Team:Austin Texas/kit
From 2014.igem.org
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
<h1>Background</h1> | <h1>Background</h1> | ||
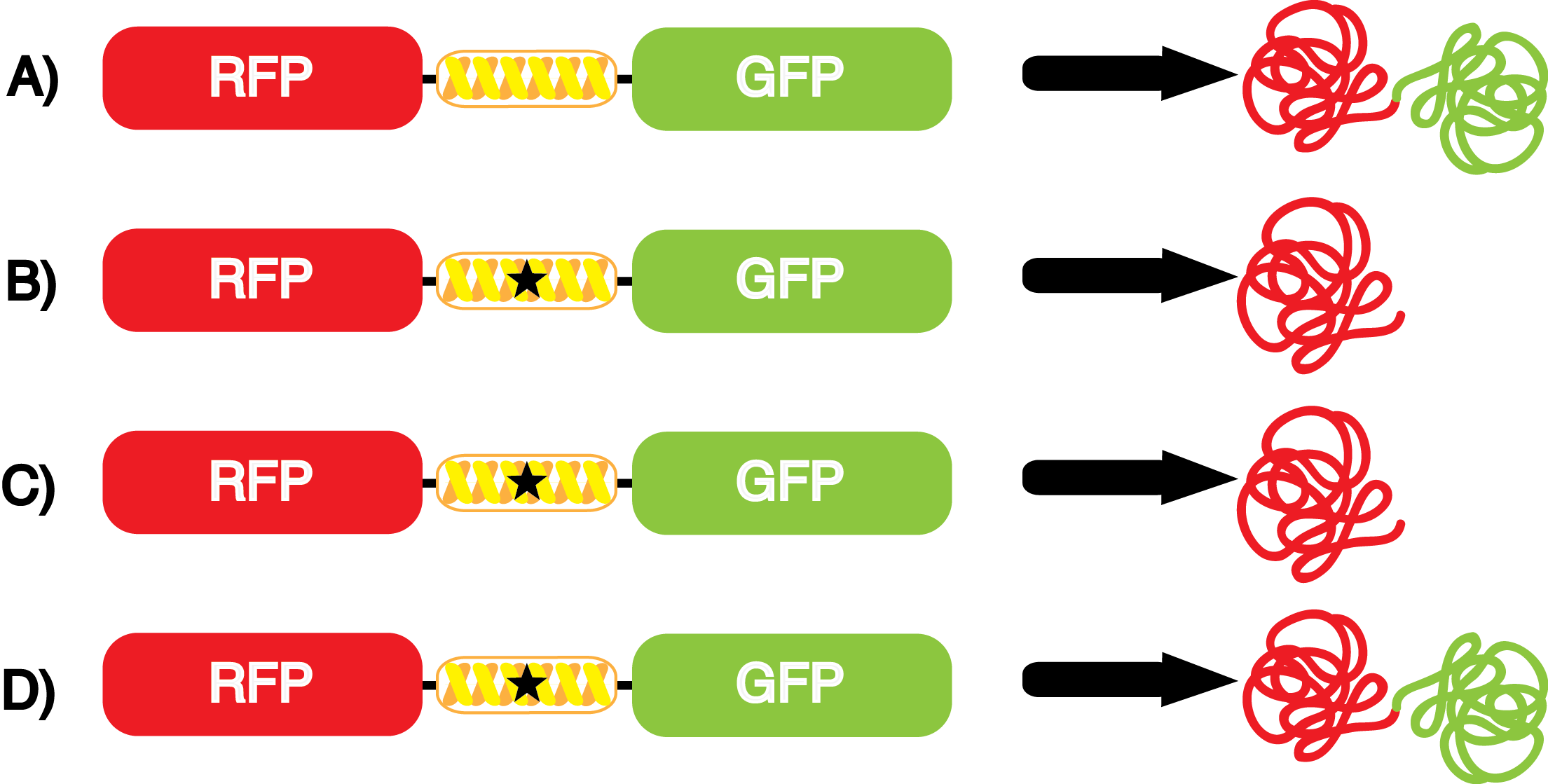
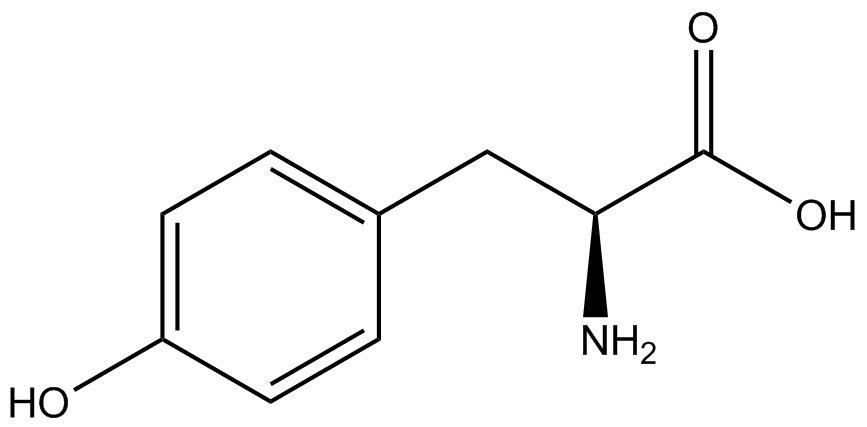
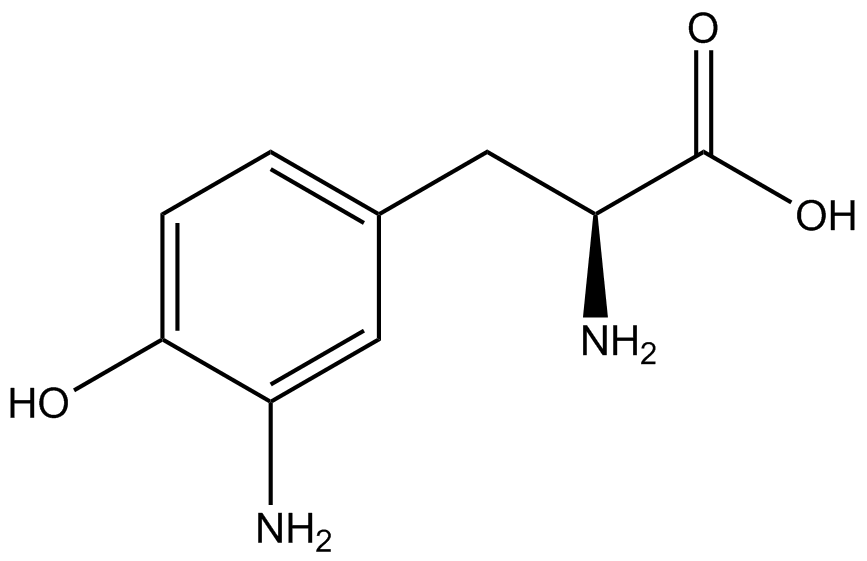
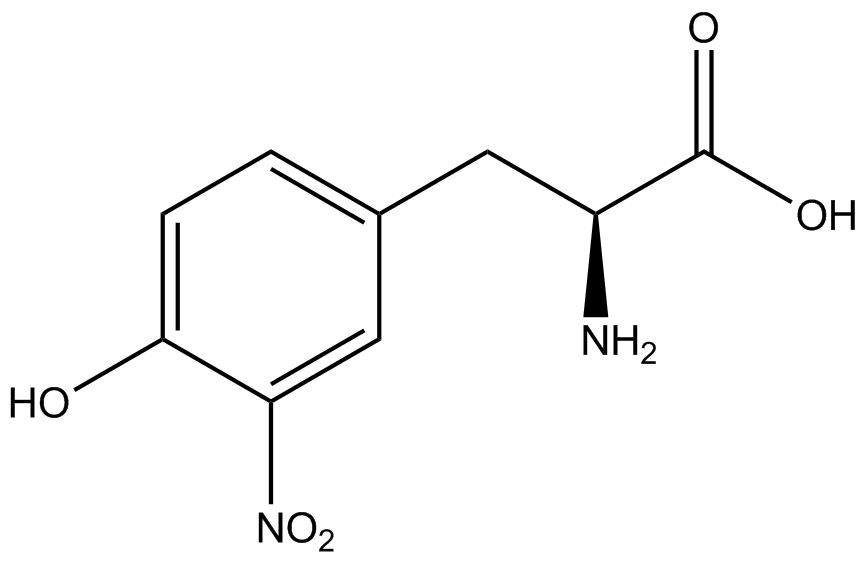
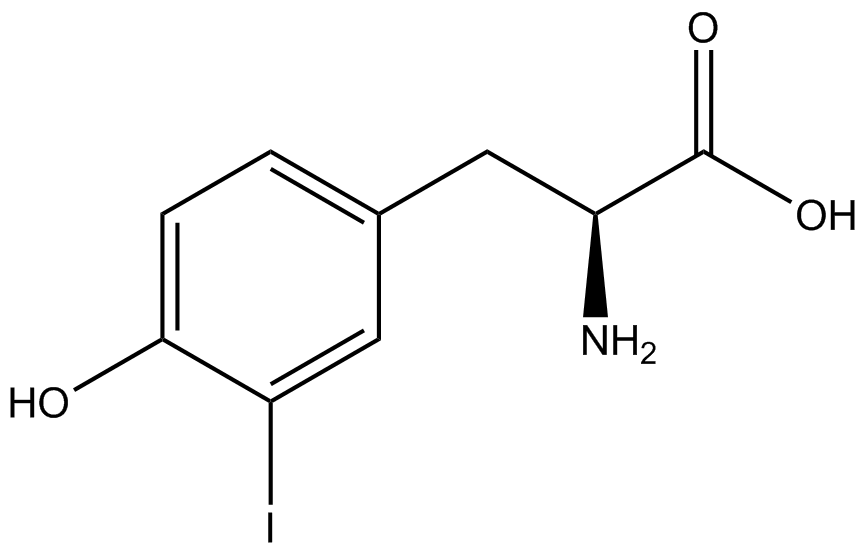
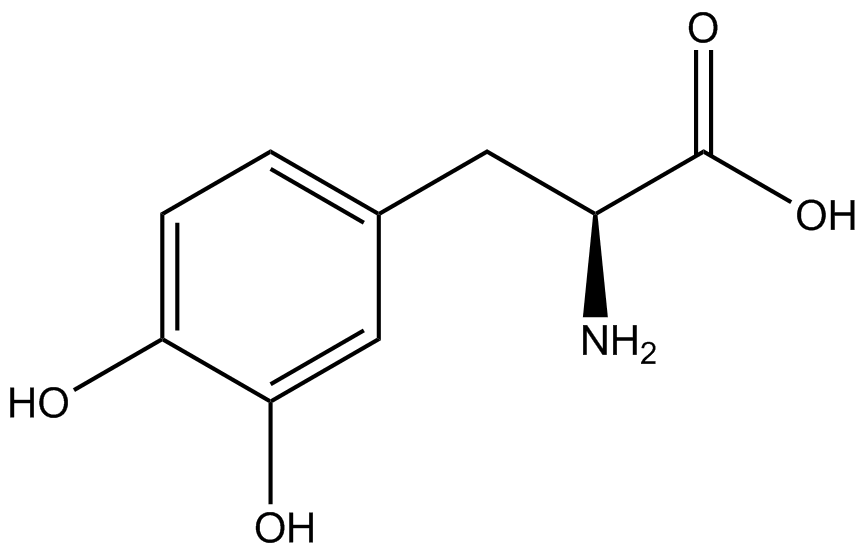
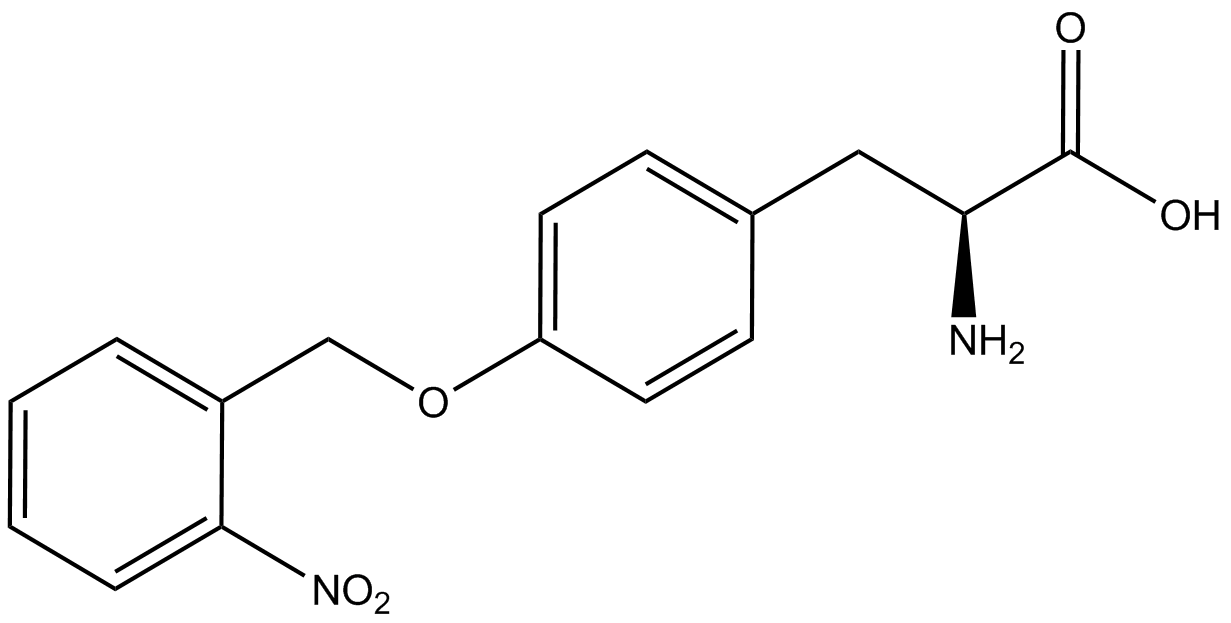
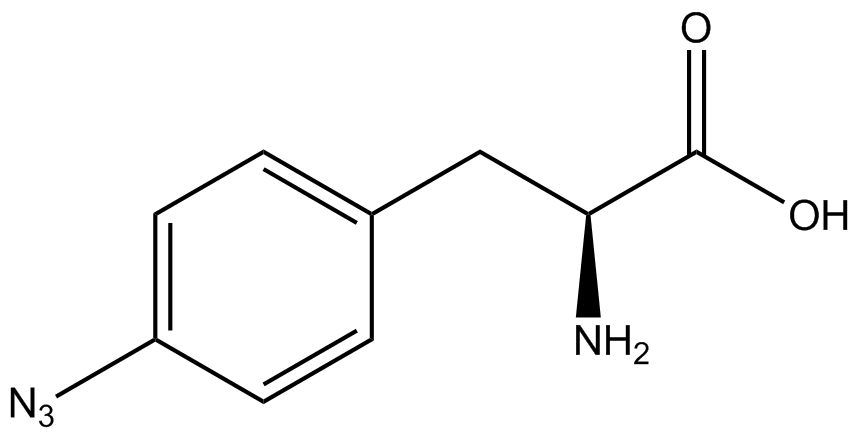
