Team:Aachen/Project/2D Biosensor
From 2014.igem.org
(→Principle of Operation) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
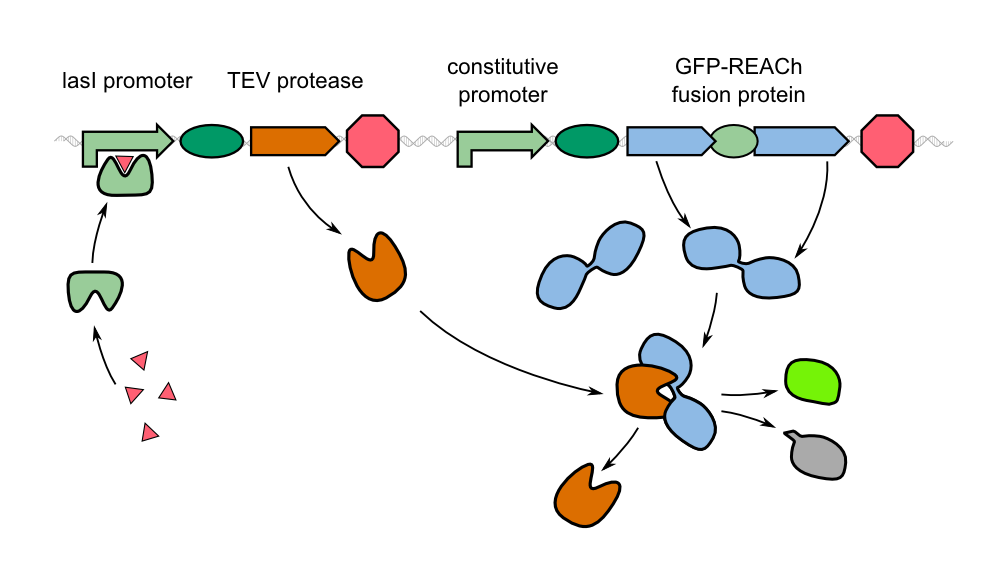
Our '''sensor cells are immobilized in agar chips'''. To make the chips, we mix the ''Cellock Holmes'' cells with liquid LB agar. In the course of our project, we designed a casting mold specifically for the production of our agar chips. When the agar has cooled down, the chips are cut out of the mold and ready to use. | Our '''sensor cells are immobilized in agar chips'''. To make the chips, we mix the ''Cellock Holmes'' cells with liquid LB agar. In the course of our project, we designed a casting mold specifically for the production of our agar chips. When the agar has cooled down, the chips are cut out of the mold and ready to use. | ||
| - | + | ''Add: Flow chart of chip measurement'' | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
To detect ''P. aeruginosa'' cells, the chip is placed on a hard surface that is potentially contaminated with the pathogen. Subsequently, the chip is introduced into our measurement device where it is incubated at 37 °C. After a short time, the chip is illuminated with blue light. The device takes a picture of the chip and the software ''Measurarty'' analyzes any fluorescent signal. Depending on the intensity of the signal and the size of the spot, ''Cellock Holmes'' can '''calculate concentration and distribution of ''P. aeruginosa'' ''' on the sampled surface. | To detect ''P. aeruginosa'' cells, the chip is placed on a hard surface that is potentially contaminated with the pathogen. Subsequently, the chip is introduced into our measurement device where it is incubated at 37 °C. After a short time, the chip is illuminated with blue light. The device takes a picture of the chip and the software ''Measurarty'' analyzes any fluorescent signal. Depending on the intensity of the signal and the size of the spot, ''Cellock Holmes'' can '''calculate concentration and distribution of ''P. aeruginosa'' ''' on the sampled surface. | ||
Revision as of 08:49, 10 October 2014
|
|
 "
"