Team:Austin Texas/kit
From 2014.igem.org
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
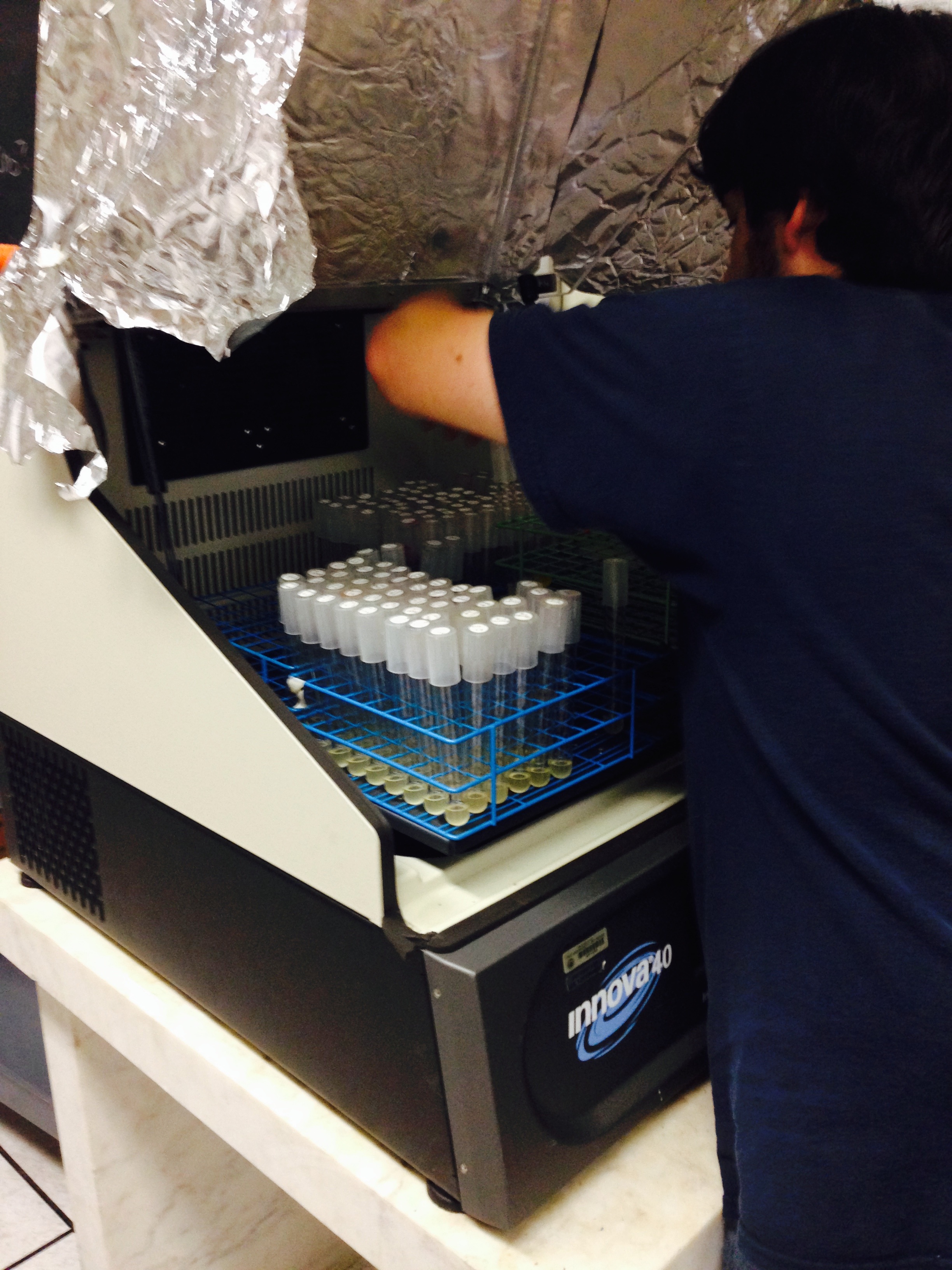
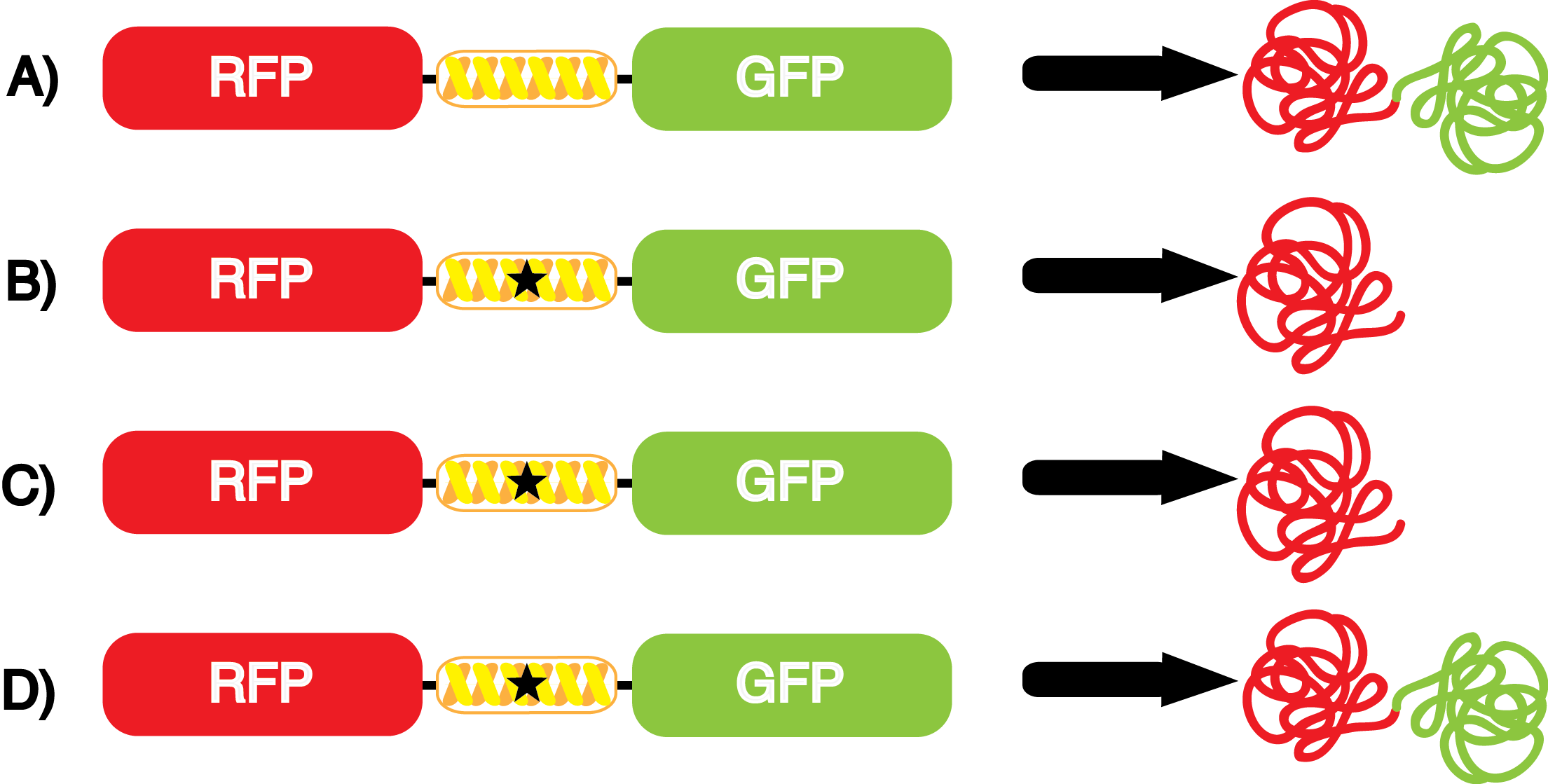
If the cultures did not have IPTG or an nCAA, an equal volume of sterile deionized water was added in order to keep the volumes between cultures constant. Once the water, the IPTG, and the ncAA were added appropriately, the cultures were allowed to grow to ~0.5 OD 600. 70 µL of each culture condition and control culture were added to a separate well in a transparent 96-well plate for fluorescence and OD readings using a fluorometer. | If the cultures did not have IPTG or an nCAA, an equal volume of sterile deionized water was added in order to keep the volumes between cultures constant. Once the water, the IPTG, and the ncAA were added appropriately, the cultures were allowed to grow to ~0.5 OD 600. 70 µL of each culture condition and control culture were added to a separate well in a transparent 96-well plate for fluorescence and OD readings using a fluorometer. | ||
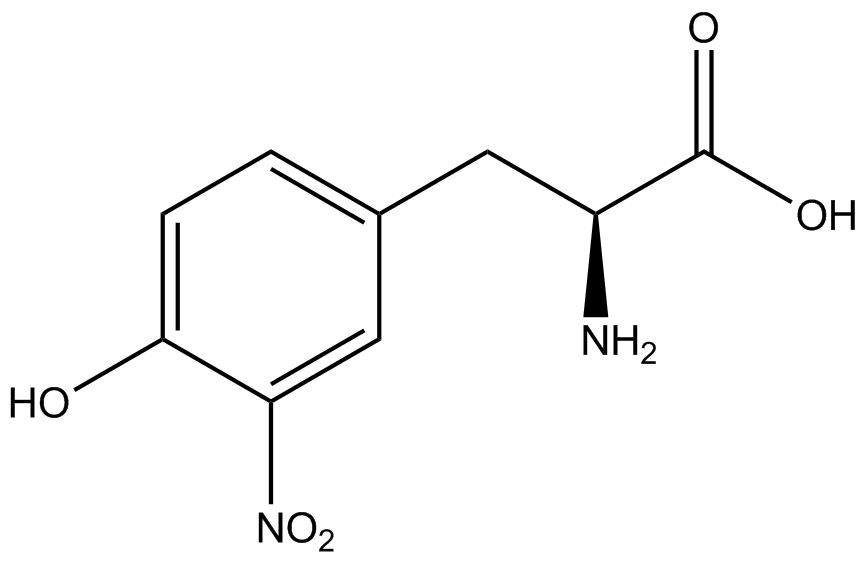
| - | + | Influences that resulted from ncAA addition were accounted for and should be noted. These include: light-sensitivity, oxidation, and interference with fluorescence readings. Certain ncAAs were protected from light due to their light-sensitive molecular structures such as ONBY and AzF. These ncAAs were prepared in a dark room and wrapped in foil. All cultures were grown in a foil-wrapped incubator for consistency. Some ncAAs are more prone to oxidation specifically as L-dopa. When oxidized, the solution turns black. To prevent oxidation, each ncAA was prepared the day of the test for consistency. By this method, the oxidation of L-dopa did not