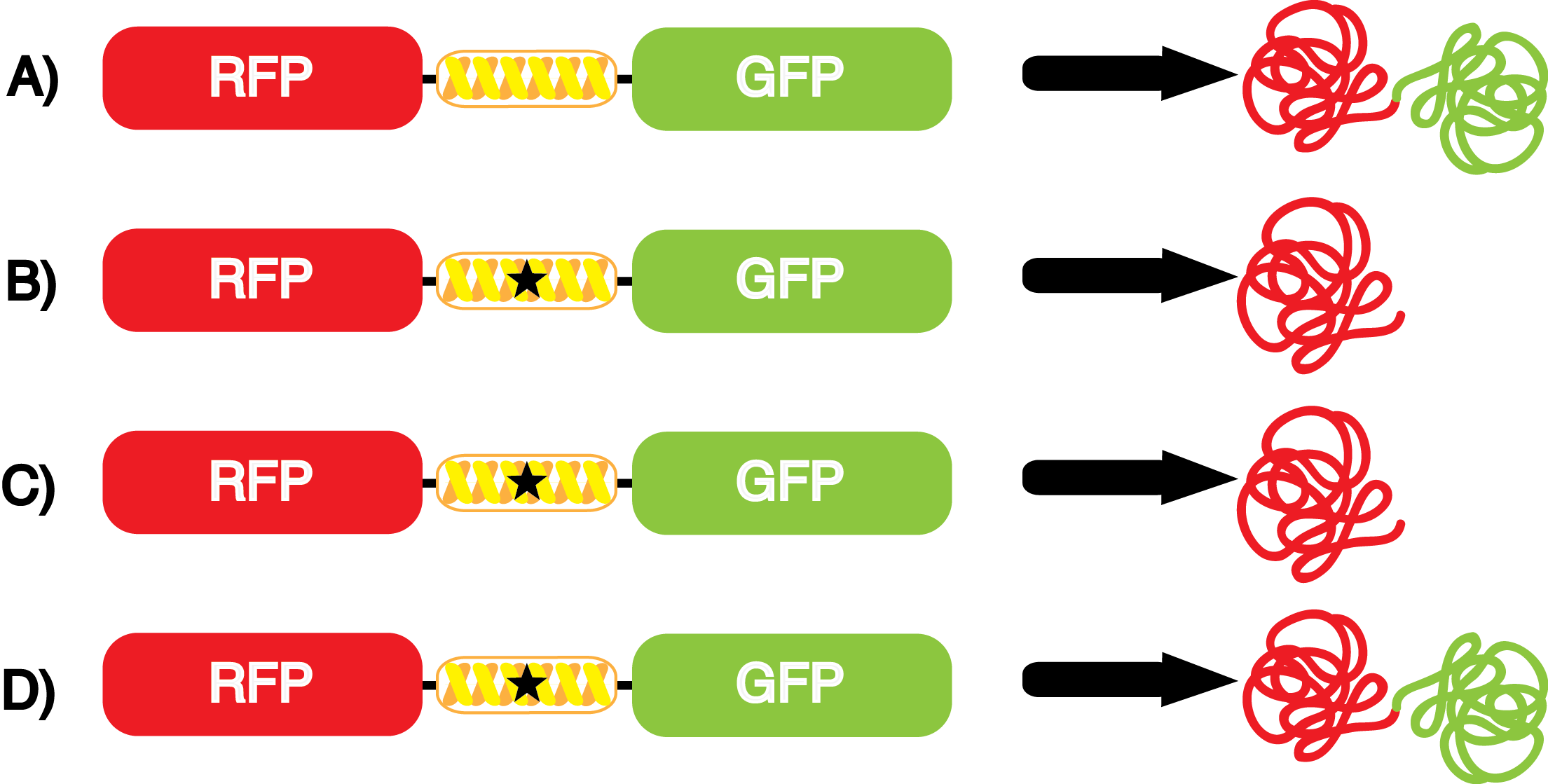
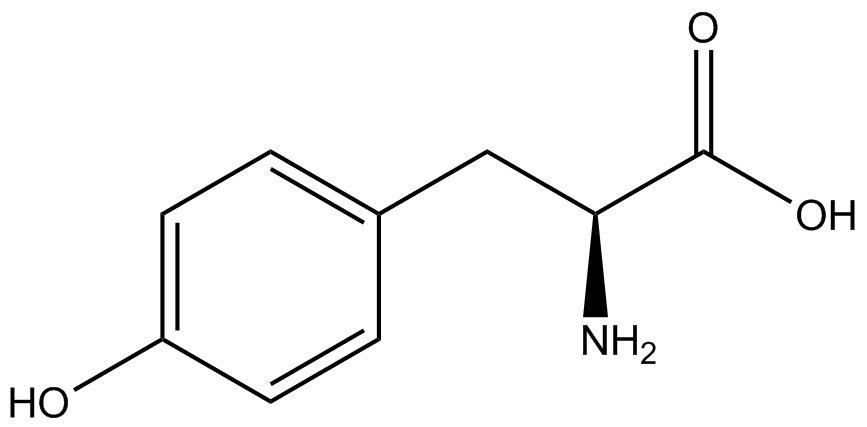
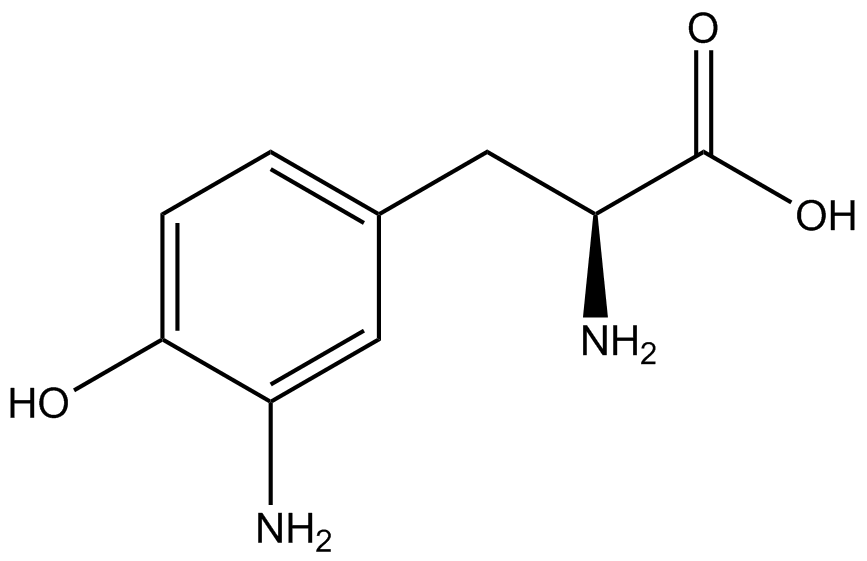
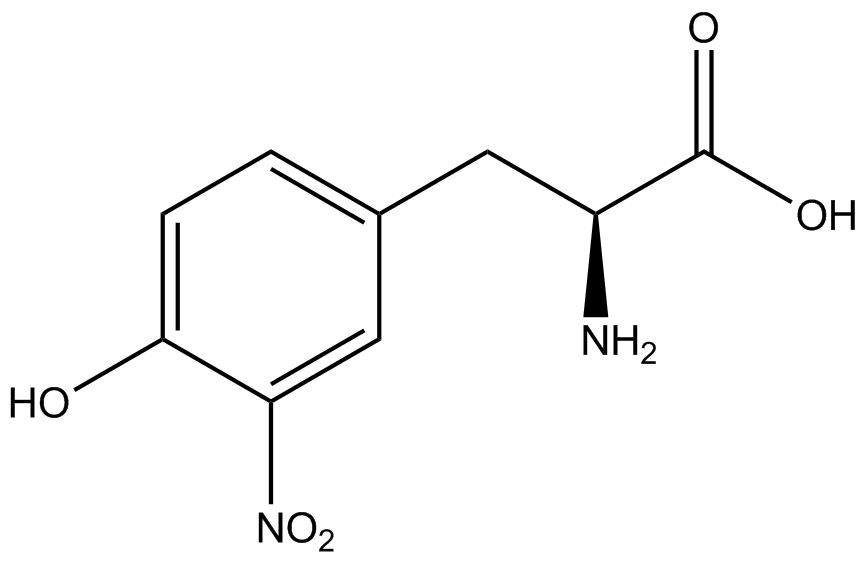
Team:Austin Texas/kit
From 2014.igem.org
| Line 160: | Line 160: | ||
*+IPTG, -ncAA | *+IPTG, -ncAA | ||
*+IPTG, +ncAA | *+IPTG, +ncAA | ||
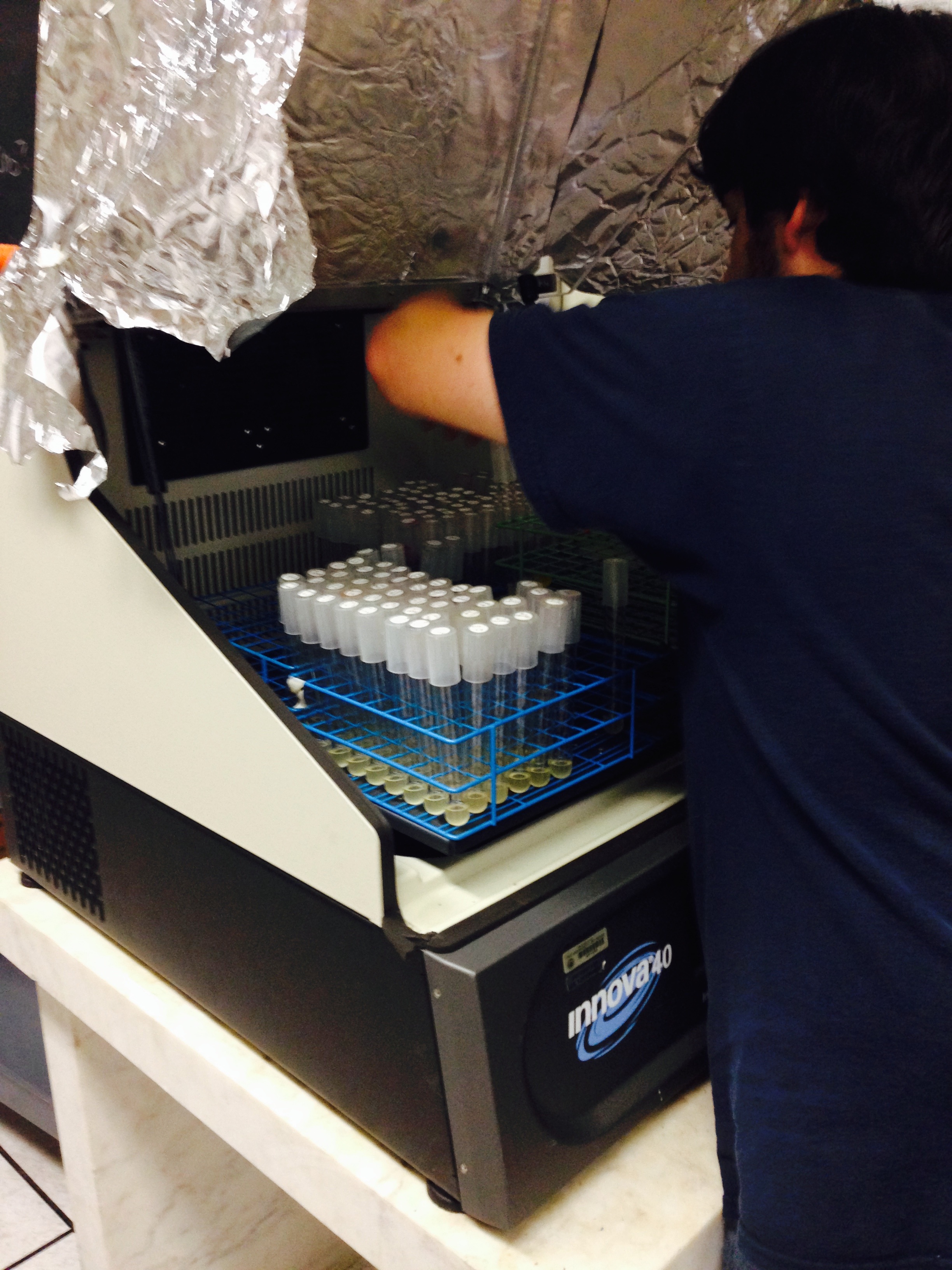
| - | If the cultures did not have IPTG or an nCAA, an equal volume of sterile deionized water was added in order to