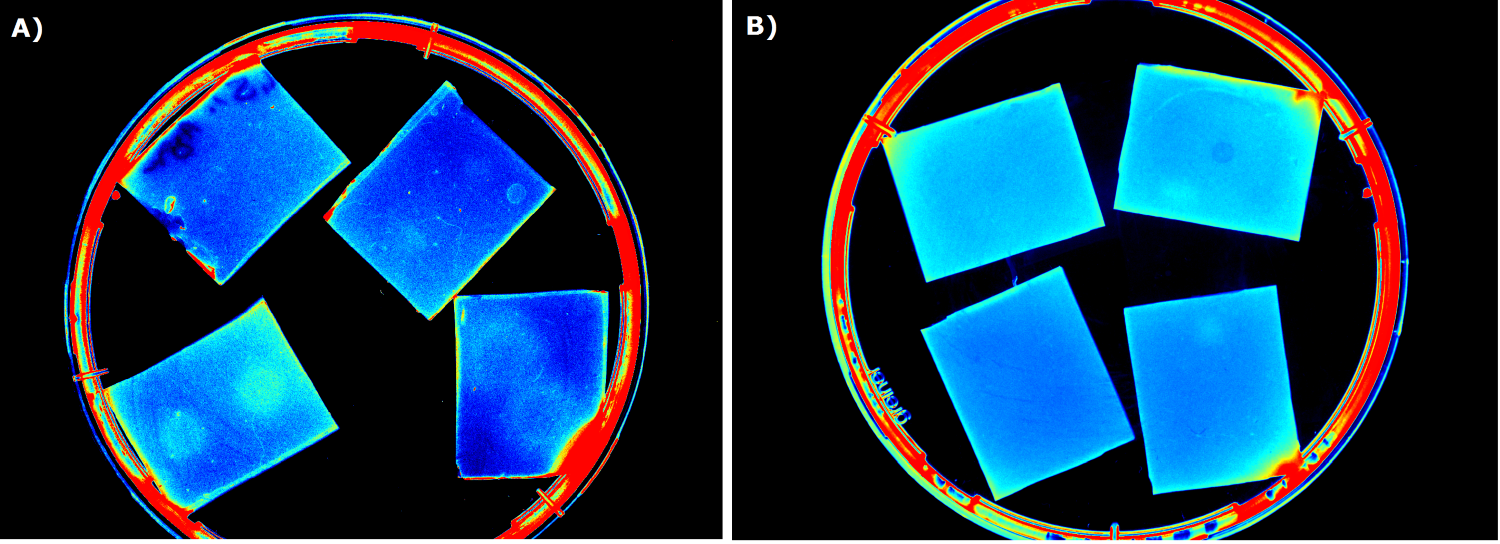
{{Team:Aachen/FigureFloat|Aachen_5days_K131026_neb_tb_1,5h.jpg |title=Testing our chips' shelf-life|subtitle= Chips of [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K131026 K131026] in NEB were stored 5 days at 4°C. The right chip was induced with 0.2 µL of 500 µg/mL HSL and an image was taken after 1.5 h.|left|width=500px}} | {{Team:Aachen/FigureFloat|Aachen_5days_K131026_neb_tb_1,5h.jpg |title=Testing our chips' shelf-life|subtitle= Chips of [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K131026 K131026] in NEB were stored 5 days at 4°C. The right chip was induced with 0.2 µL of 500 µg/mL HSL and an image was taken after 1.5 h.|left|width=500px}} | ||
| - | We tested different media ( | + | We tested different media (LB, TB, M9, NA and HM) for the preparation of our sensor chips. The details of media composition can be found in the [https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Notebook/Protocols Protocols] section. We screened for an optimized media composition that results in minimal background fluorescence and supports cell growth. The resuts of the analysis are presented in the table below. Because of the reduced fluorescence compared to TB medium when using ''WatsOn'' for sensor chip evaluation and because of sufficient cultivation conditions for our ''Cellocks'' '''LB medium was chosen over TB medium for sensor hip manufacturing'''. |
<center> | <center> | ||
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
