Team:Aachen/Project/Gal3
From 2014.igem.org
m (→An Alternative Sensing Molecule) |
|||
| (45 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
= Galectin-3 = | = Galectin-3 = | ||
| - | We are committed to constantly improve our detection methods. | + | We are committed to constantly improve our detection methods. While the current method uses the quorum sensing system, it is thus limited to bacteria that secrete autoinducers. Hence, we present an alternative approach for the detection of pathogens. In our alternative detection system, biomolecules are tagged with a fluorescent reporter that bind to the surface of the cell and reveal its presence. |
<html> | <html> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
<!-- Overview --> | <!-- Overview --> | ||
| - | <li><a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Project/Gal3# | + | <li><a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Project/Gal3#naturalfunctions" style="color:black"> |
<div class="team-item team-info" > | <div class="team-item team-info" > | ||
| + | <div class="menukachel" style="line-height:1.5em;top:40%;">Natural Functions</div> | ||
| + | <!-- <br/><br/> | ||
| + | <b>Principle of Operation</br> | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| - | + | click for more information --> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | <div class="team-item team-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/7/ | + | <div class="team-item team-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/7/76/Aachen_14-10-13_Galectin-3_iNB.png); norepeat scroll 0% 0% transparent; background-size:100%"> </div></a> |
</li> | </li> | ||
| - | <li><a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Project/Gal3# | + | <li><a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Project/Gal3#alternativesensing" style="color:black"> |
<div class="team-item team-info" > | <div class="team-item team-info" > | ||
| + | <div class="menukachel" style="line-height:1.5em;top:32%;">An Alternative Sensing Molecule</div> | ||
| + | <!-- <br/><br/> | ||
| + | <b>Principle of Operation</br> | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| - | + | click for more information --> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | <div class="team-item team-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/7/ | + | <div class="team-item team-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/7/74/Aachen_14-10-13_Galectin-3-YFP_iNB.png); norepeat scroll 0% 0% transparent; background-size:100%"> </div></a> |
</li> | </li> | ||
<li><a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Project/Gal3#gal3achievements" style="color:black"> | <li><a href="https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Project/Gal3#gal3achievements" style="color:black"> | ||