occur quickly enough to have an effect on the data. Most ncAA solutions were transparent once prepared with the exception of 3-nitrotyrosine. The yellow-orange tint of 3-nitrotyrosine solution was accounted for by measuring the fluorescence of 1mM 3-nitrotyrosine in media and subtracting any possible background fluorescence from culture fluorescence grown in 1mM 3-nitrotyrosine. | |
| Line 224: | Line 224: | ||
Our ncAA measurement kit was able to successfully compare the fidelity and efficiency of seven different synthetase/tRNA pairs. We were able to confidently say that one synthetase/tRNA pair had a higher fidelity than another. While the measurements may not be perfectly accurate due to the nature of this test, the measurement kit is designed more around ease of use, cost-efficiency, and portability. The ncAA measurement kit can be used to quickly test a synthetase/tRNA pair's quality with minimal effort, as opposed to other more accurate but more intensive or expensive measures such as mass spectrometry. While mass spectrometry can give much more definitive information about a synthetase/tRNA pair, there are many different factors that could make it unreasonable for undergraduate research. It is a technique that requires a fair amount of skill to do properly, and can be very costly as well. Thus, our measurement kit works best as a preliminary test to get a solid frame of reference for how a synthetase/tRNA pair works in a cell. This application could greatly speed up the process of developing a new synthetase/tRNA pair, as well as characterizing large groups of synthetase/tRNA pairs. | Our ncAA measurement kit was able to successfully compare the fidelity and efficiency of seven different synthetase/tRNA pairs. We were able to