Team:ETH Zurich/expresults/qs
From 2014.igem.org
(→How to read the matrices below.) |
(→How to read the matrices below.) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==How to read the matrices below.== | ==How to read the matrices below.== | ||
1. Matrix pLux | 1. Matrix pLux | ||
| - | In all the measurements made for this matrix the promoter pLux was the basis. In this case the promoter was induced in six different variations shown. The blue | + | In all the measurements made for this matrix the promoter pLux was the basis. In this case the promoter was induced in six different variations shown. |
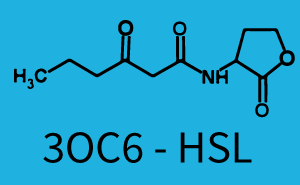
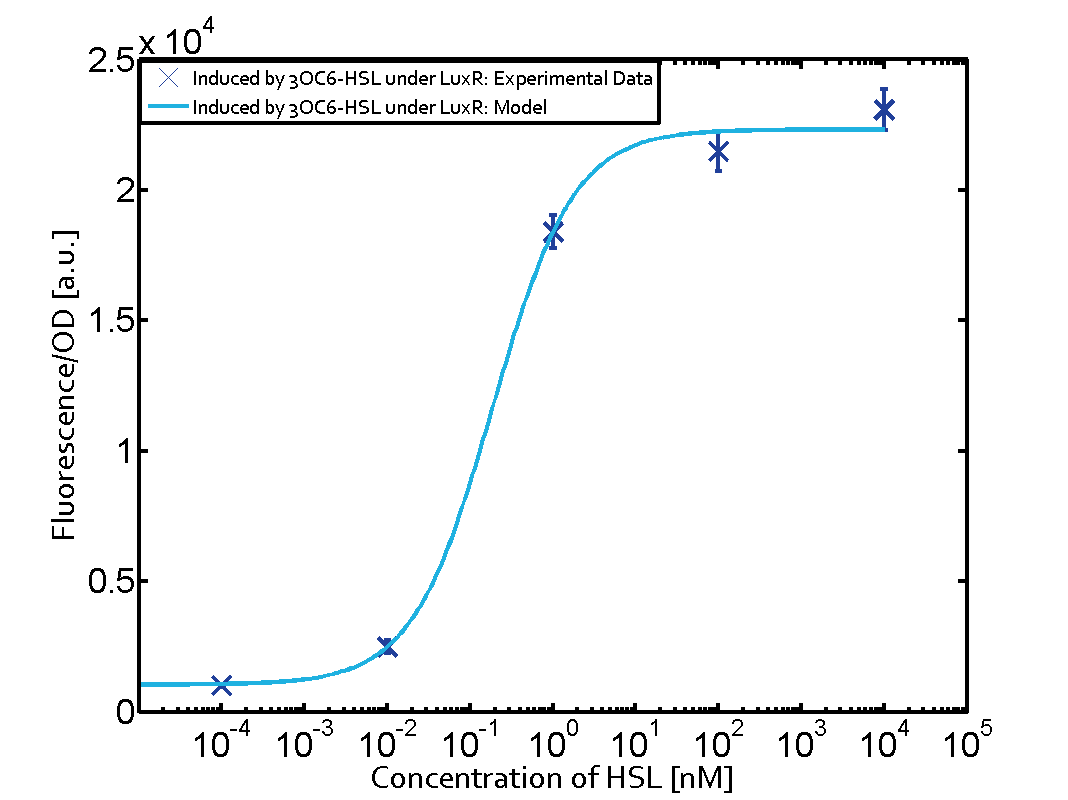
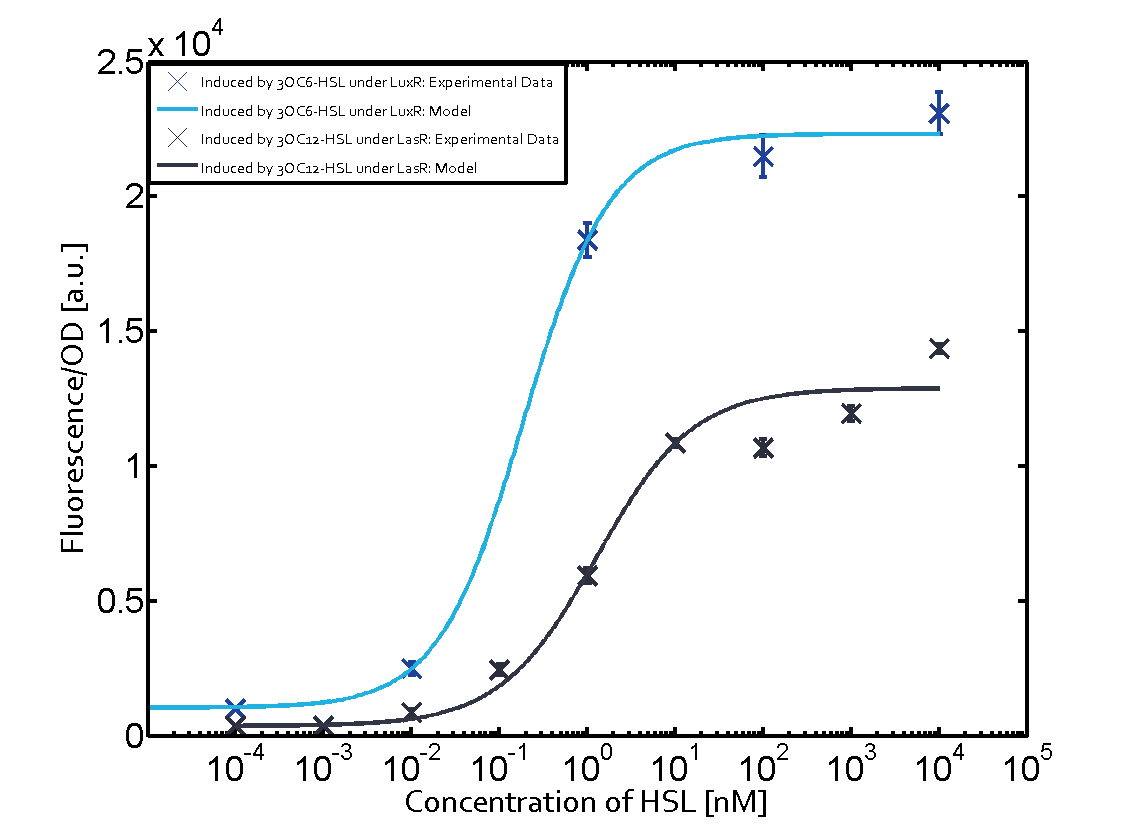
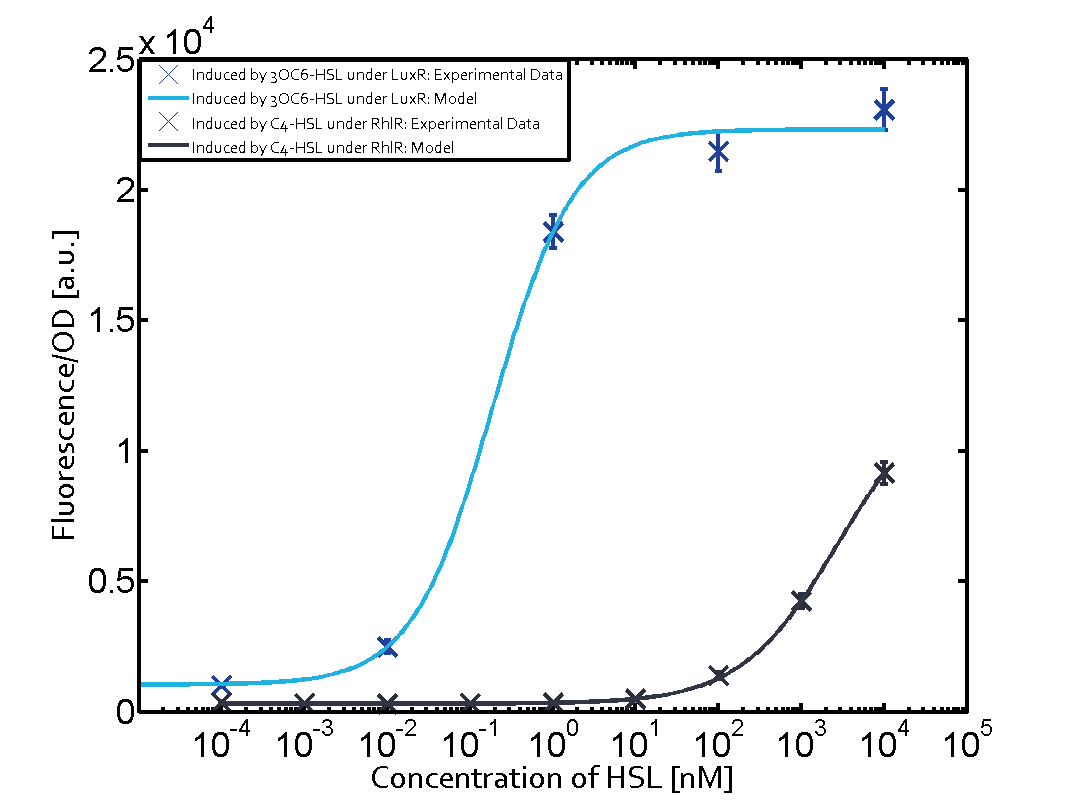
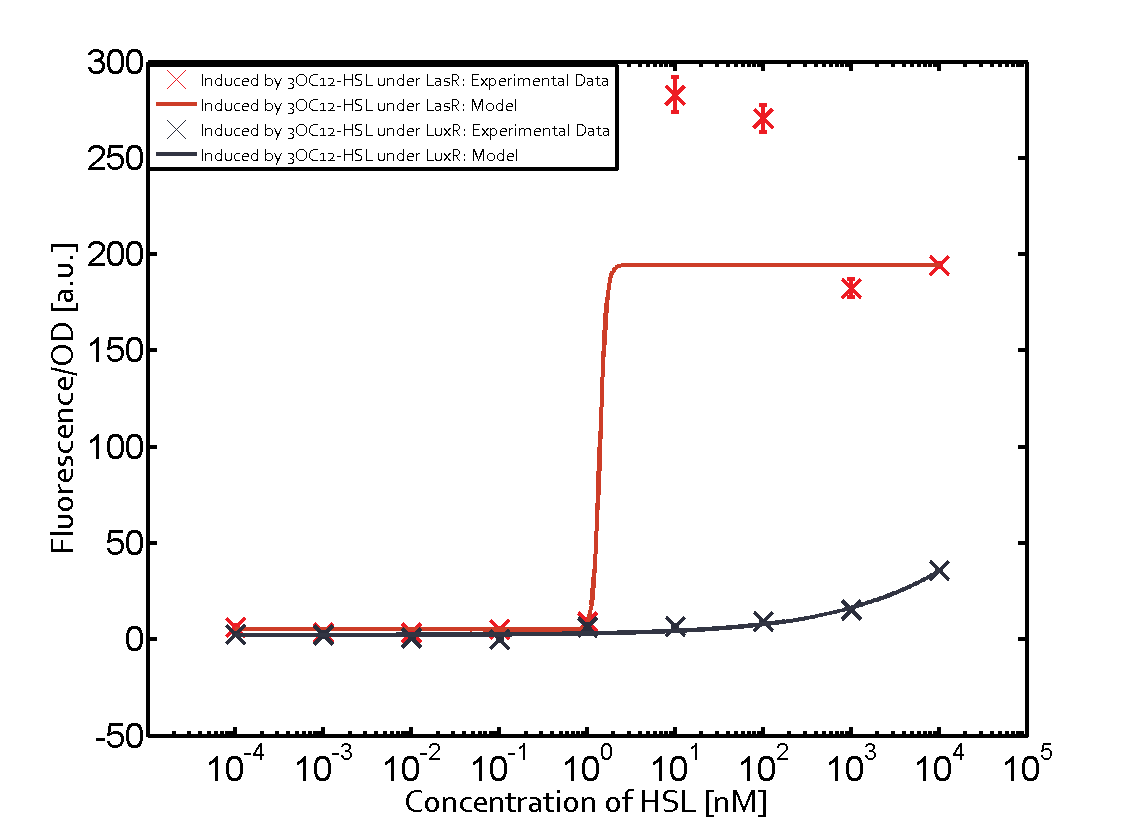
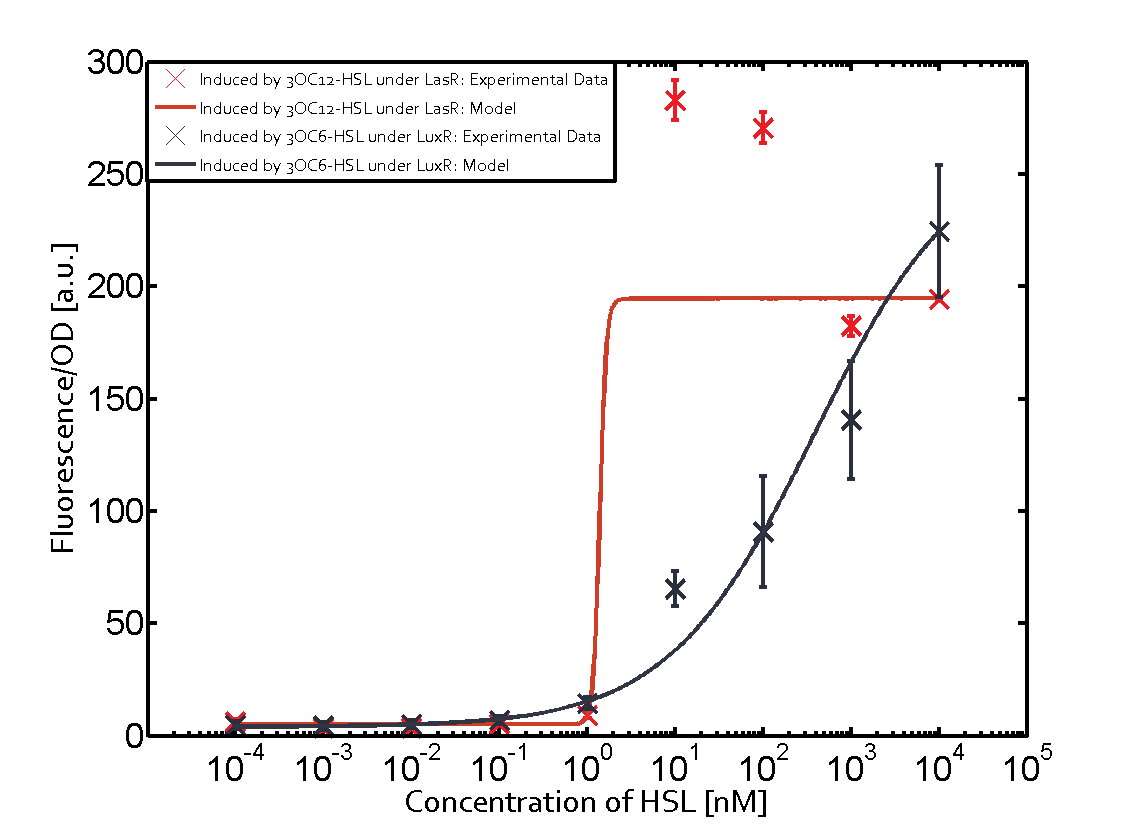
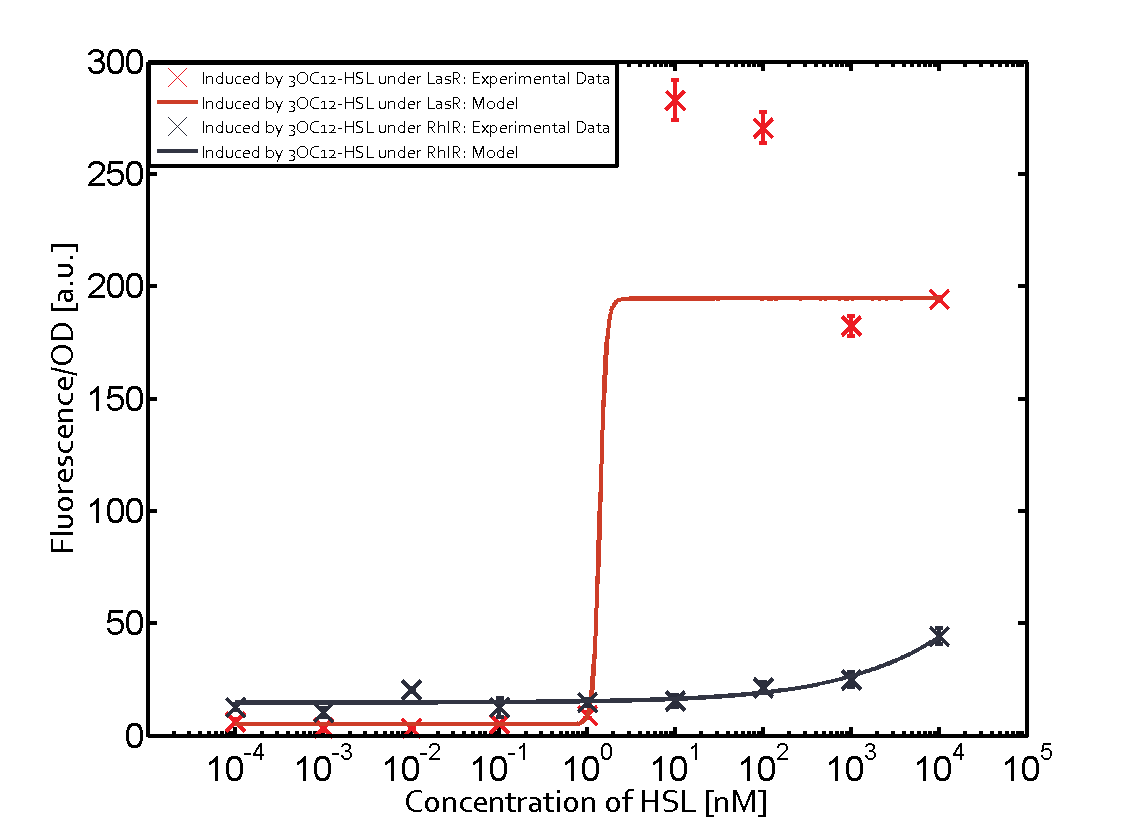