<div class="team-item team-info" > | <div class="team-item team-info" > | ||
| + | <div class="menukachel" style="line-height:1.5em;top:40%;">Achievements</div> | ||
| + | <!-- <br/><br/> | ||
| + | <b>Principle of Operation</br> | ||
<br/><br/> | <br/><br/> | ||
| - | + | click for more information --> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | <div class="team-item team-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/ | + | <div class="team-item team-img" style="background: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/e/ef/Aachen_14-10-15_Medal_Cellocks_iNB.png); norepeat scroll 0% 0% transparent; background-size:100%"> </div></a> |
</li> | </li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 52: | ||
{{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | {{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | ||
| + | [[File:Aachen_14-10-13_Galectin-3_iNB.png|150px|right]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Natural Functions of Galectin-3 = | ||
| + | <span class="anchor" id="naturalfunctions"></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Galectins are proteins of the lectin family, which possess carbohydrate recognition domains '''binding specifically to β-galactoside sugar residues'''. In humans, 10 different galantines have been identified, among which is galectin-3. | ||
| + | Galectin-3 has a size of about 31 kDA and is encoded by a single gene, LGALS3. It is found to have many physiological functions, such as '''cell adhesion, cell growth and differentiation''', and contributes to the development of '''cancer, inflammation, fibrosis''' and others. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Human galectin-3 is a protein of the lectin-family that was shown to bind the LPS of multiple human pathogens. Some of them, including ''P. aeruginosa'' protect themselves against the human immune system by mimicking the lipopolysaccharides (LPS) present on human erythrocytes. | ||
| + | By making fusion proteins of galectin-3 with fluorescent reporter proteins, pathogens can be labelled and '''made visible by fluorescence-microscopy'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | ||
[[File:Aachen_14-10-13_Galectin-3-YFP_iNB.png|150px|right]] | [[File:Aachen_14-10-13_Galectin-3-YFP_iNB.png|150px|right]] | ||
| Line 55: | Line 71: | ||
<span class="anchor" id="alternativesensing"></span> | <span class="anchor" id="alternativesensing"></span> | ||
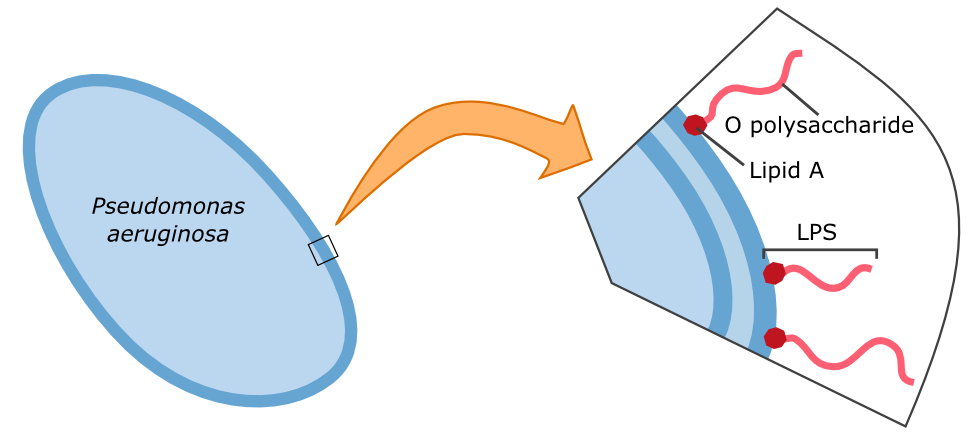
| - | {{Team:Aachen/FigureFloat|Aachen_14-10-09_Pseudomonas_LPS_iNB.png|title=Cell wall composition of '' | + | {{Team:Aachen/FigureFloat|Aachen_14-10-09_Pseudomonas_LPS_iNB.png|title=Cell wall composition of ''P. aeruginosa''|subtitle=Gram-negative bacteria have two cell membranes. The LPS are embedded in the outer membrane and are composed of a lipid and an O polysaccharide.|width=420px}} |