confidently say that one synthetase/tRNA pair had a higher fidelity than another. While the measurements may not be perfectly accurate due to the nature of this test, the measurement kit is designed more around ease of use, cost-efficiency, and portability. The ncAA measurement kit can be used to quickly test a synthetase/tRNA pair's quality with minimal effort, as opposed to other more accurate but more intensive or expensive measures such as mass spectrometry. While mass spectrometry can give much more definitive information about a synthetase/tRNA pair, there are many different factors that could make it unreasonable for undergraduate research. It is a technique that requires a fair amount of skill to do properly, and can be very costly as well. Thus, our measurement kit works best as a preliminary test to get a solid frame of reference for how a synthetase/tRNA pair works in a cell. This application could greatly speed up the process of developing a new synthetase/tRNA pair, as well as characterizing large groups of synthetase/tRNA pairs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
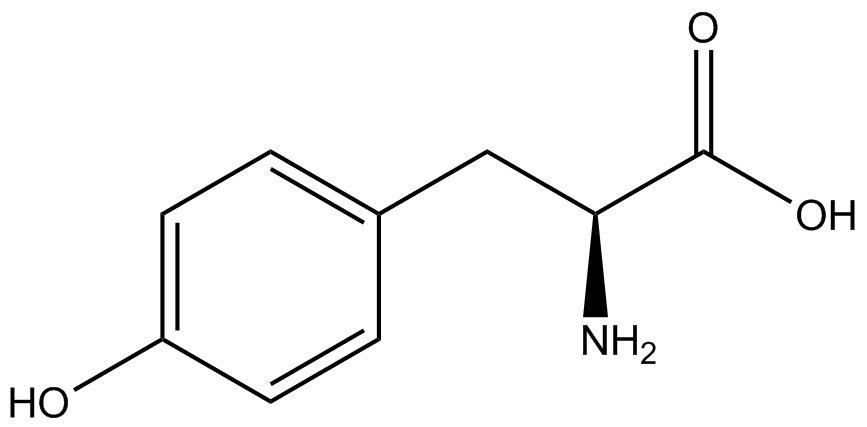
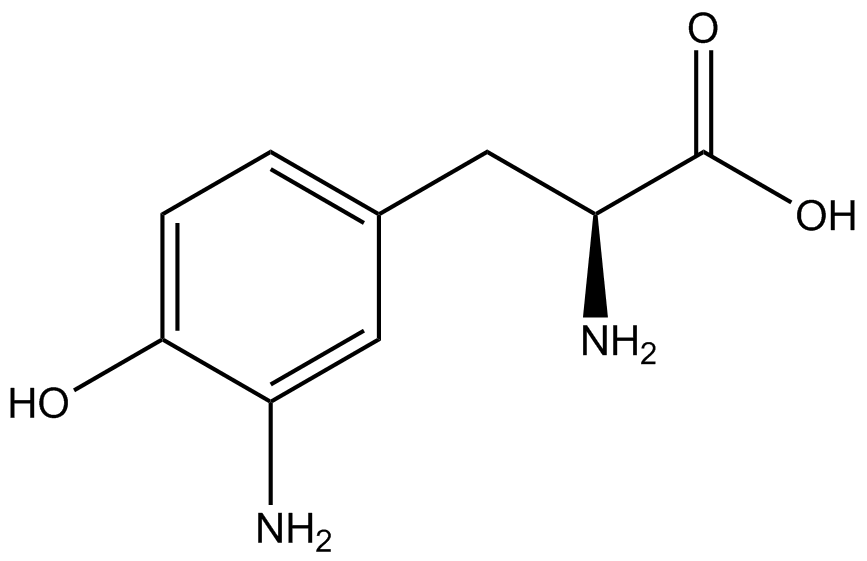
| + | Due to the nature of the ncAA Kit Test, <i>in vivo</i> influences will affect certain data and results. This knowledge is very useful by providing a broader and biological perspective of <i>in vivo</i> perspective of cellular health. In general, the presence of ncAAs slowed the growth of amberless ''E. coli'', sometimes quite significantly. This artificially inflated some of the final values that we calculated, which decreased the accuracy of the results. Influences that resulted from ncAA addition such as light-sensitivity, oxidation, and interference with fluorescence readings were accounted for in order to make the final measurements as accurate as possible. | ||
