Team:Aachen/Interlab Study
From 2014.igem.org
AZimmermann (Talk | contribs) (→Experimental Design) |
(→Interlab Study) |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| + | {{CSS/Main}} | ||
| + | {{Team:Aachen/Stylesheet}} | ||
{{Team:Aachen/Header}} | {{Team:Aachen/Header}} | ||
= Interlab Study = | = Interlab Study = | ||
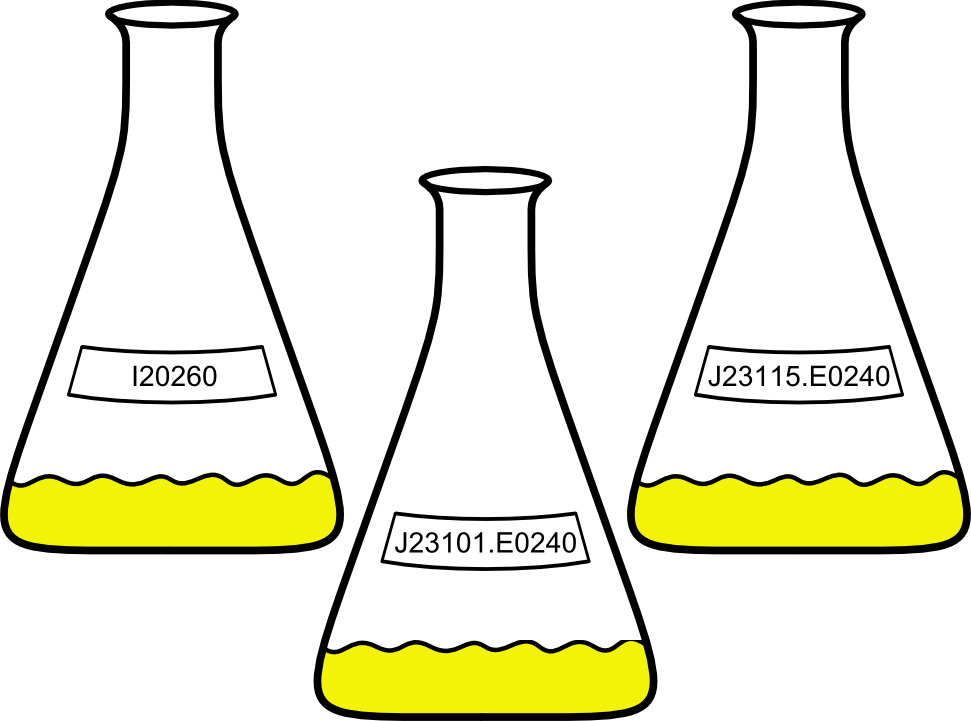
| - | + | As our team is competing in the Measurement track for this year's competition, we were also required to participate in the [https://2014.igem.org/Tracks/Measurement/Interlab_study iGEM 2014 Measurement Interlab Study]. This study aims to '''collect data from iGEM teams all over the world''' on the fluorescence of '''three genetic devices expressing GFP'''. The devices differ in their plasmid copy properties and the strength of the promoter. | |
| - | As our team is competing in the Measurement track for this year's competition, we were also required to participate in the [https://2014.igem.org/Tracks/Measurement/Interlab_study iGEM 2014 Measurement Interlab Study]. This study aims to '''collect data from iGEM teams all over the world''' on the fluorescence of '''three genetic devices expressing GFP'''. The devices differ in their plasmid copy properties and the strength of the | + | |
| - | We introduced the three constructs into ''E. coli'' cells and measured '''fluorescence as well as optical density''' of the liquid cultures over a period of 18 hours, using '''a spectrophotometer and a plate reader''', respectively. The obtained results confirmed our hypothesis that the fluorescence of the BioBrick in the high copy plasmid pSB1C3, J23101.E0240, would exhibit a stronger signal than the constructs I20260, which is | + | We introduced the three constructs into ''E. coli'' cells and measured '''fluorescence as well as optical density''' of the liquid cultures over a period of 18 hours, using '''a spectrophotometer and a plate reader''', respectively. The obtained results confirmed our hypothesis that the fluorescence of the BioBrick in the high copy plasmid pSB1C3, J23101.E0240, would exhibit a stronger signal than the constructs I20260, which is the low to mid copy plasmid pSB3K3, and J23115.E0240, which has a weaker promoter than J23101.E0240. During the experiment, we could observe a typical growth curve for ''E.coli'' including lag, exponential, stationary and death phase. We could show that the fluorescence we measured is rather a function of each cell than the whole culture, since all cultures had comparable optical densities. |
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| - | + | <ul class="menusmall-grid" style="width:1040px"> | |
| - | + | ||
| + | <li style="width:186px;margin-left: 11px;margin-right: 11px;margin-bottom: 11px;margin-top: 11px;"> | ||
| + | <a class="menulink" href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Interlab_Study#isexperimentaldesign" style="color:black"> | ||
| + | <div class="menusmall-item menusmall-info" style="height: 180px; width: 180px;"><div class="menukachel" style="top:32%; line-height:1.5em;">Experimental Design</div></div> | ||
| + | <div class="menusmall-item menusmall-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/1/10/Aachen_14-10-13_Yellow_Flask_iNB.png); norepeat scroll 0% 0% transparent; background-size:100%;height: 180px; width: 180px;"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li style="width:186px;margin-left: 11px;margin-right: 11px;margin-bottom: 11px;margin-top: 11px;"> | ||