keep the volumes between cultures constant. Once the water, the IPTG, and the ncAA were added appropriately, the cultures were allowed to grow to ~0.5 OD 600. 70 µL of each culture condition and control culture were added to a separate well in clear-bottom black 96-well plate for fluorescence and OD readings using a | + | If the cultures did not have IPTG or an nCAA, an equal volume of sterile deionized water was added in order to keep the volumes between cultures constant. Once the water, the IPTG, and the ncAA were added appropriately, the cultures were allowed to grow to ~0.5 OD 600. 70 µL of each culture condition and control culture were added to a separate well in clear-bottom black 96-well plate for fluorescence and OD readings using a plate reader. |
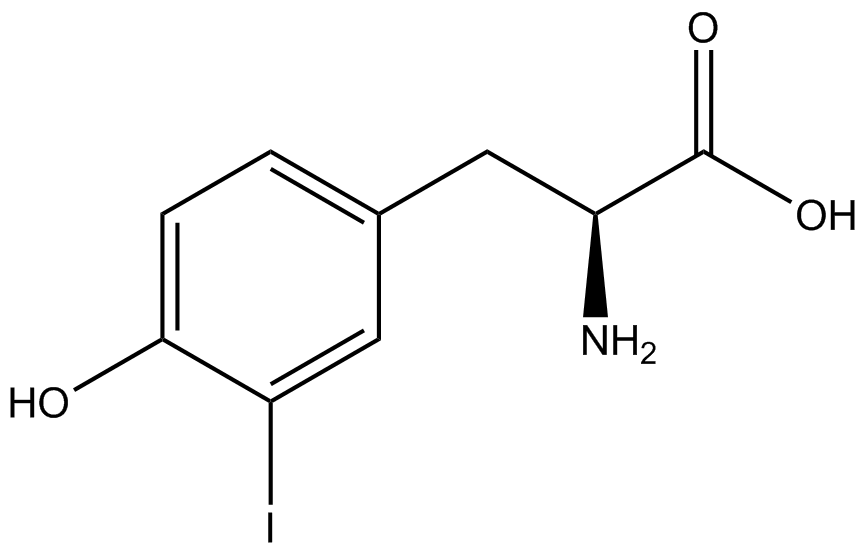
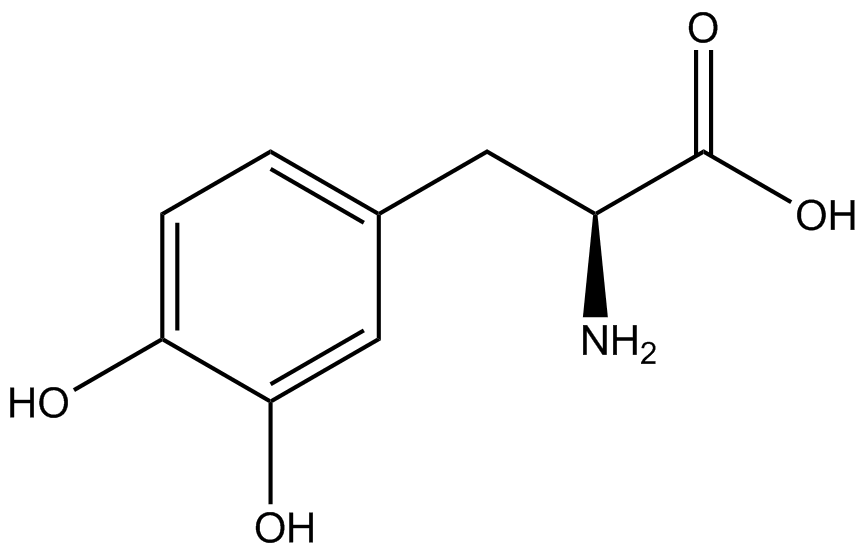
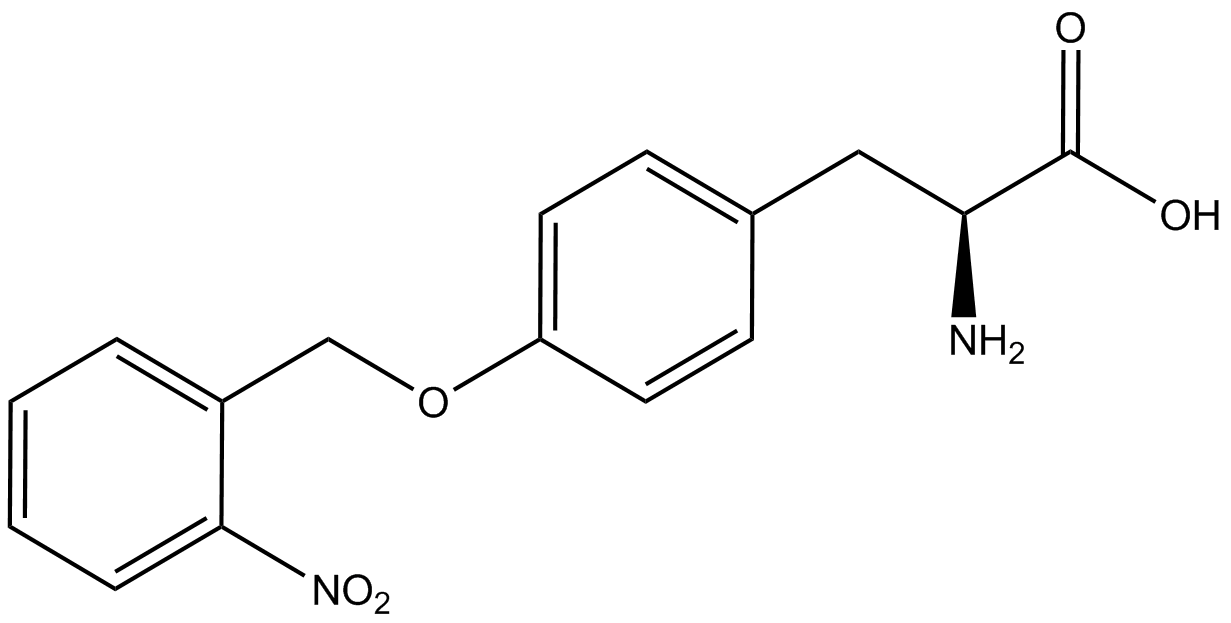
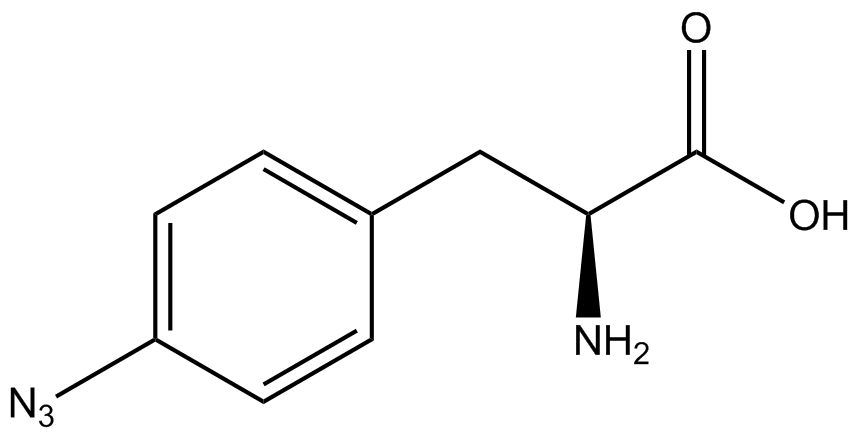