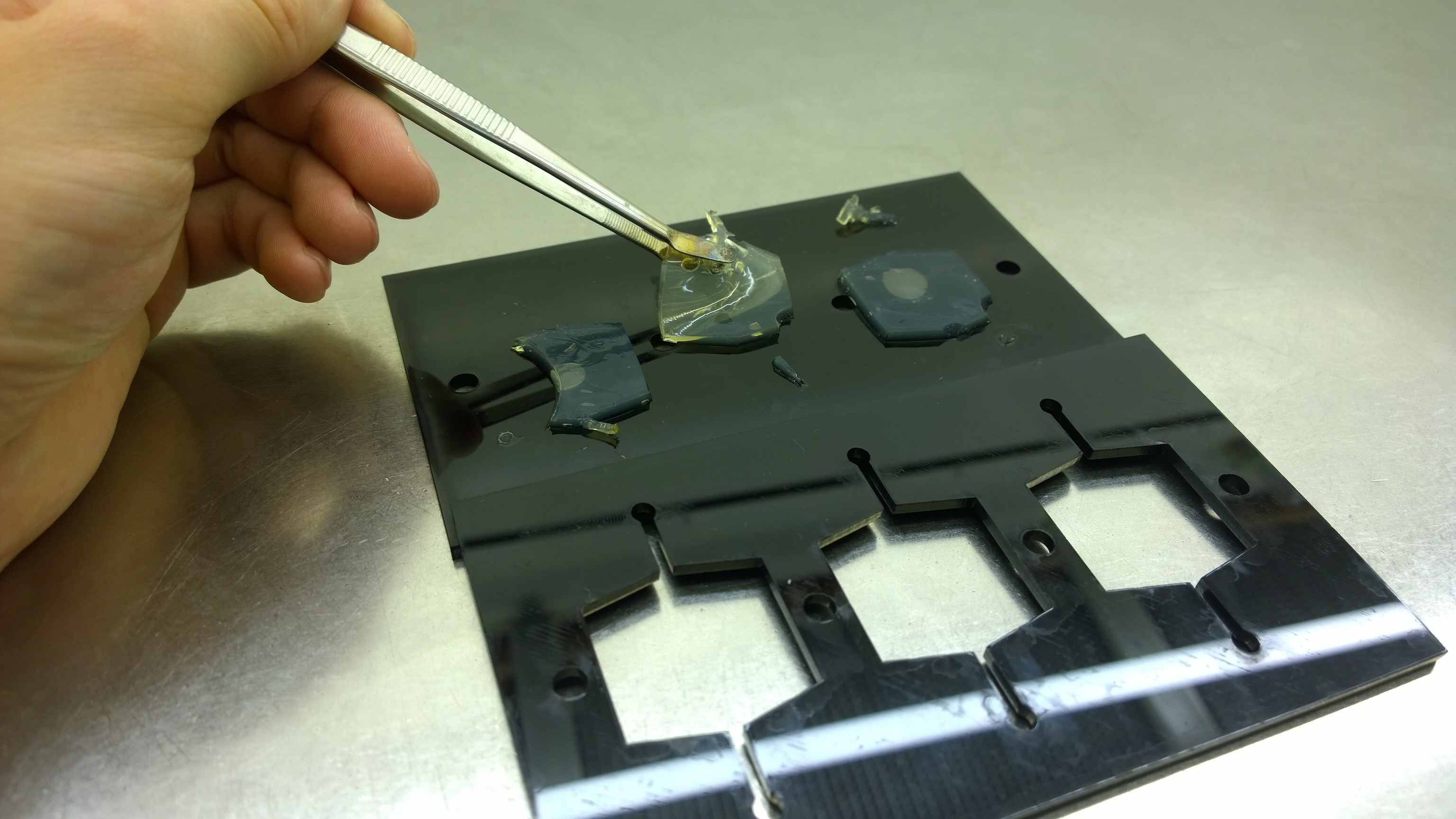
{{Team:Aachen/FigureFloat|Aachen_2_chipform.jpg|title=Sensor chip manufacturing using the closed mold|subtitle=When injecting the liquid agar into a closed mold we encounter problems due to frequent bubble formation.|left|width=500px}} | {{Team:Aachen/FigureFloat|Aachen_2_chipform.jpg|title=Sensor chip manufacturing using the closed mold|subtitle=When injecting the liquid agar into a closed mold we encounter problems due to frequent bubble formation.|left|width=500px}} | ||
| + | |||
=== Optimal agarose concentration for sensor chip manufacturing === | === Optimal agarose concentration for sensor chip manufacturing === | ||
For the sensor chip manufacturing, agarose was preferred over agar, because of a uniform linkage that resulted in a better chip homogeneity. In addition, agarose reduced diffusion of the inducer molecules through the chip. A reduced diffusion is vital to observe distinct fluorescent spots on the sensor chips and thus further optimzation of our 2D biosensor was done using agarose-based chips. | For the sensor chip manufacturing, agarose was preferred over agar, because of a uniform linkage that resulted in a better chip homogeneity. In addition, agarose reduced diffusion of the inducer molecules through the chip. A reduced diffusion is vital to observe distinct fluorescent spots on the sensor chips and thus further optimzation of our 2D biosensor was done using agarose-based chips. | ||
Revision as of 00:32, 18 October 2014
|
|
|
|
|
|
 "
"