| + | <a class="menulink" href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Interlab_Study#isexpectedresults" style="color:black"> | ||
| + | <div class="menusmall-item menusmall-info" style="height: 180px; width: 180px;"><div class="menukachel" style="top:32%; line-height:1.5em;">Expected Results</div></div> | ||
| + | <div class="menusmall-item menusmall-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/7/78/Aachen_14-10-13_Green_Flask_iNB.png); norepeat scroll 0% 0% transparent; background-size:100%;height: 180px; width: 180px;"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li style="width:186px;margin-left: 11px;margin-right: 11px;margin-bottom: 11px;margin-top: 11px;"> | ||
| + | <a class="menulink" href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Interlab_Study#ismaterials" style="color:black"> | ||
| + | <div class="menusmall-item menusmall-info" style="height: 180px; width: 180px;"><div class="menukachel" style="top:32%; line-height:1.5em;">Materials & Methods</div></div> | ||
| + | <div class="menusmall-item menusmall-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/3/30/Aachen_14-10-13_Empty_Falcon_iNB.png); norepeat scroll 0% 0% transparent; background-size:100%;height: 180px; width: 180px;"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li style="width:186px;margin-left: 11px;margin-right: 11px;margin-bottom: 11px;margin-top: 11px;"> | ||
| + | <a class="menulink" href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Interlab_Study#isresults" style="color:black"> | ||
| + | <div class="menusmall-item menusmall-info" style="height: 180px; width: 180px;"><div class="menukachel" style="top:40%">Results</div></div> | ||
| + | <div class="menusmall-item menusmall-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/b/b7/Aachen_14-10-13_Graph_Panel_iNB.png); norepeat scroll 0% 0% transparent; background-size:100%;height: 180px; width: 180px;"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li style="width:186px;margin-left: 11px;margin-right: 11px;margin-bottom: 11px;margin-top: 11px;"> | ||
| + | <a class="menulink" href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Interlab_Study#isdiscussion" style="color:black"> | ||
| + | <div class="menusmall-item menusmall-info" style="height: 180px; width: 180px;"><div class="menukachel" style="top:40%">Discussion</div></div> | ||
| + | <div class="menusmall-item menusmall-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/3/3b/Aachen_14-10-13_Graph_with_Error_Bars_Panel_iNB.png); norepeat scroll 0% 0% transparent; background-size:100%;height: 180px; width: 180px;"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </ul> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Aachen_14-10-13_Yellow_Flask_iNB.png|right|150px]] | ||
==Experimental Design== | ==Experimental Design== | ||
| - | For the Interlab Study, we tested GFP-containing BioBricks for fluorescence and optical density. Subject of the study were the BioBricks I20260, J23101.E0240 and J23115.E0240. The latter consists of a [http://parts.igem.org/Part:pSB3K3 pSB3K3] backbone with an insert, a combination of the promoter [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23101 J23101], the RBS [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0032 B0032], the GFP coding sequence [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0040 E0040] and the terminator [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0015 B0015]. J23101.E0240 has the same insert as I20260, but has [http://parts.igem.org/Part:pSB1C3 pSB1C3] as a backbone. J23115.E0240 only differs from J23101.E0240 in the use of another | + | <span class="anchor" id="isexperimentaldesign"></span> |