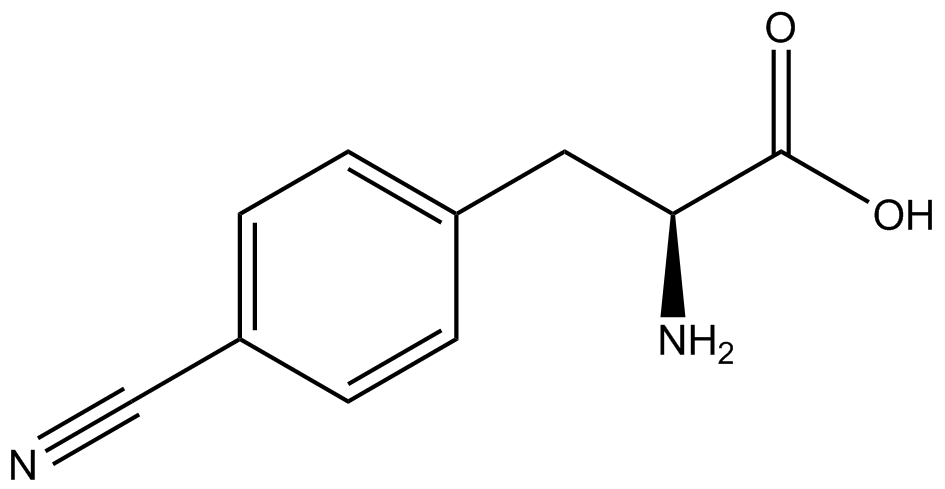
| - | The genetic code is a composition of 20 highly conserved amino acids that are essential to all organisms on Earth. While the genetic code is specific, it is also degenerate, meaning that more than one codon can encode for the incorporation of a specific amino acid. For example, there are six serine codons and three stop codons (called amber, ochre, and opal). By recoding one of the redundant codons, the recoded codon can signal for the incorporation of a non-canonical amino acid (ncAA) rather than the codon's original usage. Of the three stop codons, the amber codon is the least abundant and thus, the easiest and most efficient to recode. | + | The genetic code is a composition of 64 nucleotide triplets (codons) that code for 20 highly conserved amino acids that are essential to all organisms on Earth. While the genetic code is specific, it is also degenerate, meaning that more than one codon can encode for the incorporation of a specific amino acid. For example, there are six serine codons and three stop codons (called amber, ochre, and opal). By recoding one of the redundant codons, the recoded codon can signal for the incorporation of a non-canonical amino acid (ncAA) rather than the codon's original usage. Of the three stop codons, the amber codon is the least abundant and thus, the easiest and most efficient to recode. |
Revision as of 16:30, 17 October 2014
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"