| - | This curve | + | The dark blue points in the graph top left show the activation of gene expression when pLux is induced by 3OC6-HSL (Lux-AHL) binding to the corresponding LuxR regulator. The observed transition occurs at a concentration of approximately 1nM 3OC6-HSL. The light-blue curve plotted shows the latter but not experimental but the model. |
| - | Cross-talk can be observed for the cases where the 3OC12-HSL (Las-AHL) binds the LuxR regulator or when 3OC12-HSL bind to its corresponding regulator LasR and then binding to the pLux. For the | + | This curve from the model and the dark blue data point gained in experiments were plotted as a reference in all the other graphs describing pLux. |
| + | |||
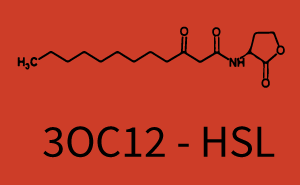
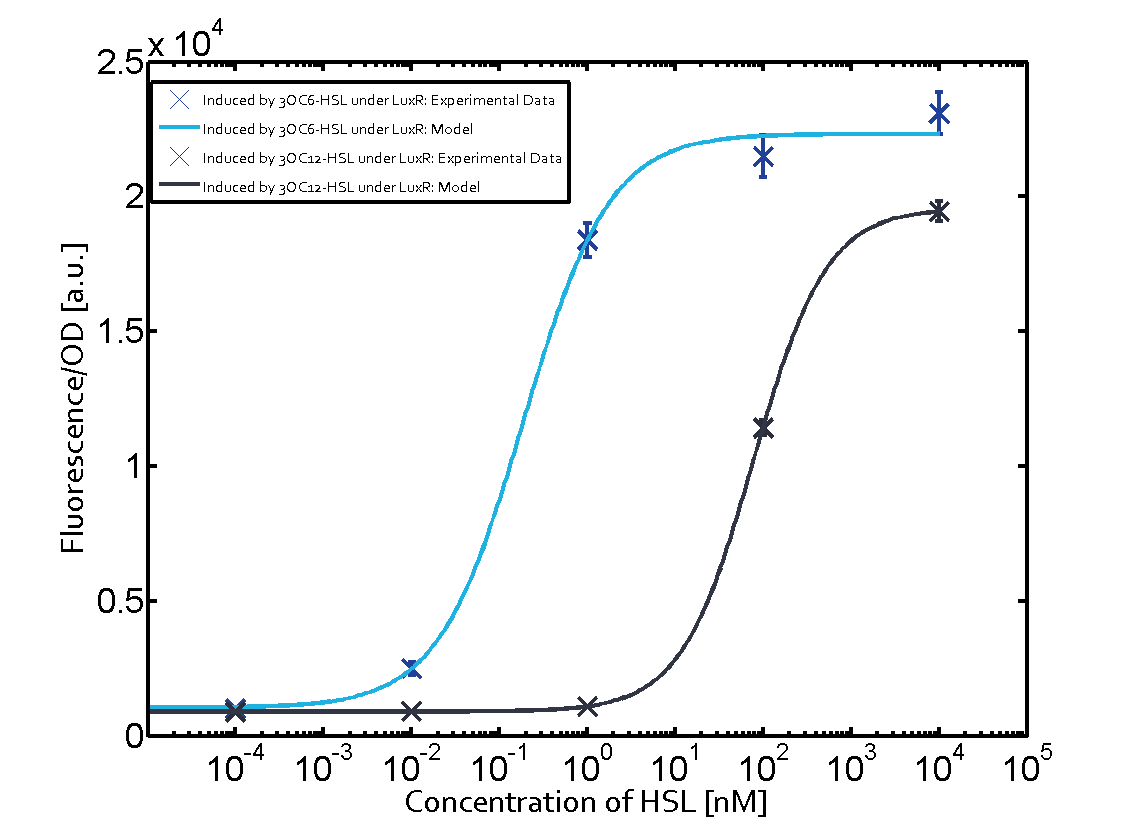
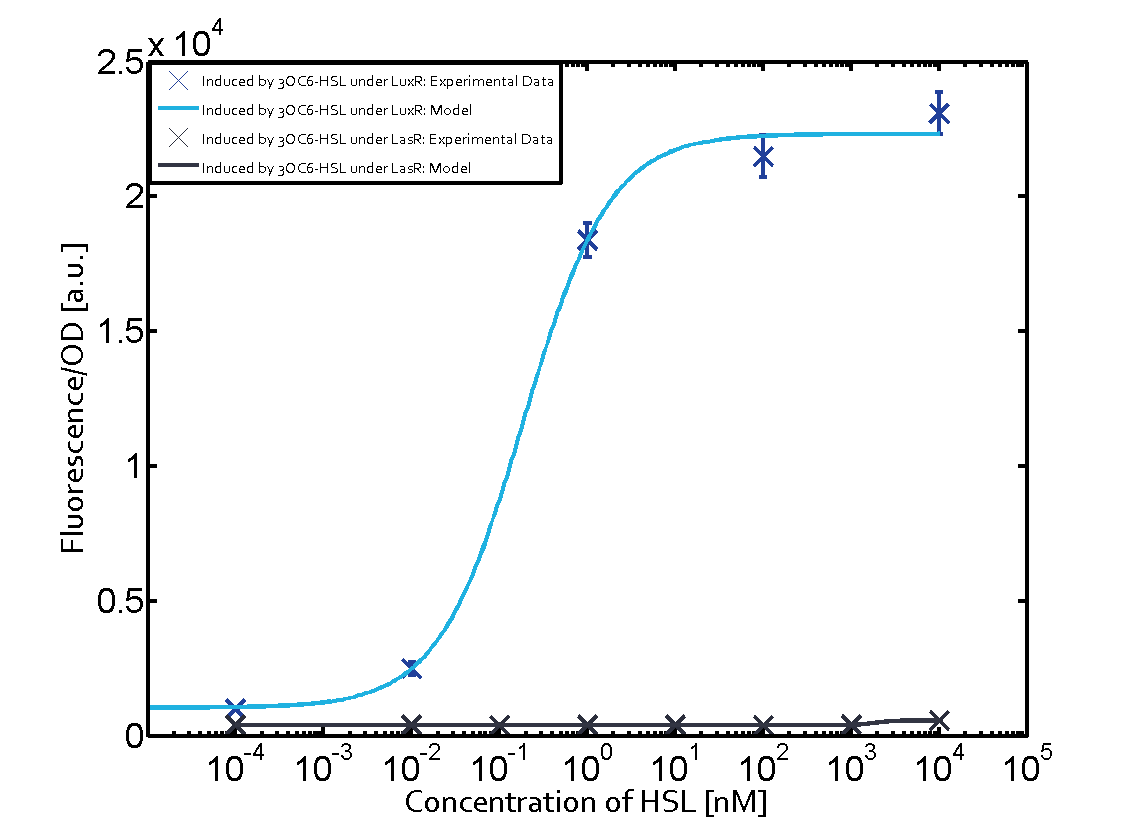
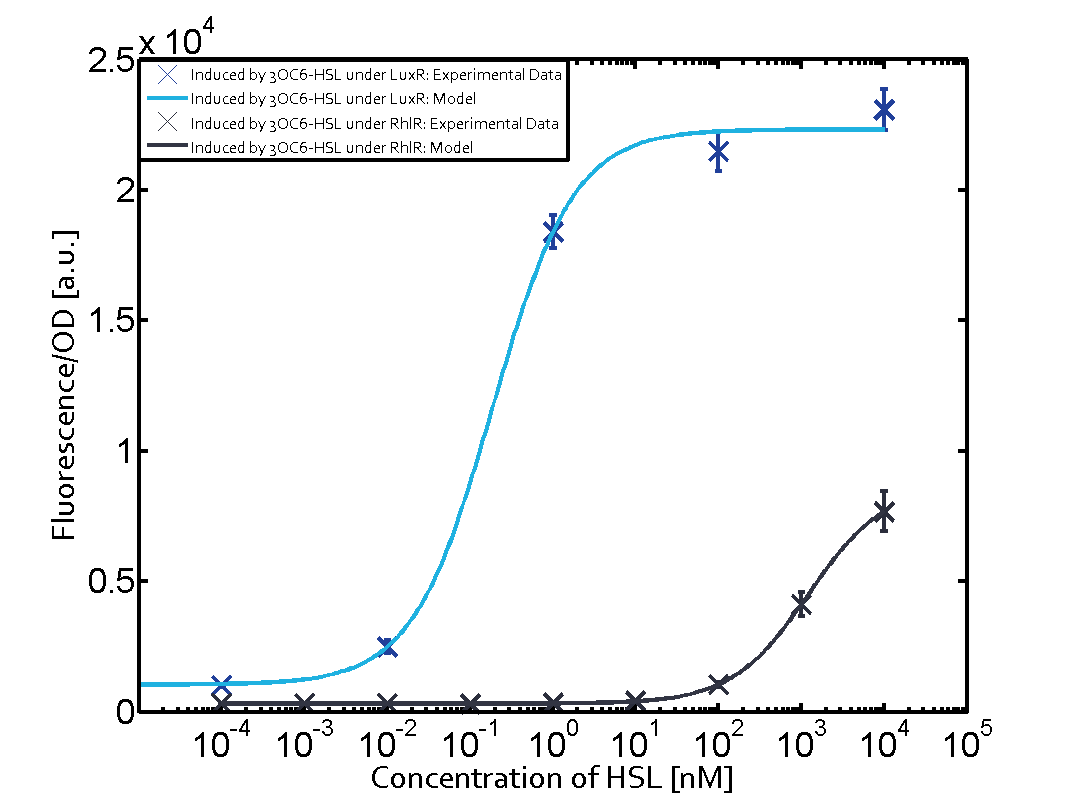