| + | |||
| + | For the Interlab Study, we tested GFP-containing BioBricks for fluorescence and optical density. Subject of the study were the BioBricks I20260, J23101.E0240 and J23115.E0240. The latter consists of a [http://parts.igem.org/Part:pSB3K3 pSB3K3] backbone with an insert, a combination of the promoter [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23101 J23101], the RBS [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0032 B0032], the GFP coding sequence [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0040 E0040] and the terminator [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0015 B0015]. J23101.E0240 has the same insert as I20260, but has [http://parts.igem.org/Part:pSB1C3 pSB1C3] as a backbone. J23115.E0240 only differs from J23101.E0240 in the use of another promoter, namely [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23115 J23115]. As a '''negative control''', we used just B0015 in pSB1C3. | ||
{{Team:Aachen/Figure|Flasks.png|align=center|width=400px}} | {{Team:Aachen/Figure|Flasks.png|align=center|width=400px}} | ||
| Line 21: | Line 72: | ||
Over a time span of 18 hours the optical density and fluorescence of cultures containing these BioBricks were measured every 2 hours using the spectrophotometer and plate reader, respectively. | Over a time span of 18 hours the optical density and fluorescence of cultures containing these BioBricks were measured every 2 hours using the spectrophotometer and plate reader, respectively. | ||
| + | |||
{{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | {{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Aachen_14-10-13_Green_Flask_iNB.png|right|150px]] | ||
==Expected Results== | ==Expected Results== | ||
| - | + | <span class="anchor" id="isexpectedresults"></span> | |
| - | + | Fluorescence was expected to develop in cultures containing I20260, J23101.E0240 and J23115.E0240, as all include the GFP coding sequence. However, the signal was expected to be stronger in J23101.E0240 than in I20260 since pS1C3 is a high copy plasmid while pSB3K3 is a low to mid copy plasmid. Because of this, a higher fluorescence was expected of J23101.E0240 compared to I20260 even though they share the same insert. J23115.E0240, too, was supposed to produce a fluorescent signal, but J23115 (the mutated version K823012 was used) is a lot weaker promoter than J23101. Therefore, a lot lower - if any - fluorescence is expected with this BioBrick. | |
| + | |||
| + | {{Team:Aachen/Figure|Aachen_14-10-16_Plasmid_Promoter_Strength_iNB.png|title=Diagram illustrating the different plasmid and promoter properties|subtitle=Plasmid pSB1C3 has a higher copy number than pSB3K3, and J23101 is a stronger promoter than J23115.|width=800px}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | B0015 was used as our '''negative control''' as the insert only contains a terminator and no expression cassette for GFPmut3b, and so no fluorescence was expected. | ||
| - | |||
