Team:ETH Zurich/modeling/qs
From 2014.igem.org
(→Model) |
|||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
The Quorum sensing module is mainly involved in receiving signals from the sender cells. The sender cells secrete some signaling molecules (inducers) which diffuse out of their membrane, then diffuse in receiver cells membrane, and bind to the regulator molecules in the receiver cells, thus activating the transcription of certain genes. In order to characterize the quorum sensing module with a transfer function, we consider different initial inputs of external AHL, and see how much output is produced, as it was done in the quorum sensing experiments. | The Quorum sensing module is mainly involved in receiving signals from the sender cells. The sender cells secrete some signaling molecules (inducers) which diffuse out of their membrane, then diffuse in receiver cells membrane, and bind to the regulator molecules in the receiver cells, thus activating the transcription of certain genes. In order to characterize the quorum sensing module with a transfer function, we consider different initial inputs of external AHL, and see how much output is produced, as it was done in the quorum sensing experiments. | ||
| + | |||
As diffusion through the membrane is very fast<sup>[[Team:ETH_Zurich/project/references|[27]]]</sup>, according to Fick's law of diffusion, internal and external concentration of AHL can always be considered as equal. When an initial external AHL concentration is given, AHL diffuses in the cells very quickly (minus than 20 seconds)<sup>[[Team:ETH_Zurich/project/references|[27]]]</sup> until internal AHL concentration equals external concentration. Then as soon as some internal AHL is consumed in the cell, it is uptaken again without affecting external concentration a lot, because external volume is very high compared to internal volume. Therefore we can consider in this module that external AHL (which is equal to internal AHL) only degrades, with the rate of extracellular decay. | As diffusion through the membrane is very fast<sup>[[Team:ETH_Zurich/project/references|[27]]]</sup>, according to Fick's law of diffusion, internal and external concentration of AHL can always be considered as equal. When an initial external AHL concentration is given, AHL diffuses in the cells very quickly (minus than 20 seconds)<sup>[[Team:ETH_Zurich/project/references|[27]]]</sup> until internal AHL concentration equals external concentration. Then as soon as some internal AHL is consumed in the cell, it is uptaken again without affecting external concentration a lot, because external volume is very high compared to internal volume. Therefore we can consider in this module that external AHL (which is equal to internal AHL) only degrades, with the rate of extracellular decay. | ||
Revision as of 23:26, 16 October 2014
Quorum Sensing
Model
The Quorum sensing module is mainly involved in receiving signals from the sender cells. The sender cells secrete some signaling molecules (inducers) which diffuse out of their membrane, then diffuse in receiver cells membrane, and bind to the regulator molecules in the receiver cells, thus activating the transcription of certain genes. In order to characterize the quorum sensing module with a transfer function, we consider different initial inputs of external AHL, and see how much output is produced, as it was done in the quorum sensing experiments.
As diffusion through the membrane is very fast[27], according to Fick's law of diffusion, internal and external concentration of AHL can always be considered as equal. When an initial external AHL concentration is given, AHL diffuses in the cells very quickly (minus than 20 seconds)[27] until internal AHL concentration equals external concentration. Then as soon as some internal AHL is consumed in the cell, it is uptaken again without affecting external concentration a lot, because external volume is very high compared to internal volume. Therefore we can consider in this module that external AHL (which is equal to internal AHL) only degrades, with the rate of extracellular decay.