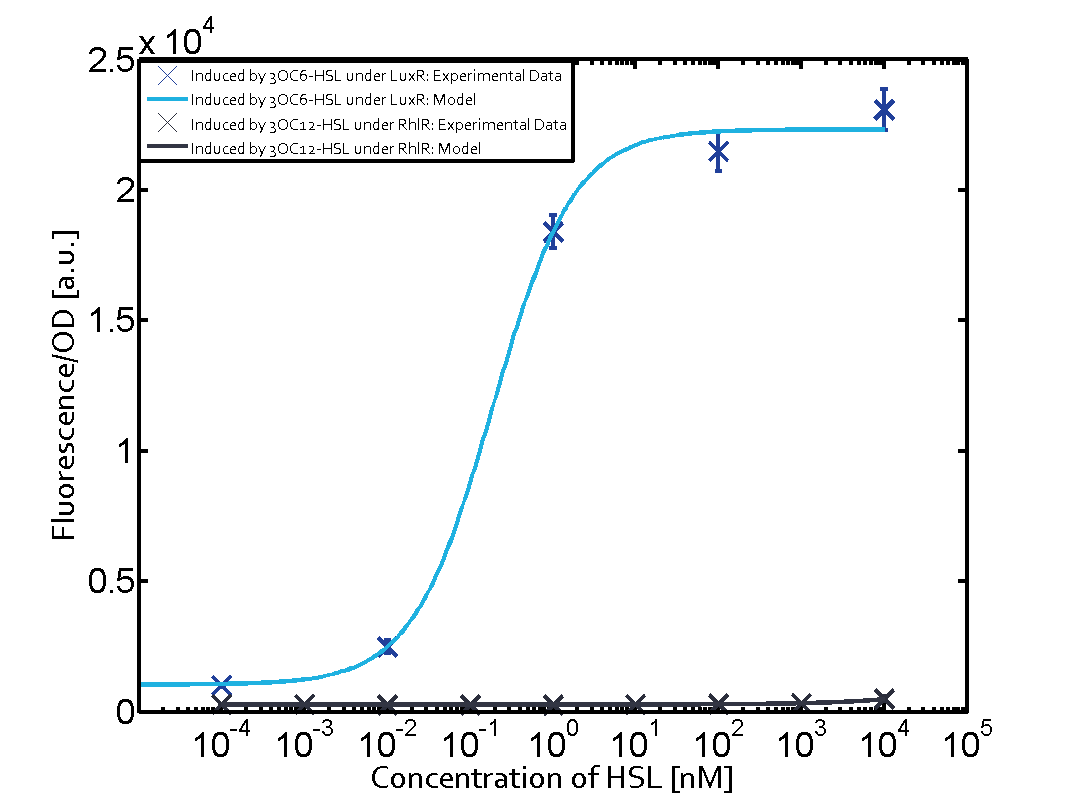
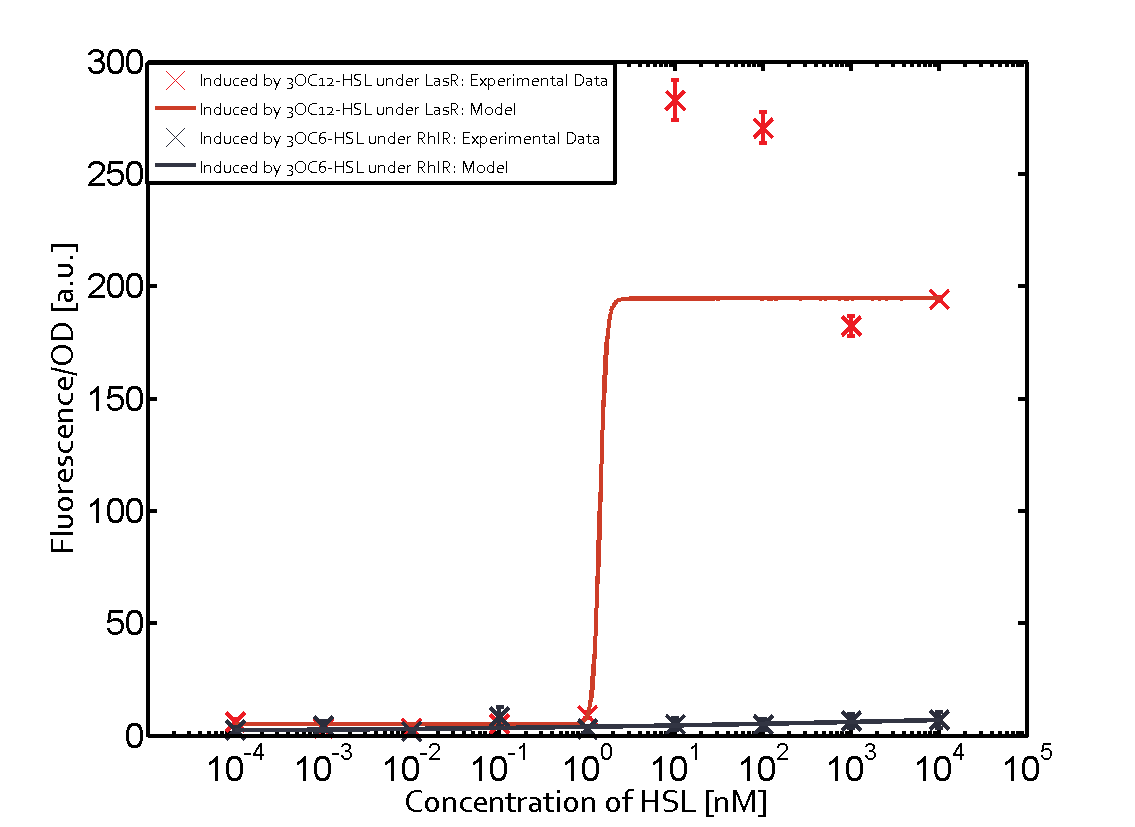
| + | Cross-talk can be observed for the cases where the 3OC12-HSL (Las-AHL) binds the LuxR regulator or when 3OC12-HSL bind to its corresponding regulator LasR and then binding to the pLux as seen in top middle and center. | ||
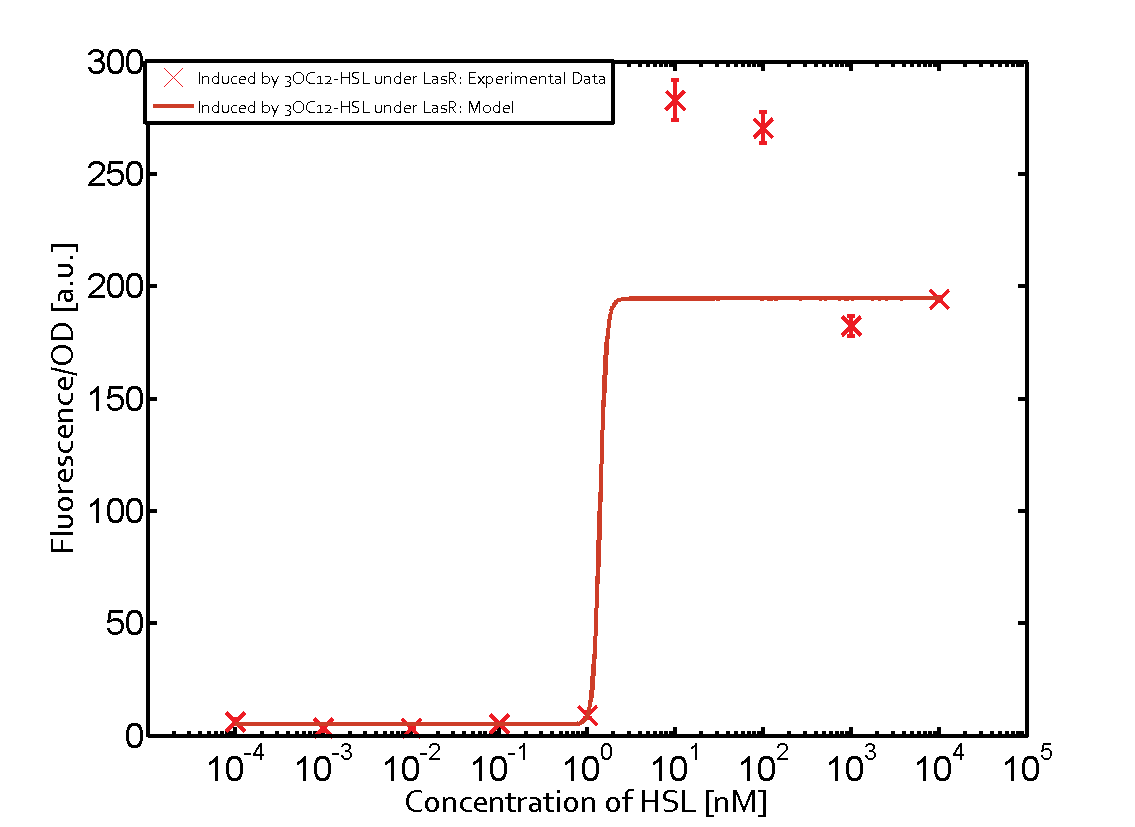
| + | For the case of Las-AHL binding the LasR and then pLux the transition occurs at 1nM and reaches 0.5 fold the fluorescence as pLux induced by 3OC6-HSL binding LuxR. | ||
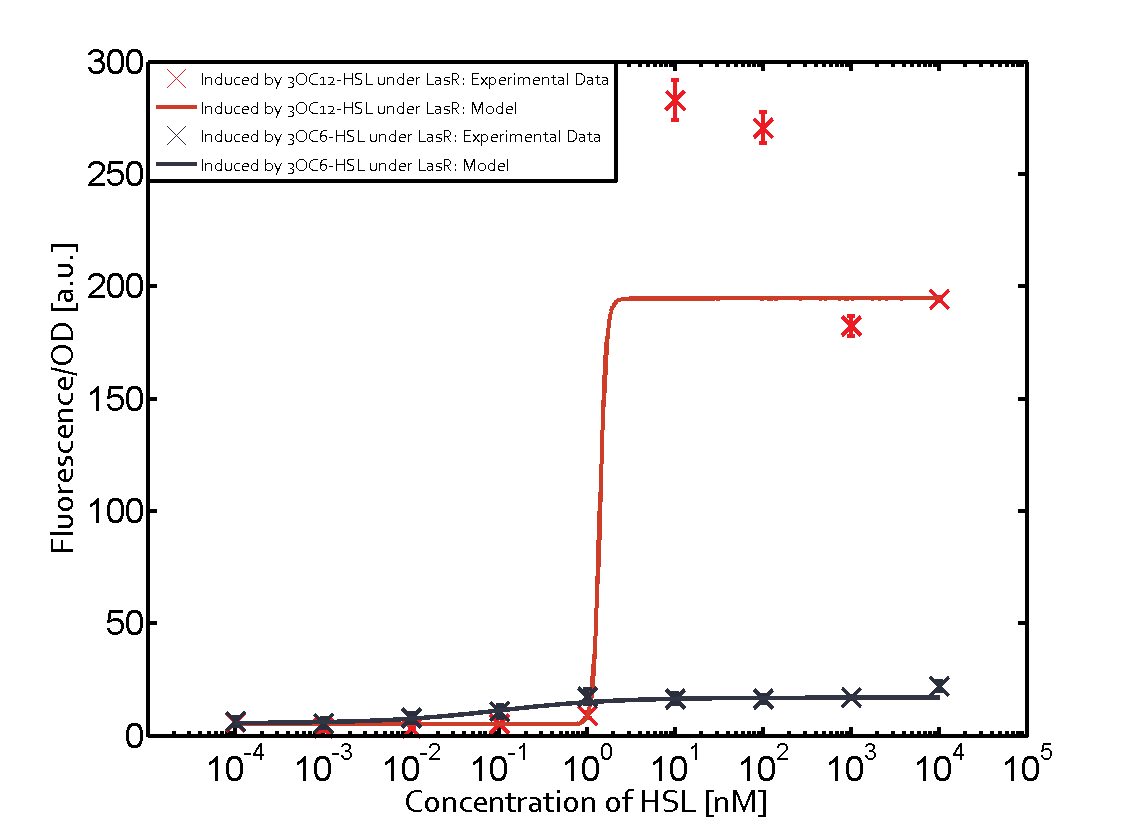
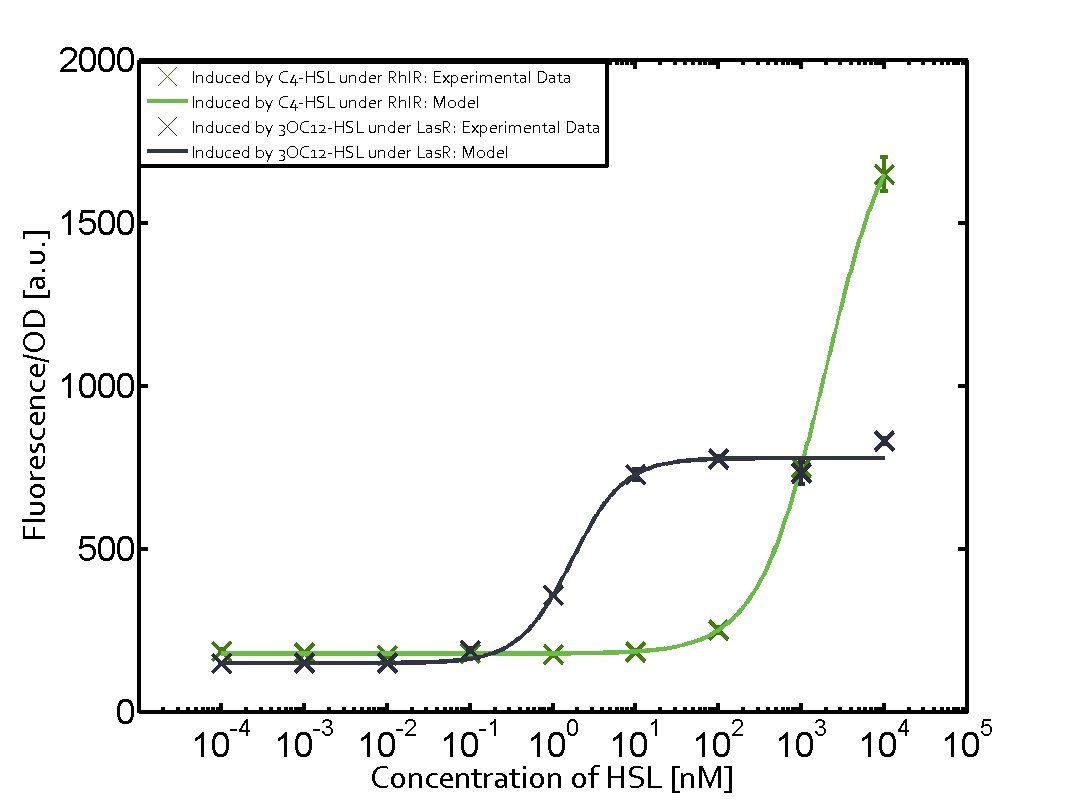
In the case of 3OC12-HSL binding LuxR and inducing the promoter pLux, the transition is observed at approximately 100nM and severe cross-talk is observed. | In the case of 3OC12-HSL binding LuxR and inducing the promoter pLux, the transition is observed at approximately 100nM and severe cross-talk is observed. | ||