| - | + | Characteristic parts of the '''lipopolysaccharide structure (LPS)''' of ''P. aeruginosa'' can be bound by galectin-3. Specifically, the O polysaccharide (see figure on the left) of the LPS is recognized by galectin-3. Therefore, this specific binding of galectin-3 enables the construction of a fluorescent based detection system. A fusion protein of galectin-3 and a reporter protein, such as a fluorescent protein, can be built and applied in the detection of ''P. aeruginosa''. | |
| - | In our approach, a '''galectin-3-YFP fusion protein''' is built and expressed in ''E. coli'' | + | In our approach, a '''galectin-3-YFP fusion protein''' is built and expressed in ''E. coli'', including a his-tag and a snap-tag for purification. The fusion protein can then be incorporated into a '''cell-free biosensor system'''. These biosensors have many advantages over systems that use living cells such as an uncomplicated storage. Furthermore, from a [https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Safety biosafety] and social acceptance point of view, it is advantageous if the sensor system does not contain alive genetically modified organisms. |
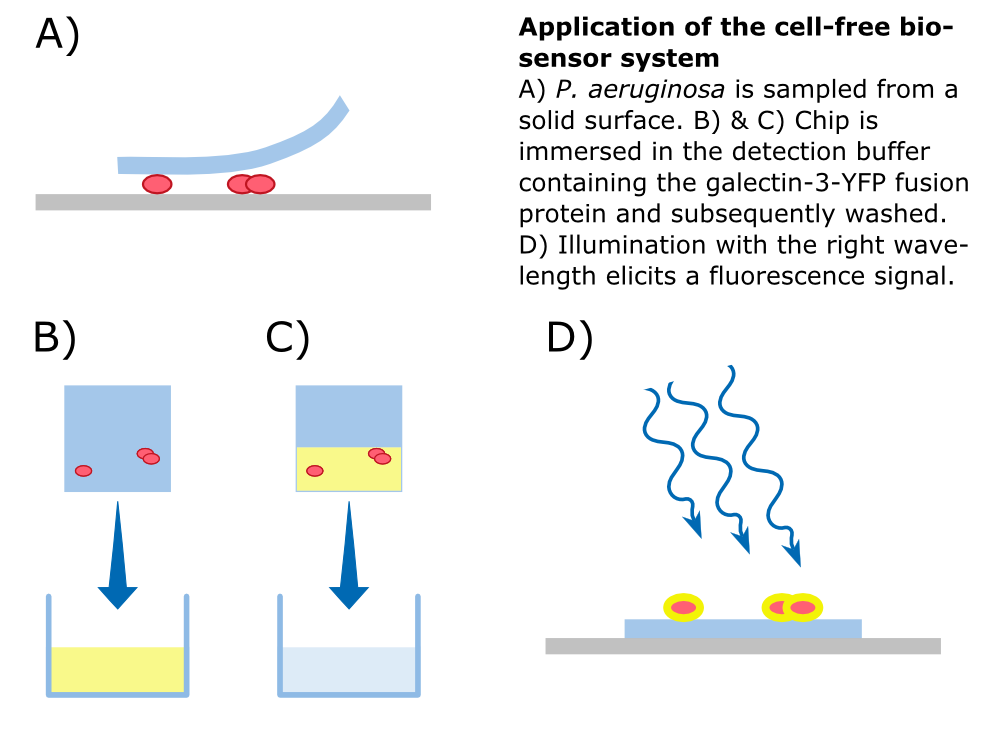
{{Team:Aachen/FigureFloatRight|align=center|Aachen_14-10-09_Cell_Free_Biosensor_iNB.png|width=500px}} | {{Team:Aachen/FigureFloatRight|align=center|Aachen_14-10-09_Cell_Free_Biosensor_iNB.png|width=500px}} | ||
| Line 66: | Line 82: | ||
| - | + | To detect ''P. aeruginosa'' cells, an agar chip could be used to sample a solid surface. However, other materials but agar can be considered to collect pathogens. The cells stick to the sampling chip which is then immersed in a detection buffer containing the galectin-3-YFP fusion protein. Excess protein is removed during washing in a suitable buffer. The galectin-3 remains bound to the pathogen and '''illumination with 514 nm''', the excitation wavelength of YFP, in a modified version of our measurement device reveals the location of the cells. The picture taken by the measurement device can then be analyzed by our software ''Measurarty''. | |
| - | To detect ''P. aeruginosa'' cells, an agar chip could be used to sample a solid surface. However, other materials but agar can be considered to collect | + | |
{{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | {{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | ||
| - | [[File:Aachen_14-10- | + | [[File:Aachen_14-10-15_Medal_Cellocks_iNB.png|right|150px]] |
| - | = | + | = Achievements = |
| - | <span class="anchor" id=" | + | <span class="anchor" id="gal3achievements"></span> |