Chemical Species
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| LuxAHL | 30C6-HSL is an acyl homoserine lactone which mainly binds to LuxR. |
| LuxR | Constitutively expressed regulator protein that can bind LuxAHL and stimulate transcription of Bxb1. |
| RLux | LuxR and LuxAHL complex which can dimerize. |
| DRLux | Dimerized form of RLux. |
| mRNABxb1 | mRNA of the Bxb1 integrase being transcribed by the Lux promoter. |
| Bxb1 | Serine integrase that can fold into two conformations - Bxb1a and Bxb1b. We chose to use a common connotation for both conformations - Bxb1. |
| LasAHL | 30C12-HSL is an acyl homoserine lactone which mainly binds to LasR. |
| LasR | Constitutively expressed regulator protein that can bind LasAHL and stimulate transcription of ΦC31. |
| RLas | LasR and LasAHL complex which can dimerize. |
| DRLas | Dimerized form of RLas. |
| mRNAΦC31 | mRNA of the ΦC31 integrase being transcribed by the Lux promoter. |
| ΦC31 | Serine integrase that can fold into two conformations - ΦC31a and ΦC31b. We chose to use a common connotation for both conformations - ΦC31. |
Reactions
For the Lux system: $$ \begin{align} &\rightarrow LuxR \\ LuxAHL+LuxR & \leftrightarrow RLux\\ RLux+RLux &\leftrightarrow DRLux\\ DRLux+P_{luxOFF} & \leftrightarrow P_{luxON}\\ P_{luxON}&\rightarrow P_{luxON}+mRNA_{Bxb1}\\ mRNA_{Bxb1}&\rightarrow Bxb1\\ LuxAHL &\rightarrow \\ LuxR &\rightarrow \\ RLux &\rightarrow\\ DRLux &\rightarrow\\ mRNA_{Bxb1} &\rightarrow\\ Bxb1 &\rightarrow \end{align}$$
- For the Las system
\begin{align} &\rightarrow LasR \\ LasAHL+LasR & \leftrightarrow RLas \\ RLas+RLas & \leftrightarrow DRLas\\ DRLas+P_{LasOFF} & \leftrightarrow P_{LasON}\\ P_{LasON}&\rightarrow P_{LasON}+mRNA_{\phi C31}\\ mRNA_{\phi C31}&\rightarrow \phi C31\\ Las-AHL &\rightarrow \\ LasR &\rightarrow \\ RLas &\rightarrow\\ DRLas &\rightarrow\\ mRNA_{\phi C31} &\rightarrow \\ \phi C31 &\rightarrow \\ \end{align}
Differential Equations
Applying mass action kinetic laws, we obtain the following set of differential equations. $$\begin{align*} \frac{d[LuxAHL]}{dt} &= k_{-RLux}[R_{Lux}]-k_{RLux}[LuxAHL][LuxR]-d_{LuxAHL}[LuxAHL]\\ \frac{d[LuxR]}{dt} &= \alpha_{LuxR} -k_{RLux}[LuxAHL][LuxR] + k_{-RLux}[RLux] - d_{LuxR}[LuxR] \\ \frac{d[RLux]}{dt} &= k_{RLux}[LuxAHL][LuxR] - k_{-RLux}[RLux] - 2 k_{DRLux} [RLux]^2 + 2 k_{-DRLux} [DRLux] - d_{RLux} [RLux] \\ \frac{d[DRLux]}{dt} &= k_{DRLux} [RLux]^2 - k_{-DRLux} [DRLux] - d_{DRLux} [DRLux] \\ \frac{d[P_{LuxON}]}{dt} &= k_{P_{LuxON}} [P_{LuxOFF}][DRLux] - k_{-P_{LuxON}} [P_{LuxON}]\\ \frac{d[mRNA_{Bxb1}]}{dt} &= L_{P_{Lux}} + k_{mRNA_{Bxb1}} [P_{LuxON}] - d_{mRNA_{Bxb1}} [mRNA_{Bxb1}]\\ \frac{d[Bxb1]}{dt} &= k_{Bxb1} [mRNA_{Bxb1}] - d_{Bxb1}[Bxb1]\\ \end{align*}$$
The same holds true for the Las system.
From the original set of reactions, we reduce the rate of production of mRNABxb1 as a Hill function of RLux instead of Mass action kinetics in terms of PLuxON and PLuxOFF. For more information please check the characterization section.