| + | |||
Are these three paragraphs discussing the results/significance of the results? Yes, we want to talk about possible sources of error, but we don't need three paragraphs for that. We want to talk about what our results mean in a larger context: Does the kit work? Can it be easily improved on? What does our kit do for other labs, for other iGEM teams? For the field of ncAAs? Is the kit definitive by itself? Were there limitations? What might influence good/bad results? Can we unequivocally argue that dopa/3-amino and other ncAA synthetases are worthless? | Are these three paragraphs discussing the results/significance of the results? Yes, we want to talk about possible sources of error, but we don't need three paragraphs for that. We want to talk about what our results mean in a larger context: Does the kit work? Can it be easily improved on? What does our kit do for other labs, for other iGEM teams? For the field of ncAAs? Is the kit definitive by itself? Were there limitations? What might influence good/bad results? Can we unequivocally argue that dopa/3-amino and other ncAA synthetases are worthless? | ||
| Line 233: | Line 237: | ||
''' | ''' | ||
'''Increase the ease of accessibility and portability of methods to other laboratories of a new measurement technique of your choosing.''' | '''Increase the ease of accessibility and portability of methods to other laboratories of a new measurement technique of your choosing.''' | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<h1>Conclusion</h1> | <h1>Conclusion</h1> | ||
Revision as of 03:17, 17 October 2014
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"