{{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | {{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Aachen_14-10-13_Empty_Falcon_iNB.png|right|150px]] | ||
==Materials and Methods== | ==Materials and Methods== | ||
| + | <span class="anchor" id="ismaterials"></span> | ||
===Constructs and strains=== | ===Constructs and strains=== | ||
| - | All constructs used were transformed into [https://www.neb.com/products/c3019-neb-10-beta-competent-e-coli-high-efficiency NEB 10β] cells. The constructs I20260 as well as B0015 were taken directly from the iGEM 2014 distribution plates. The constructs J23101.E0240 as well as J23115.E0240 were made using the [http://parts.igem.org/Help:Assembly/3A_Assembly 3A Assembly]. Therefore, the subparts J23101, J23115 as well as E0240 were transformed directly from the 2014 distribution plates into [https://www.neb.com/products/c3019-neb-10-beta-competent-e-coli-high-efficiency NEB 10β] cells. Afterwards the plasmids were recovered using the [https://us.vwr-cmd.com/bin/public/demidoccdownload/50001659/7057R_ge_healthcare_illustra_nucleic_acid_sample_preparation.pdf illustra plasmidPrep Mini Spin Kit]. The purified plasmids J23101 and J23115 were cut with the restriction enzymes EcoRI and SpeI, while E0240 was cut with XbaI and PstI. The restricted plasmids were then ligated together using the T4 DNA Ligase. Afterwards, the ligation product was introduced into the pSB1C3 linearized backbone provided by iGEM headquarters with the 2014 distribution which we had also cut with EcoRI and PstI. All restrictions and ligations were performed using enzymes and buffers of the [http://shop2.neb-online.de/4DCGI/ezshop?action=Direktanzeige&Artikelnummer=NEBIGEM1%40&WorldNr=01&ButtonName=website&skontaktid=1055557&skontaktkey=RrbLvNPZxLRIFbyyyGOZambWfZKxFK NEB iGEM Kit] | + | All constructs used were transformed into [https://www.neb.com/products/c3019-neb-10-beta-competent-e-coli-high-efficiency NEB 10β] cells. The constructs I20260 as well as B0015 were taken directly from the iGEM 2014 distribution plates. The constructs J23101.E0240 as well as J23115.E0240 were made using the [http://parts.igem.org/Help:Assembly/3A_Assembly 3A Assembly]. Therefore, the subparts J23101, J23115 as well as E0240 were transformed directly from the 2014 distribution plates into [https://www.neb.com/products/c3019-neb-10-beta-competent-e-coli-high-efficiency NEB 10β] cells. Afterwards the plasmids were recovered using the [https://us.vwr-cmd.com/bin/public/demidoccdownload/50001659/7057R_ge_healthcare_illustra_nucleic_acid_sample_preparation.pdf illustra plasmidPrep Mini Spin Kit]. The purified plasmids J23101 and J23115 were cut with the restriction enzymes EcoRI and SpeI, while E0240 was cut with XbaI and PstI. The restricted plasmids were then ligated together using the T4 DNA Ligase. Afterwards, the ligation product was introduced into the pSB1C3 linearized backbone provided by iGEM headquarters with the 2014 distribution which we had also cut with EcoRI and PstI. All restrictions and ligations were performed using enzymes and buffers of the [http://shop2.neb-online.de/4DCGI/ezshop?action=Direktanzeige&Artikelnummer=NEBIGEM1%40&WorldNr=01&ButtonName=website&skontaktid=1055557&skontaktkey=RrbLvNPZxLRIFbyyyGOZambWfZKxFK NEB iGEM Kit]. The final product was once again transformed into [https://www.neb.com/products/c3019-neb-10-beta-competent-e-coli-high-efficiency NEB 10β] cells. |