Characterization: KmLux and KmLas
Data
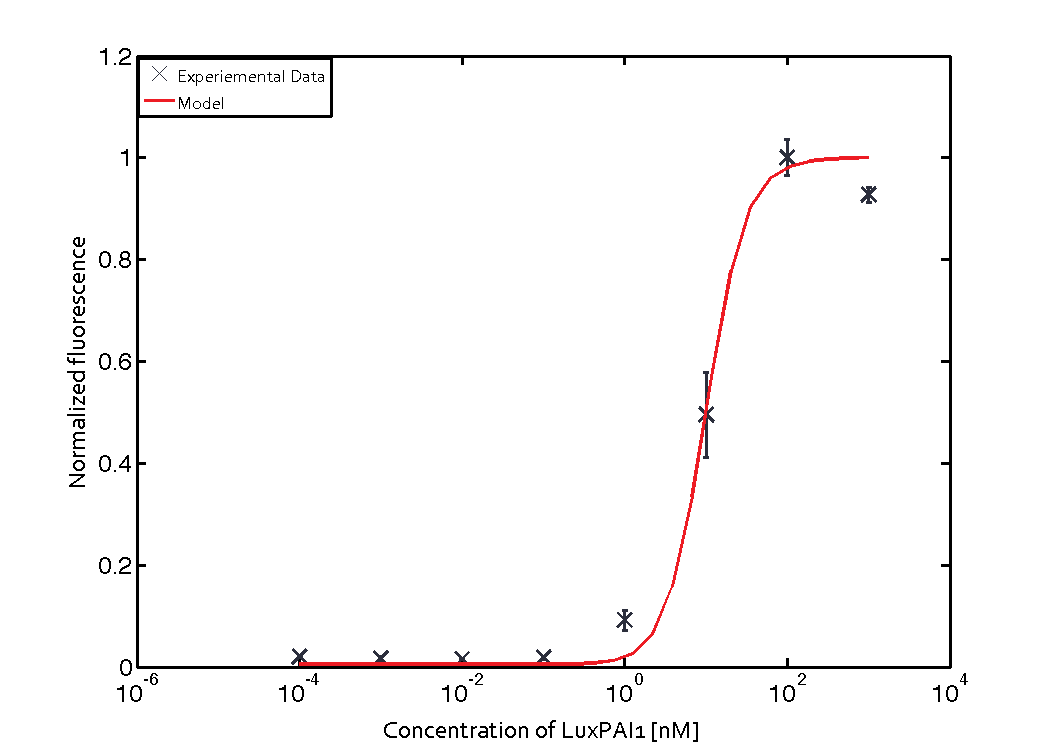
For the Quorum sensing module we used established experimentally determined parameters for the rate of formation of RLux (reference). Since, in the literature the other parameters were estimated or fitted to their data, we decided to determine the parameters specific to our system. Hence, we used our data for the remaining parameters. Our data was mainly a transfer function of normalized GFP concentration as a function of input LuxAHL concentrations. (link to data)
Assumptions
Assumption A
We assumed that the dimerization of RLux to DRLux is quick. Quasi steady state approximation (QSSA) as follows
$$\frac{d[DRLux]}{dt} = k_{DRLux} [RLux]^2 - k_{-DRLux} [DRLux] - d_{DRLux} [DRLux] \approx 0\\$$
Assumption B
Further, from literature, we found that DRLux is specific to DNA and the dissociation constant is low (km = 0.1nM) {Reference}. Therefore, we using QSSA again,
$$\frac{d[P_{LuxON}]}{dt} = k_{P_{LuxON}} [P_{LuxOFF}][DRLux] - k_{-P_{LuxON}} [P_{LuxON}] \approx 0\\$$
Solving, we get the rate of production of mRNABxb1 as
$$\frac{d[mRNA_{Bxb1}]}{dt} = L_{P_{Lux}} + \frac{k_{mRNA_{Bxb1}}[RLux]^2}{K_{mLux}^2 + [RLux]^2 }- d_{mRNA_{Bxb1}} [mRNA_{Bxb1}]\\$$
where
$$K_{mLux} = \sqrt{\frac {k_{-P_{LuxON}}}{k_{P_{LuxON}}}.\frac {k_{-DRLux} + d_{DRLux}}{k_{DRLux}}}$$
is a lumped parameter which we fitted to our data.
Similarly, lumped parameter KmLas was derived for the las system and fitted to a transfer function of normalized GFP concentration as a function of input Las-AHL.
Parameter fitting
We used MEIGO Toolbox to fit the parameters to the experimental data. We used the concentrations at the end of five hours from each simulation and fit it to the experimental concentrations at the same time.
Using the 'DHC' local-solver (Direct search method) in MEIGO, we found the lumped parameters $$K_{mLux} = 0.0124 \pm 0.00051 nM$$
and
$$K_{mLas} = 0.3818 \pm 0.0082 nM$$
respectively.
Range of validity of the assumptions
These assumptions hold true for all input LuxAHL and LasAHL concentrations.
Leakiness
The leakiness of promoters is a major issue in our system. As the signal propagates row-wise, error diffusion could lead to a totally different pattern. The goal is then to master the leakiness. This issue was particularly observed in the case of the Lux promoter during our experiments set. This leakiness is dependent on the LuxR concentration in the cell. Therefore, an assumption would be that Lux(see the [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062:Experience Registry] for more exhaustive information)
Cross-talk
Alternate Design
As cross-talk is a burning issue in quorum sensing, we thought about a theoretical solution. Edinburgh iGEM team 2014also worked on communication between E. coli. They developed new communication channels via metabolic wiring. By assuming that quorum sensing molecules would not cross-talk with metabolites, we used their idea to develop a model on molecular level. The idea is finally to combine our whole-cell model and their idea on metabolites.