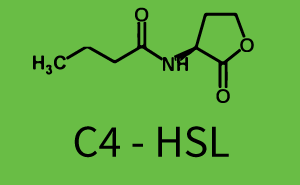
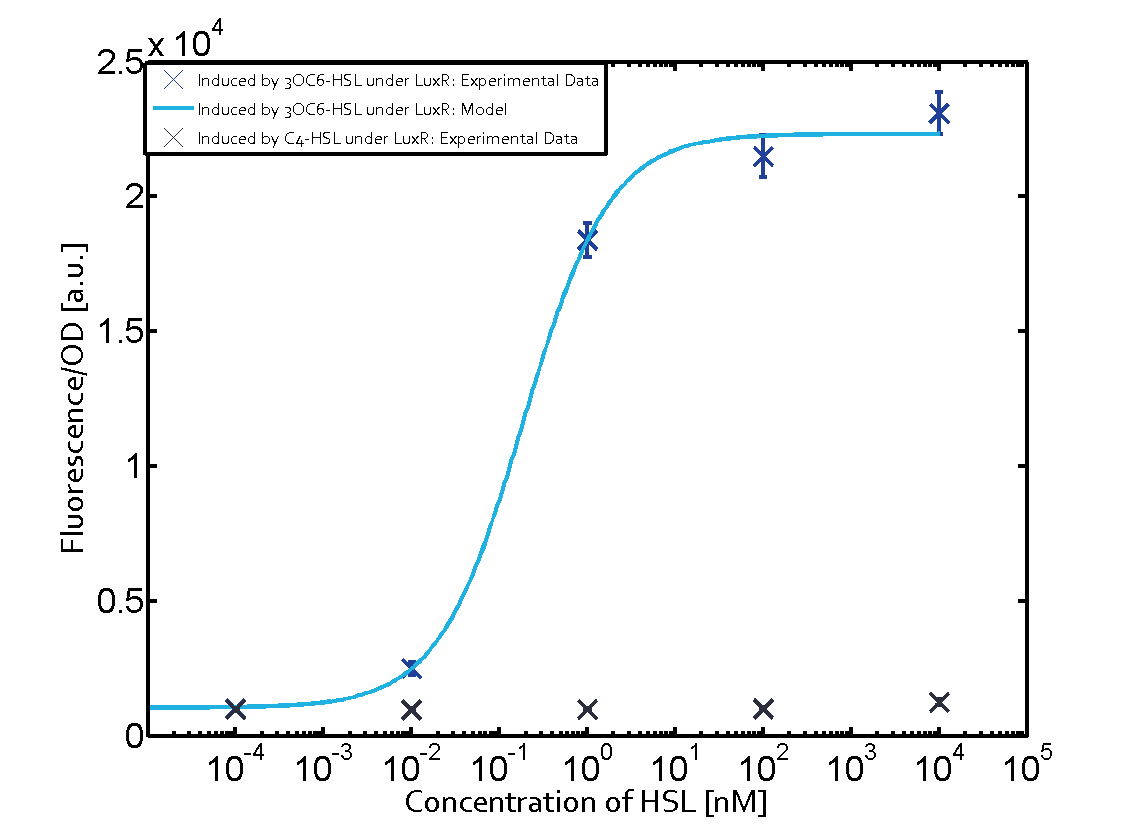
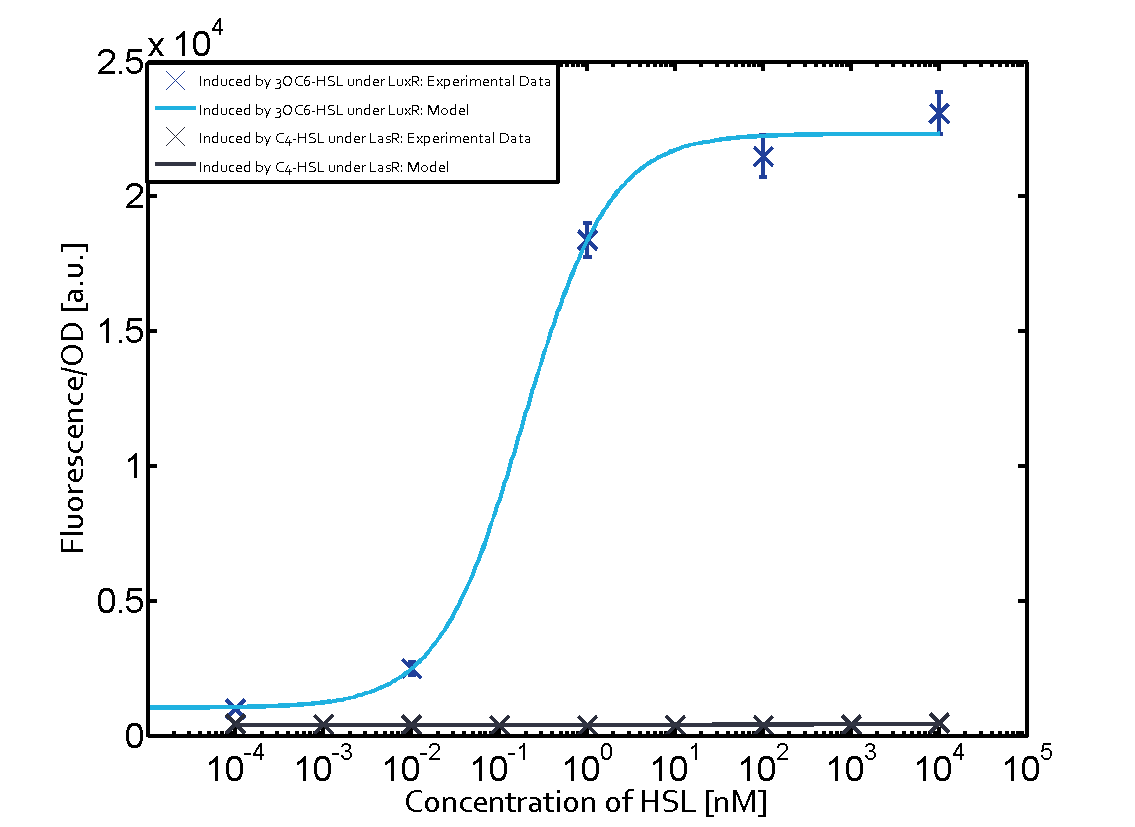
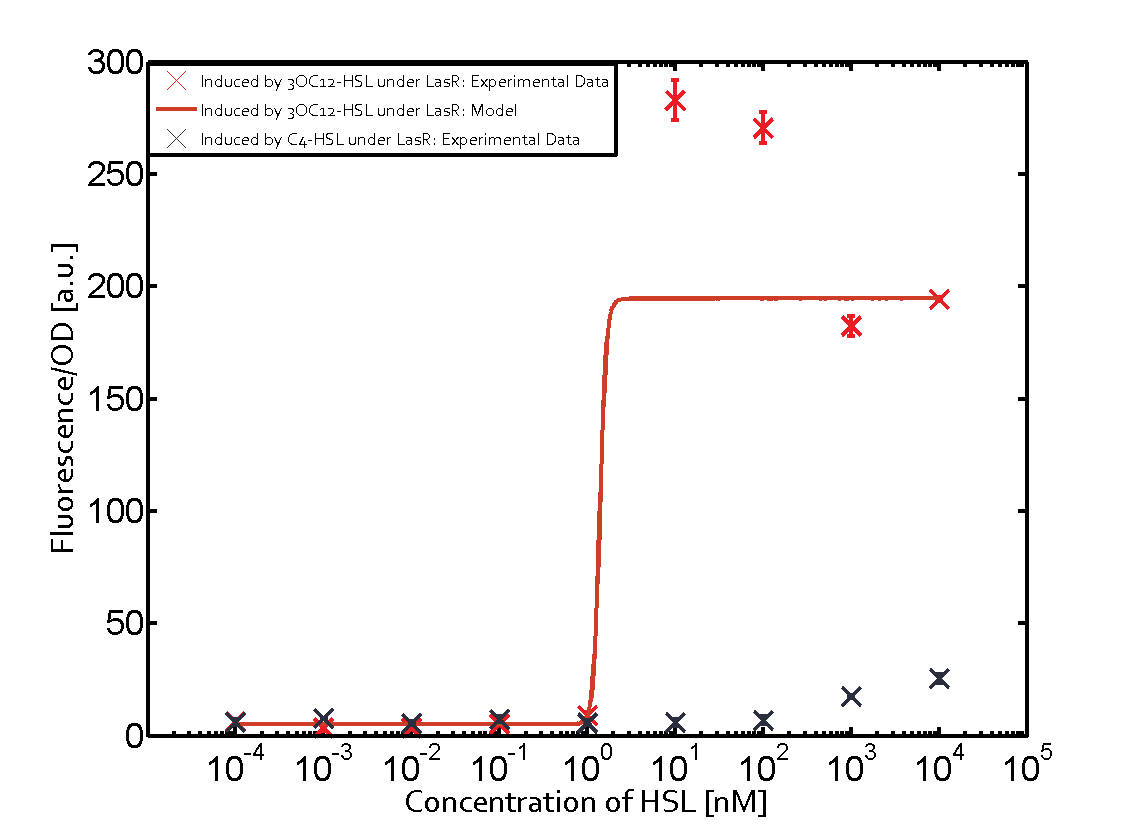
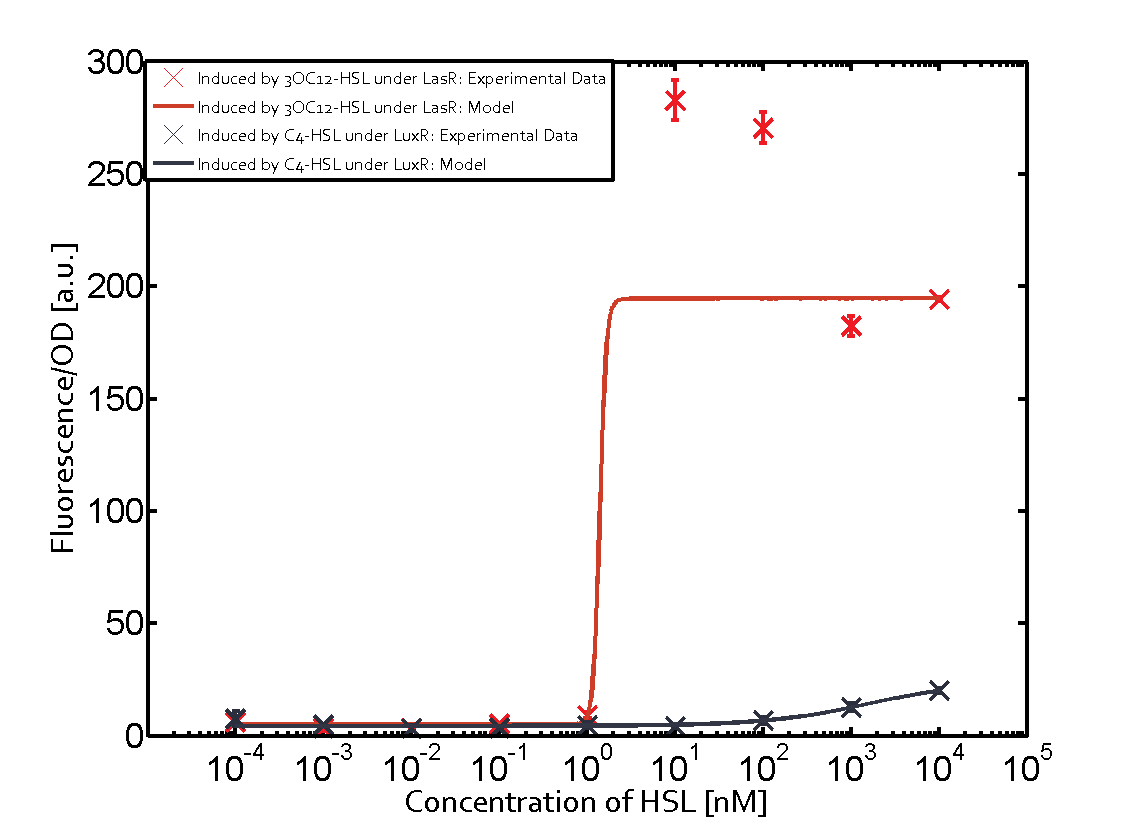
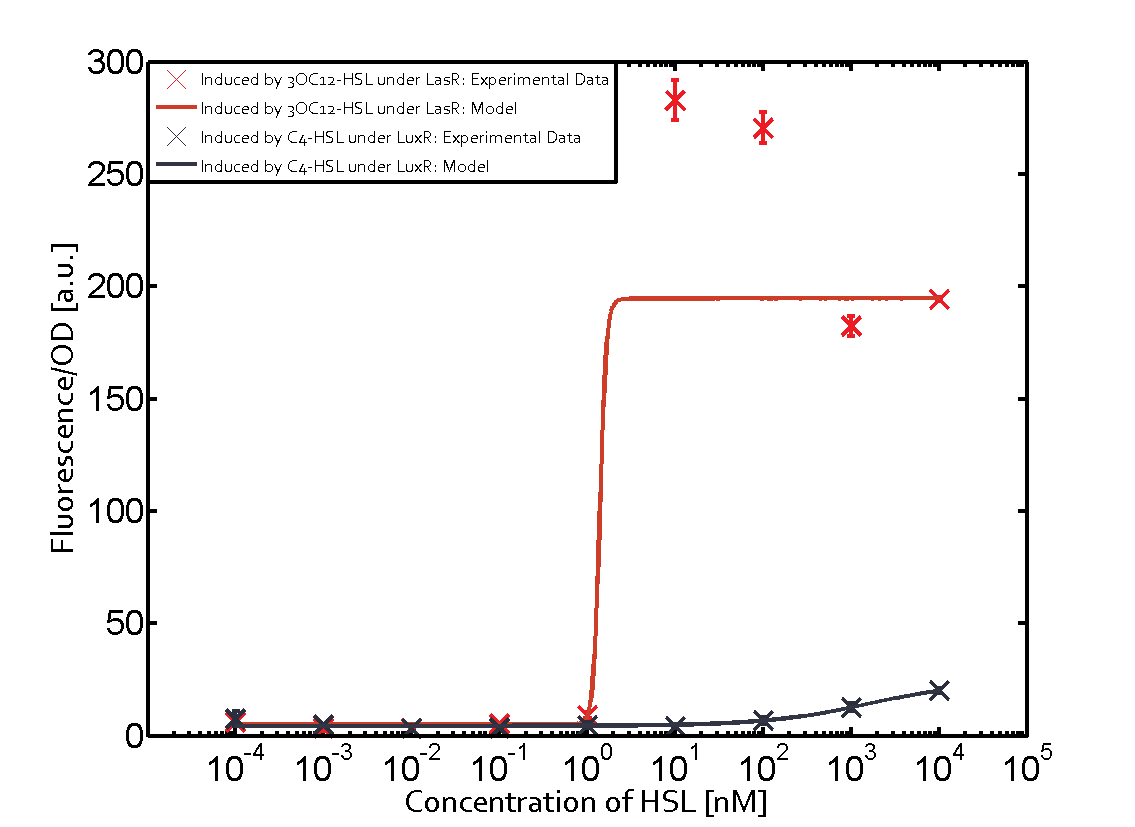
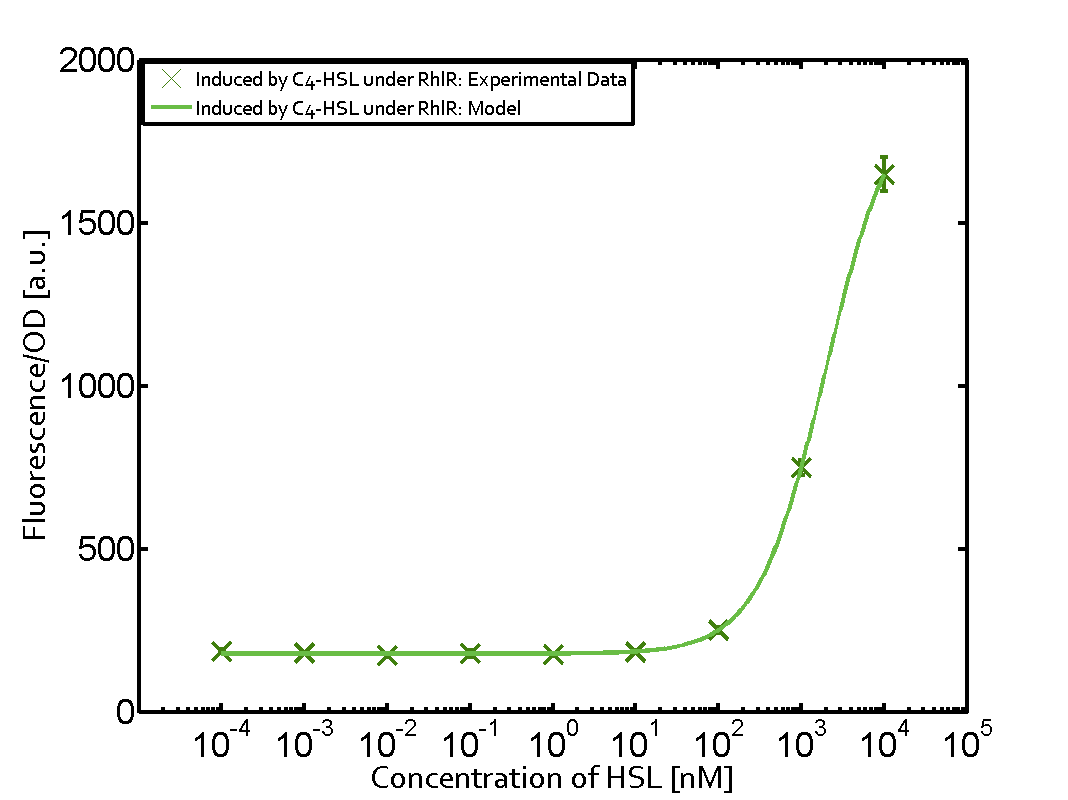
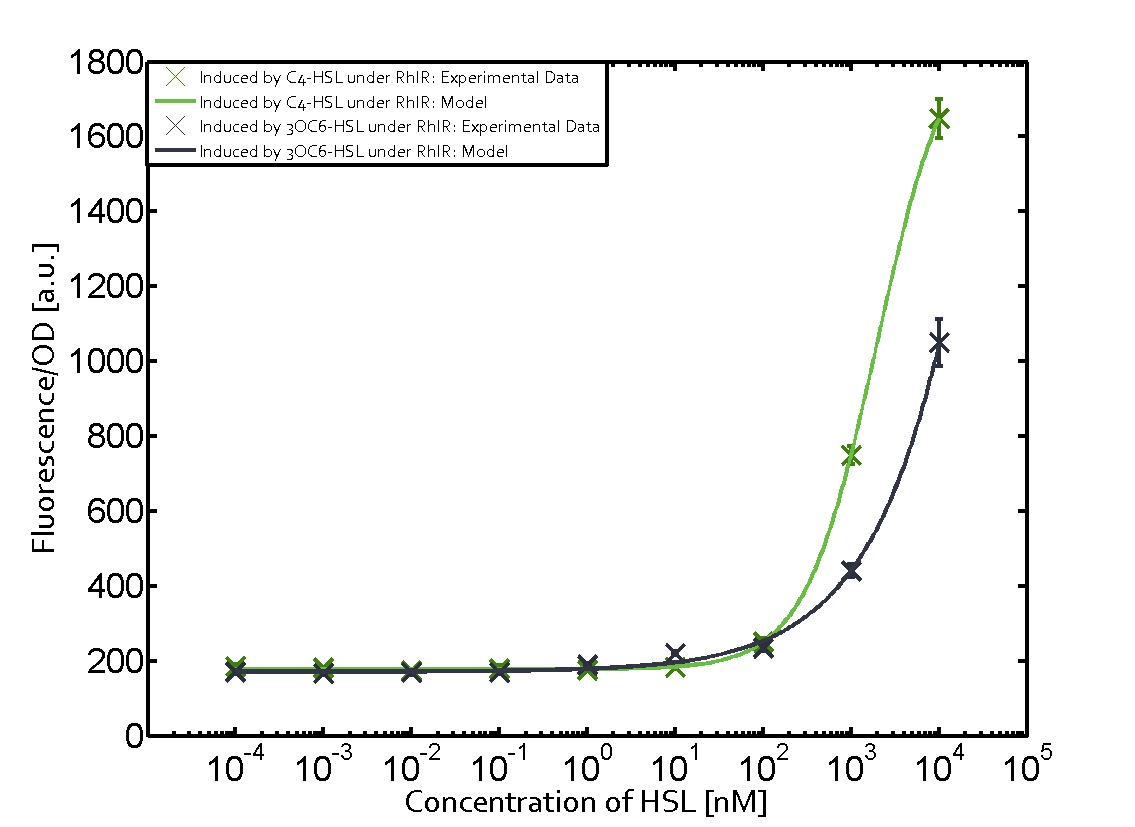
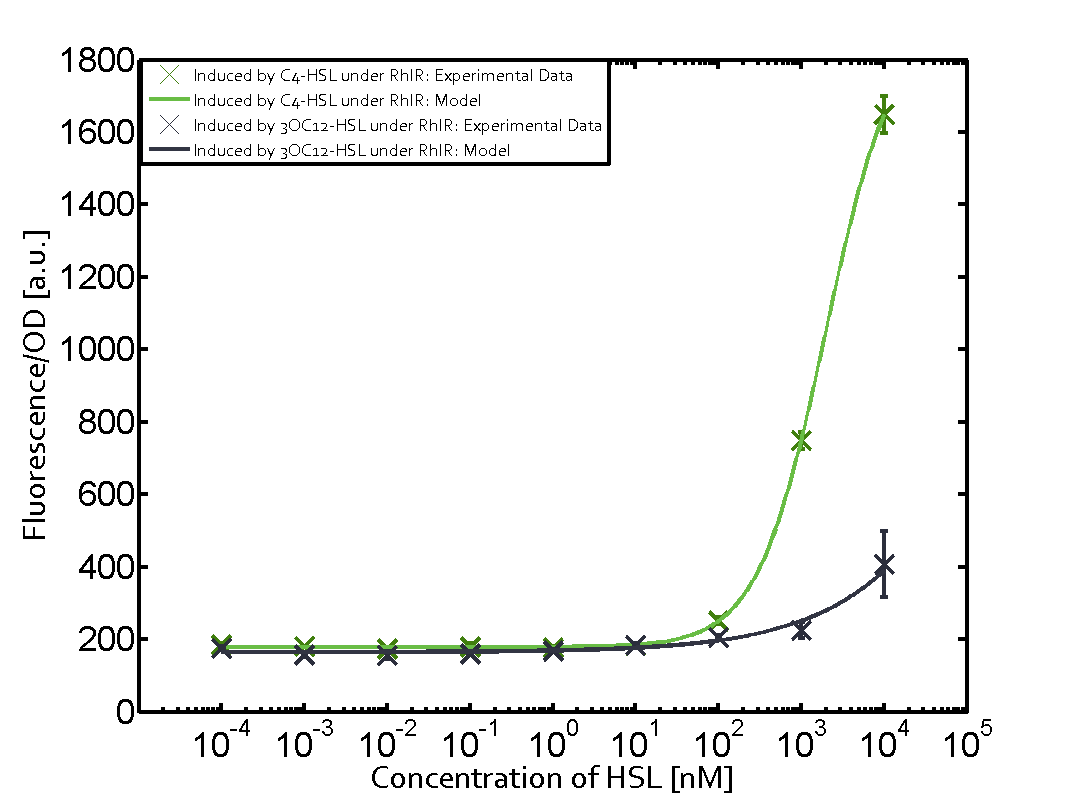
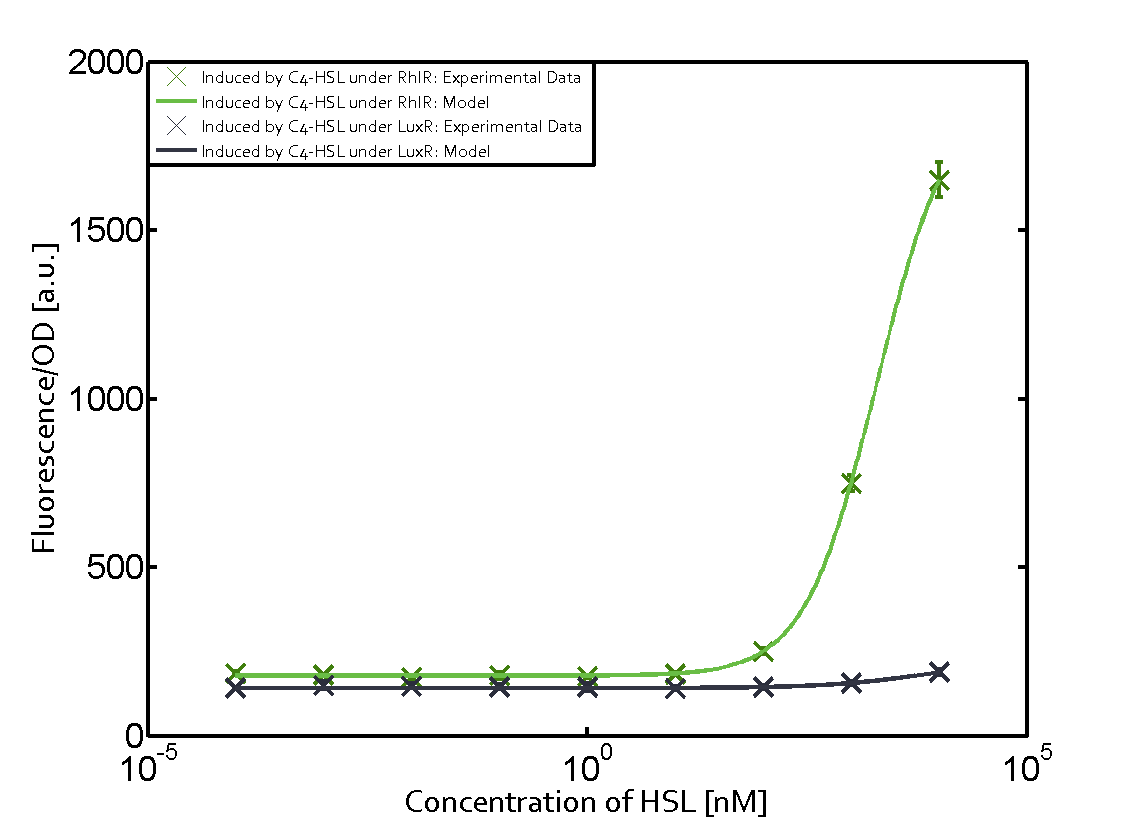
The promoter pLux was not tested in combination with the RhlR regulator and the C4-HSL. | The promoter pLux was not tested in combination with the RhlR regulator and the C4-HSL. | ||
| - | + | Observation of C4-HSL has shown that there is no significant cross-talk with the LuxR and LasR regulators binding C4-HSL and subsequently the pLux. | |
{{:Team:ETH_Zurich/expresults/qs/tab-plux}} | {{:Team:ETH_Zurich/expresults/qs/tab-plux}} | ||