The correct identity of the resulting constructs were confirmed by sequencing. The sequencing data (consensus sequences) can be found [https://2014.igem.org/File:Sequencing_Interlab_Study_iGEM_Aachen_2014.zip here]. | The correct identity of the resulting constructs were confirmed by sequencing. The sequencing data (consensus sequences) can be found [https://2014.igem.org/File:Sequencing_Interlab_Study_iGEM_Aachen_2014.zip here]. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 103: | ||
===Inoculation and Cultivation=== | ===Inoculation and Cultivation=== | ||
| - | The cultivation of our bacteria was performed in 500 | + | The cultivation of our bacteria was performed in 500 ml shake flasks filled with 50 ml [https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Notebook/Protocols#LB_medium LB medium]. The cultures were kept at 37°C and 300 rpm shaking frequency. Appropiate antibiotics were added to each media (kanamycin for I20260, chloramphenicol for B0015, J23101.E0240 and J23115.E0240). Both antibiotics were added from a 1000X stock stored at -20°C for a final concentration of 35 µg/ml chloramphenicol and 50 µg/ml kanamycin, respectively. |
| - | The precultures were inoculated from the same cryo stocks. They were cultivated for 16 hours and then sampled for OD measurement with a spectrophotometer. Then 2 | + | The precultures were inoculated from the same cryo stocks. They were cultivated for 16 hours and then sampled for OD measurement with a spectrophotometer. Then 2 ml of each preculture were centrifuged (5 minutes, 6000 g) and then washed twice with PBS buffer. Afterwards, all cultures were inoculated to have the same starting OD. Inoculations were carried out under sterile conditions at the clean bench. |
===Sampling=== | ===Sampling=== | ||
| - | To draw samples, the shake flasks were taken out of the | + | To draw samples, the shake flasks were taken out of the 37°C room and brought onto a nearby bench. 3 ml of sample were taken out next to a Bunsen burner flame and pipetted into three 2 ml cuvettes. As soon as all samples were taken the flasks were taken back onto the shaker in the 37°C room. The whole process of taking samples for all 12 flasks (3 biological replicates for each construct) took 5 minutes and samples were taken every 2 hours. |
After 4 hours, we had to dilute the samples with LB medium in a ratio of 1:4, and from the 6th to 18th hour we had to dilute in a ratio of 1:9. | After 4 hours, we had to dilute the samples with LB medium in a ratio of 1:4, and from the 6th to 18th hour we had to dilute in a ratio of 1:9. | ||
| - | After the measurement of OD in the spectrometer, 100 | + | After the measurement of OD in the spectrometer, 100 µl of each sample were taken out and put on a 96-well plate (Thermo microfluor 1, flat-bottom, black) to measure fluorescence. |
Each measurement occured in a technical triplicate, resulting in 36 different samples being processed in every sampling step. | Each measurement occured in a technical triplicate, resulting in 36 different samples being processed in every sampling step. | ||
| Line 93: | Line 153: | ||
As for the OD measurement, we used LB medium as our blank. Since samples for fluorescence measurement were acquired from the cuvettes for the OD measurement, sample processed in plate reader had the same dilutions. | As for the OD measurement, we used LB medium as our blank. Since samples for fluorescence measurement were acquired from the cuvettes for the OD measurement, sample processed in plate reader had the same dilutions. | ||