| - | + | Due to the generous support of Sophia Böcker and Prof. Dr. Elling of the Helmholtz Institute for Biomedical Engineering in Aachen, we got access to a pET17-derived expression plasmid for a His- and SNAP-tagged YFP-galectin-3 fusion protein. We transformed the fusion protein into ''E. coli'' Rosetta cells and conducted a batch fermentation to obtain large amounts of protein. | |
| - | + | With the help of David Schönauer and Alan Mertens from the RWTH Aachen Institute of Biotechnolgy we then purified the fusion protein using FPLC. | |
| + | Subsequently, we aimed to test the binding of the Gal-3 fusion protein to the LPS of ''P. aeruginosa'' as shown previously (Kupper, Böcker, Liu et al., 2013). Apparently, because of insufficient sensitivity of the used fluorescence microscope, this could not be confirmed and would require further experiments, idealy using other detection methods. | ||
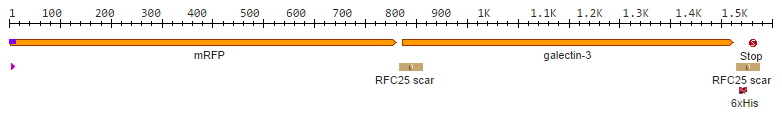
| - | + | After we received the collection of [https://2014.igem.org/Team:Aachen/Collaborations/Heidelberg pSBX-expression vectors] from Team Heidelberg, we used Gibson assembly to make K1319020 from K1319003 and pSBX1A3, which is the translational unit for an mRFP-Gal3 fusion protein with a C-terminal 6xHis tag: | |
| - | + | <center>{{Team:Aachen/Figure|Aachen_K1319020.png|width=800px|title=K1319009|subtitle=This BioBrick is a construction intermediate of K1319003 (gal3), E1010 (mRFP), K1319007 (6xHis tag) to K1319020 (translational unit of the fusion protein).}}</center> | |
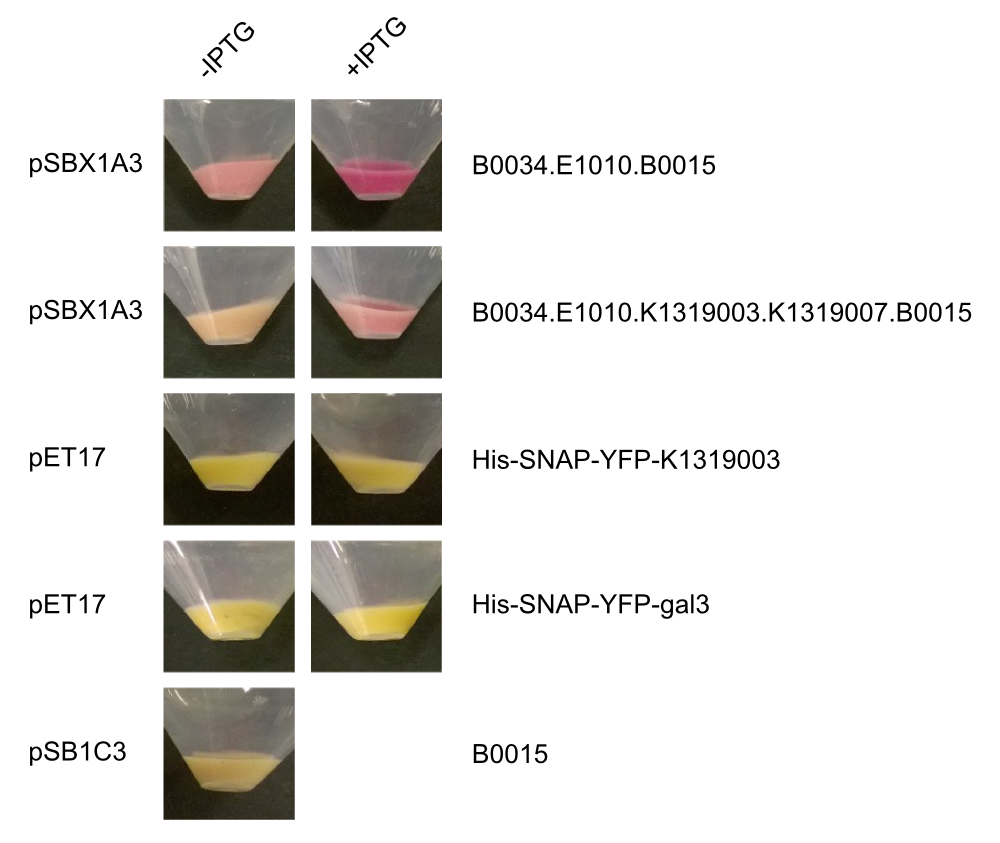
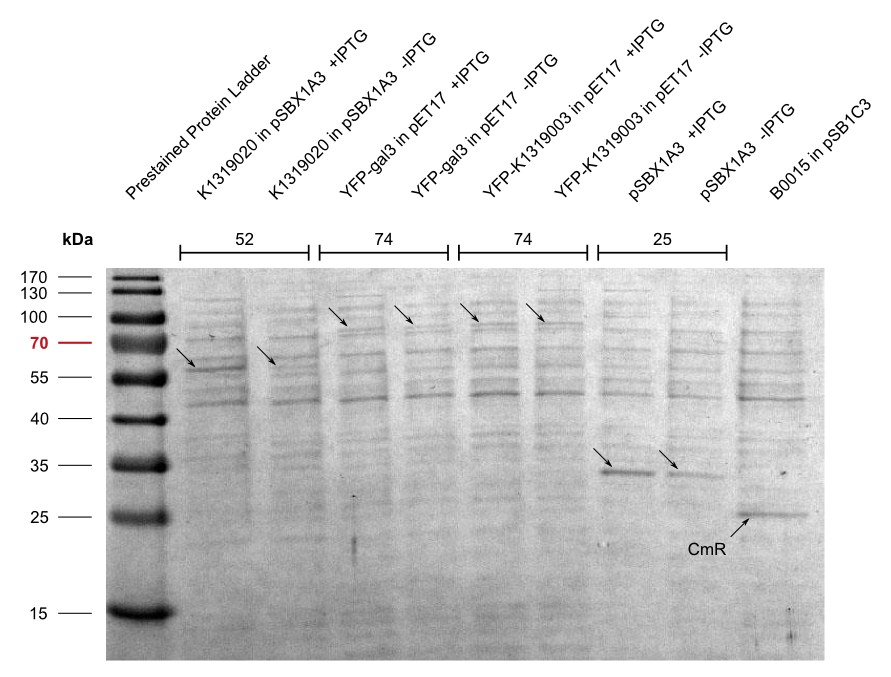
| - | + | In addition, we cloned our BioBrick K1319003 into the pET17 expression vector and expressed all combinations of fusion proteins in E. coli BL21(DE3). An SDS-PAGE showed that all fusion proteins were fully translated: | |
| - | {{Team:Aachen/ | + | {{Team:Aachen/FigureDual |
| + | |Aachen_14-10-04_Expression_Pellets_iMO.png|Aachen_Gal3_Expression.png|title1=Pellets of different fusion protein expressions|title2=SDS-PAGE of K1319020 expression|subtitle1=Expression in the pET17 vector was much more leaky than the expression in the pSBX vectors.|subtitle2=The fusion protein was fully translated to the correct molecular mass of 74 kDa.|width=425px}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | {{Team:Aachen/BlockSeparator}} | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | == References == | |
| + | Kupper, C. E., Böcker, S., Elling, L., Lui, H., Adamzyk, C., de Kamp, J. v., et al. (2013). Fluorescent SNAP-tag galectin fusion proteins as novel tools in glycobiology. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 19(30), 5457-67. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23431989. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
{{Team:Aachen/Footer}} | {{Team:Aachen/Footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 03:28, 18 October 2014
|
|
|
|
|
 "
"