Revision as of 15:36, 17 October 2014
Quorum Sensing
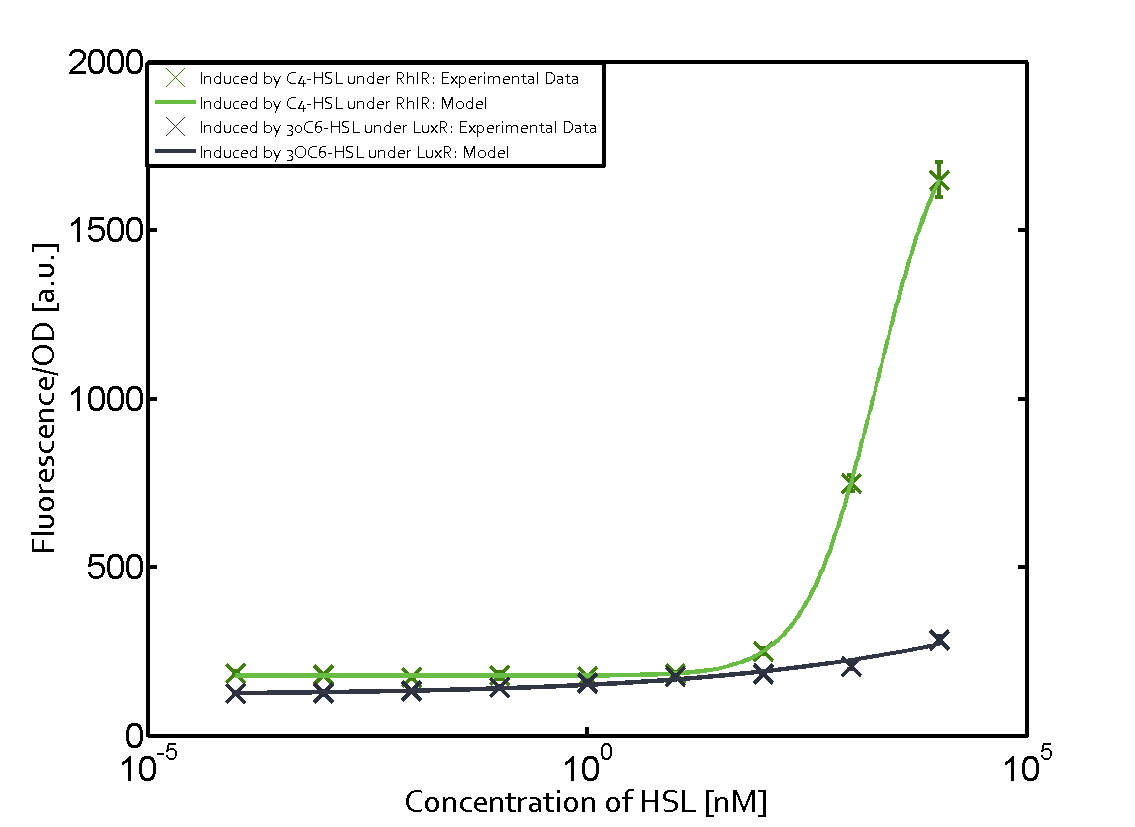
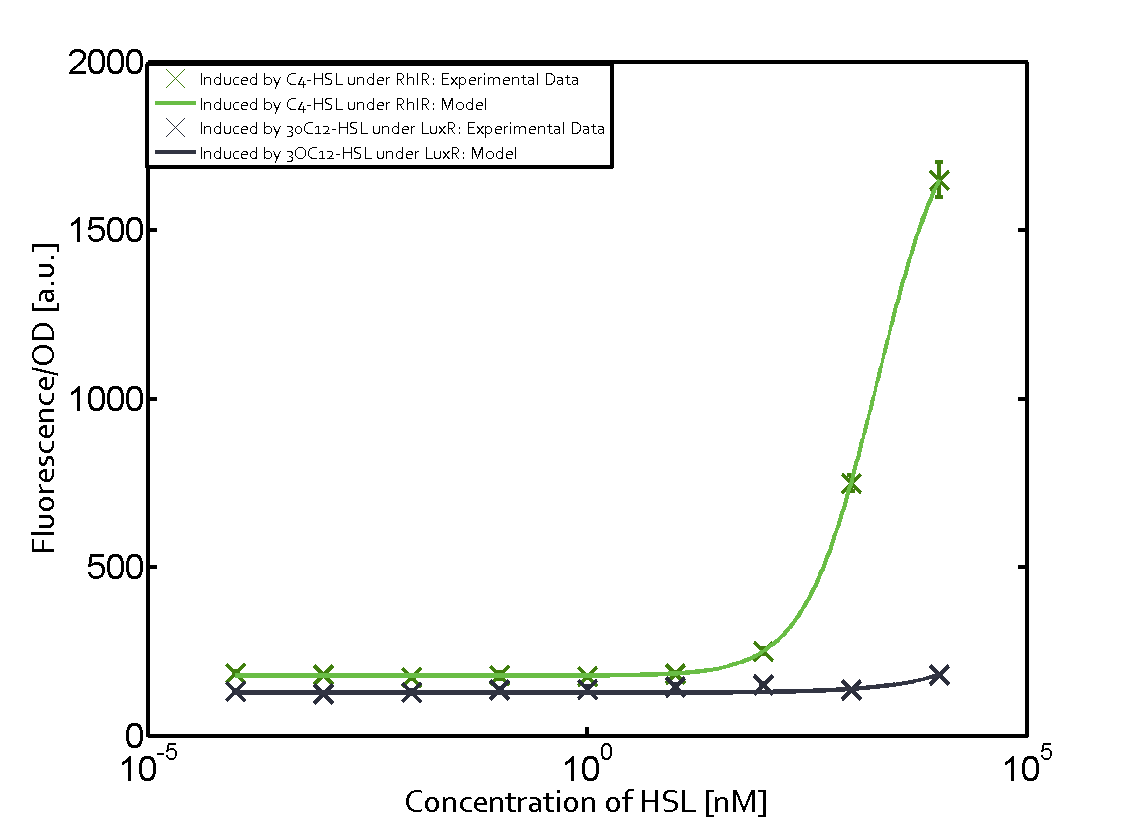
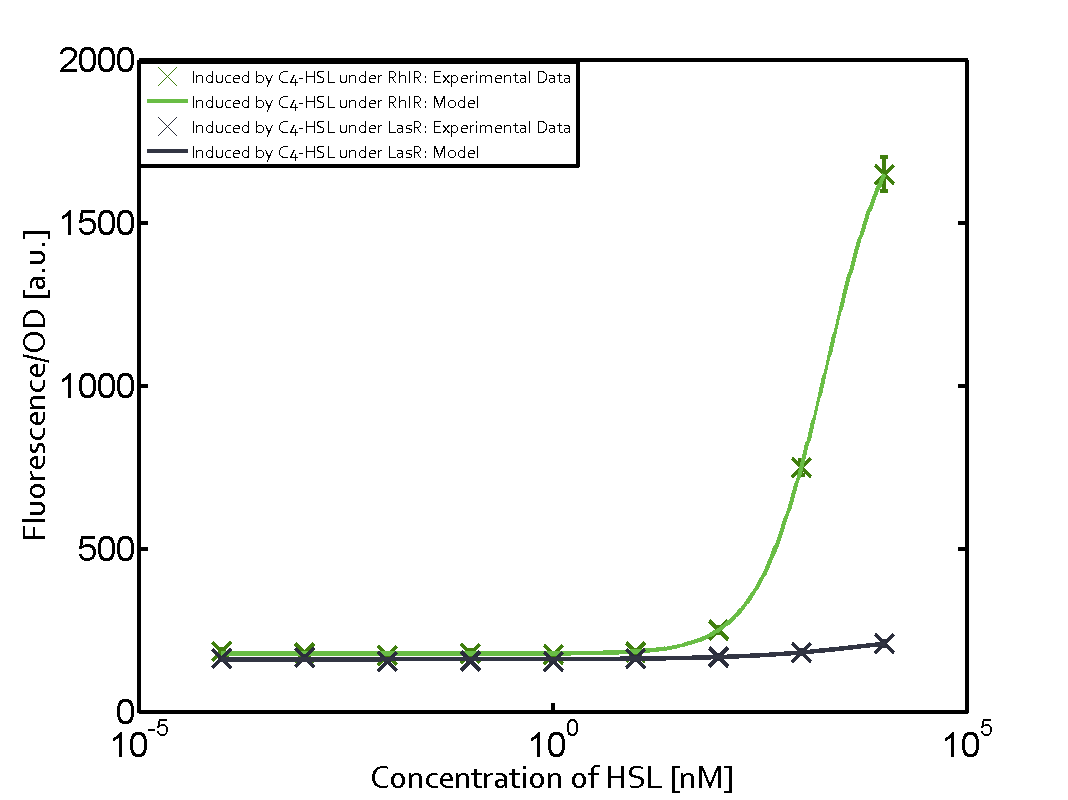
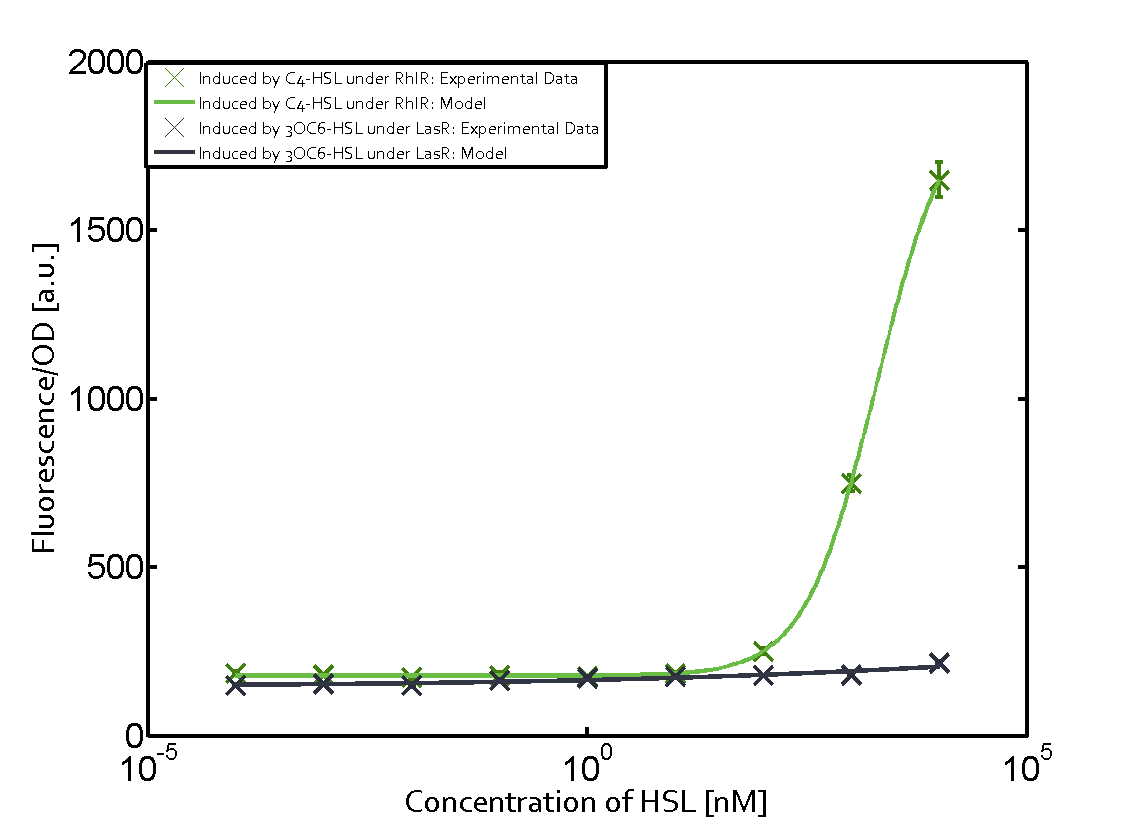
For our Mosiacoli project, we were looking for molecular systems that allow orthogonal cell-to-cell communication in order to implement connected XOR logic gates (ref project overview). As described above and elsewhere (ref to biotools) we decided to exploit the quorum-sensing systems LuxI/LuxR, LasI/LasR, and RhlI/RhlR (ref to qs parts) in order to achieve the required orthogonal cell-to-cell communication. Even though the corresponding inducer molecules are commercially available and the systems often used (ref ref), in particular in iGEM projects (ref ref), potential cross-talk activity between the different systems may be a severe problem 9ref). In order to address that