Metabolic wiring is based on the fact that when a resource is at disposal, a cell will produce an enzyme to break it down to smaller pieces. There is often a chain of metabolites. Using the fact that metabolites can diffuse through the membrane, this can allow communication (for more information, please see the Edinburgh iGEM team 2014 wiki).
Chemical Species
The species' names are generic because the implementation with particular metabolites implies biological considerations on cell growth and medium used.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Metabolite |
| B | Metabolite |
| Enz | Enzyme that catalyzes the transformation from A to B |
| [A.Enz] | Complex made of metabolite A and enzyme Enz |
| P_A | Promoter induced by A. It can be either on or off (rescued or not) |
Reactions
$$\begin{align*} &\rightarrow A \\ A + P_{Aoff} &\rightarrow P_{Aon} \\ P_{Aon} &\rightarrow P_{Aon} + Enz \\ A + Enz &\leftrightarrow [A.Enz] \\ [A.Enz] &\rightarrow B \\ A &\rightarrow \\ B &\rightarrow \\ [A.Enz] &\rightarrow \\ Enz &\rightarrow \end{align*}$$
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| αA | Production rate of metabolite A |
| dA | Degradation rate of metabolite A |
| αEnz | Production rate of enzyme Enz |
| dEnz | Degradation rate of enzyme Enz |
| αB | Production rate of metabolite B |
| dB | Degradation rate of metabolite B |
| Kd | Parameter of the Michaelis-Menten function modeling the action of enzyme Enz on the substrate, metabolite A, in order to produce metabolite B |
| n | Hill coefficient for the Hill function modeling the activation of the transcription of enzyme Enz with metabolite A as inducer |
| KA | Activation concentration for the Hill function modeling the activation of the transcription of enzyme Enz with metabolite A as inducer |
Parameters are not well-known.
Deterministic Model
We derived this model doing the following assumptions:
- Assumption 1
- The induction of the promoter PA by A is supposed to follow an Hill function.
- Assumption 2
- The enzyme-based reaction from A to B is supposed to follow a Michaelis-Menten function.
$$\begin{align} \frac{d[A]}{dt} &= \alpha_A - d_{A} [A] \\ \frac{d[Enz]}{dt} &= \alpha_{Enz} \frac{[A]^n}{K_{A}^n + [A]^n} - d_{Enz} [Enz] \\ \frac{d[B]}{dt} &= \alpha_B \frac{[Enz] [A]}{K_d + [A]} - d_{B} [B] \end{align}$$
Application to our project
Populations of bacteria will grow into a medium, which provide them metabolite A. The metabolite B will serve as communicating signal, like LasAHL or LuxAHL. It will be an input for the logic construct. As soon as metabolite B is being made available to the cell, the cell will produce the input for the logic construct.
Moreover, one type of cell will produce B as output. Therefore, the output of the logic gate signal will correspond to the production (or absence of production) of the enzyme Enz, so that the A contained in the medium can be transformed to B. Enz will play the same role as LasI or LuxI in our original model.
We separate the promoter activating the production of the enzyme with the production of the enzyme itself. Moreover, cells sense B and want to produce B. In our modules, we have to remplace equations in the sensing module and in the production module.
- Sensing Module
- For example, B would induce the production of the integrase, Bxb1.
$$ \begin{align*} \frac{d[B]}{dt} &= \alpha_B - d_{B} [B] \\ \frac{d[Bxb1]}{dt} &= \alpha_{Enz} \frac{[B]^n}{K_{B}^n + [B]^n} - d_{Bxb1} [Bxb1] \end{align*} $$
- Production Module
- Here, outputlogic is the output of the XOR logic gate, factorized in one term for simplicty's sake. For more information on this function, see the XOR gate modeling page.
$$\begin{align*} \frac{d[Enz]}{dt} &= output_{logic} - d_{Enz} [Enz] \\ \frac{d[B]}{dt} &= \alpha_B \frac{[Enz] [A]}{K_d + [A]} - d_{B} [B] \end{align*} $$
Simulations
We implemented this solution in our whole-cell model. As no parameter is known, we assumed their values to be in the range of standard rates. It gave a possible valid result that could work in our system.
 "
"