| + | |||
{{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | {{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Aachen_14-10-13_Graph_Panel_iNB.png|right|150px]] | ||
==Results== | ==Results== | ||
| + | <span class="anchor" id="isresults"></span> | ||
| + | |||
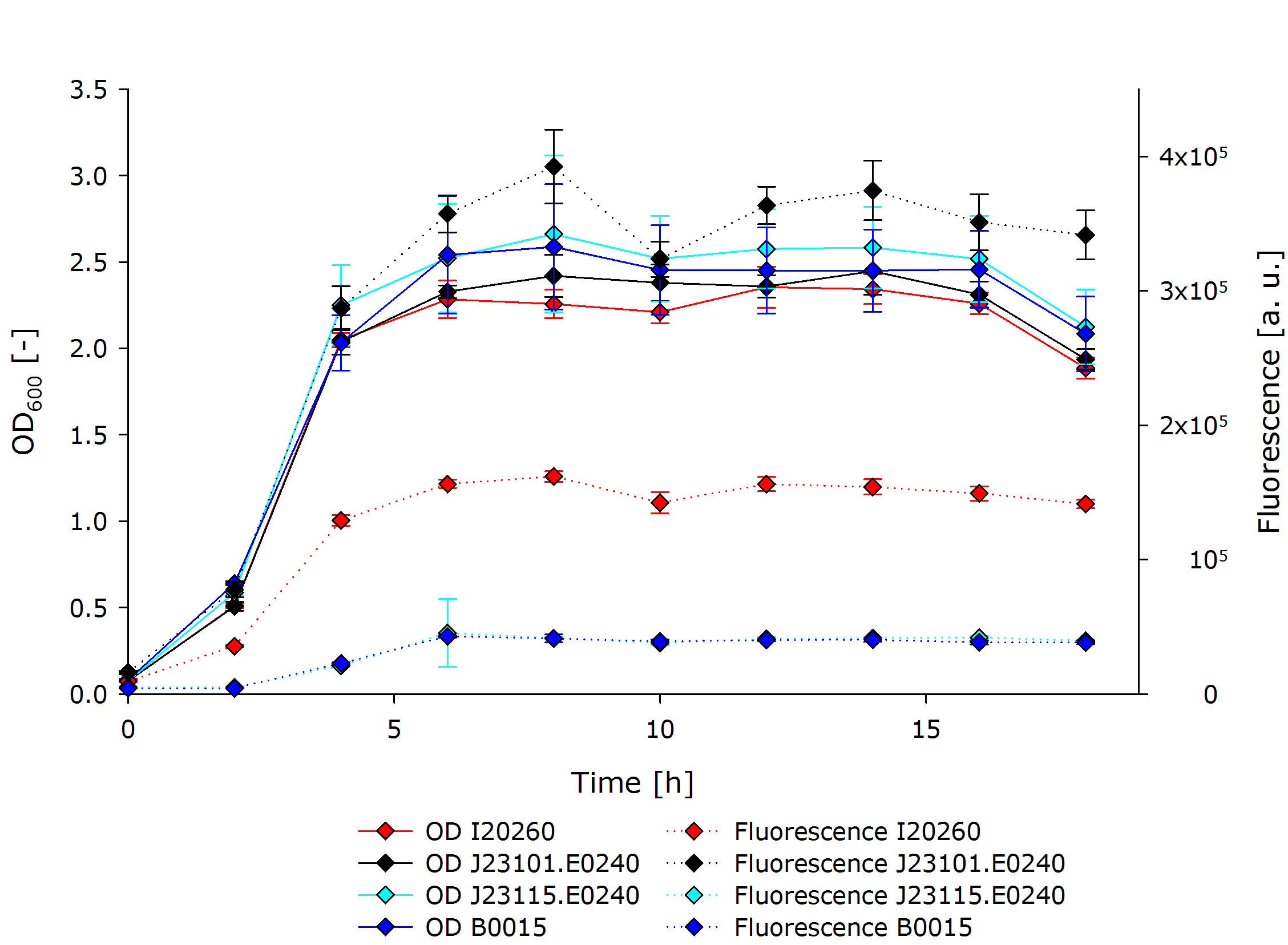
After observing the optical density (OD) and fluorescence for 18 hours while taking samples every 2 hours, the following results were obtained: | After observing the optical density (OD) and fluorescence for 18 hours while taking samples every 2 hours, the following results were obtained: | ||
| - | {{Team:Aachen/Figure| | + | {{Team:Aachen/Figure|Aachen 14-10-13 InterlabGraph1 iFG.PNG|align=center|title=Interlab Study Results|subtitle=Our measurements of fluorescence and optical density of the three genetic devices and a negative control.|width=700px}} |
This shows that all cultures had ODs in the same range throughout the experiment. After the exponential growth phase the stationary phase started shortly after 4 hours of cultivation time. The OD did not change from thereon until a cultivation time of 16 hours after which it started to decline. | This shows that all cultures had ODs in the same range throughout the experiment. After the exponential growth phase the stationary phase started shortly after 4 hours of cultivation time. The OD did not change from thereon until a cultivation time of 16 hours after which it started to decline. | ||
The development of fluorescence followed largely the pattern of the OD, but differed a lot in between the different cultures. J23101.E0240 exhibited fluorescence three times stronger than I20260, and about 10 times stronger than B0015 and J23115.E0240. The latter two did not differ in terms of fluorescent signal. | The development of fluorescence followed largely the pattern of the OD, but differed a lot in between the different cultures. J23101.E0240 exhibited fluorescence three times stronger than I20260, and about 10 times stronger than B0015 and J23115.E0240. The latter two did not differ in terms of fluorescent signal. | ||
| + | |||
{{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | {{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Aachen_14-10-13_Graph_with_Error_Bars_Panel_iNB.png|right|150px]] | ||
==Discussion== | ==Discussion== | ||
| + | <span class="anchor" id="isdiscussion"></span> | ||
| + | |||
The OD is an indirect measurement of the biomass in the shake flask. Through the correlation of both measurements the results show that the difference in biomass of the cultures is not significantly enough to affect the fluorescence data. Therefore, the fluorescence data can be interpreted as a direct result of the fluorescence per cell instead of an overall fluorescence per culture. | The OD is an indirect measurement of the biomass in the shake flask. Through the correlation of both measurements the results show that the difference in biomass of the cultures is not significantly enough to affect the fluorescence data. Therefore, the fluorescence data can be interpreted as a direct result of the fluorescence per cell instead of an overall fluorescence per culture. | ||
Latest revision as of 02:02, 18 October 2014
|
|
|
|
|
 "
"