challenge, we have investigated the possible cross-talk on several molecular levels: a) unspecific binding of inducer molecules to one specific regulator (table 1), b) unspecific binding of regulator molecules to one specific promoter sequence (table 2), and c) combinations of both.
How to read the matrices below.
1. Matrix pLux In all the measurements made for this matrix the promoter pLux was the basis. In this case the promoter was induced in six different variations shown. The dark blue points in the graph top left show the activation of gene expression when pLux is induced by 3OC6-HSL (Lux-AHL) binding to the corresponding LuxR regulator. The observed transition occurs at a concentration of approximately 1nM 3OC6-HSL. The light-blue curve plotted shows the latter but not experimental but the model. This curve from the model and the dark blue data point gained in experiments were plotted as a reference in all the other graphs describing pLux.
Cross-talk can be observed for the cases where the 3OC12-HSL (Las-AHL) binds the LuxR regulator or when 3OC12-HSL bind to its corresponding regulator LasR and then binding to the pLux as seen in top middle and center. For the case of Las-AHL binding the LasR and then pLux the transition occurs at 1nM and reaches 0.5 fold the fluorescence as pLux induced by 3OC6-HSL binding LuxR. In the case of 3OC12-HSL binding LuxR and inducing the promoter pLux, the transition is observed at approximately 100nM and severe cross-talk is observed. The promoter pLux was not tested in combination with the RhlR regulator and the C4-HSL.
Observation of C4-HSL has shown that there is no significant cross-talk with the LuxR and LasR regulators binding C4-HSL and subsequently the pLux.
In the laboratory, we measured a) a given promoter with its corresponding regulator and a different inducer molecule, b) a given promoter with an unspecific regulator and a particular inducer, and c) a given promoter with both regulator and inducer being unspecific. This gives in total 27 possible combinations (ref to sequences). The output was assessed via sfGFP and measured in terms of fluorescence on microtiter-plate scale. In addition, we assessed both the unregulated and regulated versions of the quorum sensing modules (see above ref).
PUT MATRICES/GRAPHS HERE
As indicated in the graphs above, we found and quantitatively characterized all three levels of cross-talk stated above. Unspecific inducer binding to the regulators as well as unspecific binding of the regulator to the promoter occurred in all possible combinations. To conclude, we were not able to find an orthogonal quorum-sensing pair due to inevitable cross-talk.
 "
"