Team:ETH Zurich/modeling/qs
From 2014.igem.org
(→Model) |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Model == | == Model == | ||
| - | The Quorum sensing module is mainly involved in receiving signals from the | + | The Quorum sensing module is mainly involved in receiving signals from the sender cells. The sender cells secrete some signalling molecules (inducers) which bind to the regulator molecules in the receiver cells, thus activating the transcription of certain genes. The model for this module is presented below. |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
=== Chemical Species === | === Chemical Species === | ||
| - | * | + | * Lux-AHL: |
| - | * | + | * LuxR: integrase that can fold into two conformations called ΦC31a and ΦC31b. Similarly to Bxb1, we chose to factorize these two conformations under the specie ΦC31. |
| - | * DBxb1: | + | * DBxb1: |
| - | * | + | * RLux: |
| + | |||
| + | * DRLux: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Bxb1: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Las-AHL: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * LasR: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * RLas: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * DRLas: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ΦC31 | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
Revision as of 15:47, 11 October 2014
Modeling quorum sensing
Model
The Quorum sensing module is mainly involved in receiving signals from the sender cells. The sender cells secrete some signalling molecules (inducers) which bind to the regulator molecules in the receiver cells, thus activating the transcription of certain genes. The model for this module is presented below.
Chemical Species
- Lux-AHL:
- LuxR: integrase that can fold into two conformations called ΦC31a and ΦC31b. Similarly to Bxb1, we chose to factorize these two conformations under the specie ΦC31.
- DBxb1:
- RLux:
- DRLux:
- Bxb1:
- Las-AHL:
- LasR:
- RLas:
- DRLas:
- ΦC31
Modelization of DNA-binding sites
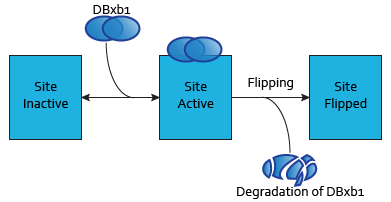
Each dimer of integrases can specifically bind to a DNA binding site. As the flipping is irreversible, these DNA binding sites can be three possible states:
- SIIntegraseName: inactive DNA binding site. No dimer is bound to this site, which has never been flipped.
- SAIntegraseName: active DNA binding site. A dimer is to this site.
- SFIntegraseName: flipped DNA binding site. This DNA binding site has been used by a flipping.
Reactions
- For Bxb1
$$ \begin{align} Bxb1 + Bxb1 &\leftrightarrow DBxb1 \\ DBxb1 + SI_{Bxb1} & \leftrightarrow SA_{Bxb1}\\ Bxb1 &\rightarrow \\ DBxb1 &\rightarrow \end{align}$$
- For ΦC31
\begin{align} \phi C31 + \phi C31 &\leftrightarrow D\phi C 31 \\ D\phi C 31 + SI_{\phi C31} & \leftrightarrow SA_{\phi C31}\\ \phi C31 &\rightarrow \\ D\phi C31 &\rightarrow \end{align}
Differential Equations
Applying mass action kinetic laws, we obtain the following set of differential equations.
$$\frac{d[Bxb1]}{dt}=-2 k_{dimBxb1}[Bxb1]^2+ 2 k_{-dimBxb1}[DBxb1]-d_{Bxb1}[Bxb1]$$
$$\frac{d[DBxb1]}{dt}=-k_{DNABxb1}[DBxb1][SI_{Bxb1}]+k_{-DNABxb1}[SA_{Bxb1}]+k_{dimBxb1}[Bxb1]^2-k_{-dimBxb1}[DBxb1a]-d_{DBxb1}[DBxb1]$$
$$\frac{d[SA_{Bxb1}]}{dt}=k_{DNABxb1}[DBxb1][SI_{Bxb1}]-k_{-DNABxb1}[SA_{Bxb1}]$$
Characterization
Data
Assumptions
Parameter fitting
Range of validity of the assumptions
Characterization
Data
Assumptions
Parameter fitting
Range of validity of the assumptions
 "
"