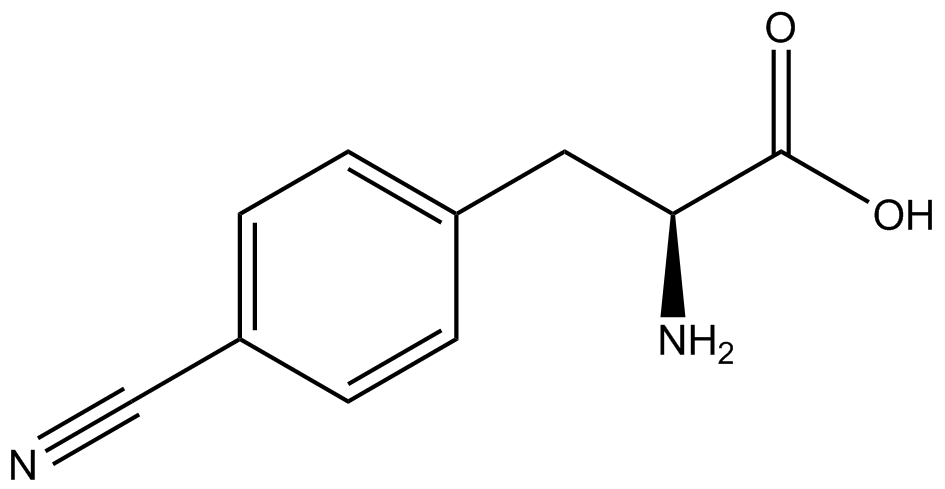
| - | + | ncAA-specific concerns accounted for and should be noted. These include: light-sensitivity, oxidation, and interference with fluorescence readings. Certain ncAAs were protected from light due to their light-sensitive molecular structures such as [https://2014.igem.org/Team:Austin_Texas/kit#ncAA_Table ONBY and AzF]. These ncAAs were prepared in a dark room and wrapped in foil. All cultures were grown in a foil-wrapped incubator for consistency. Some ncAAs are more prone to oxidation, specifically L-dopa. When oxidized, the solution turns black. To prevent oxidation, each ncAA was prepared the day of the test for consistency. By this method, the oxidation of L-dopa did not occur quickly enough to have an effect on the data. Most ncAA solutions were transparent once prepared with the exception of 3-nitrotyrosine. The yellow-orange tint of 3-nitrotyrosine solution was accounted for by measuring the fluorescence of 1mM 3-nitrotyrosine in media and subtracting any possible background fluorescence from culture fluorescence grown in 1mM 3-nitrotyrosine. | |
| + | |||
| + | RFP fluorescence was measured using: excitation - 550 nm, emission - 675 | ||
| + | GFP fluorescence was measured using: excitation - 480 nm, emission - 525 | ||
Revision as of 17:04, 17 October 2014
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"