Team:Austin Texas/photocage
From 2014.igem.org
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
[[Image:Onbyreaction.png |left| 450px|thumb| '''Figure 1.''' The ONBY ncAA used for our photocaging project. When exposed to 365 nm light, the ONB group is released, resulting in a normal tyrosine amino acid.]] | [[Image:Onbyreaction.png |left| 450px|thumb| '''Figure 1.''' The ONBY ncAA used for our photocaging project. When exposed to 365 nm light, the ONB group is released, resulting in a normal tyrosine amino acid.]] | ||
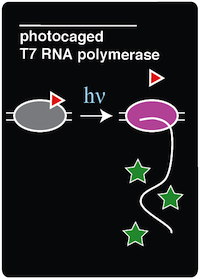
| - | + | To demonstrate an application of adding a noncanonical amino acid to the genetic code, we recreated a light-activatable T7 RNA polymerase (RNAP) for the spatio-temporal control of protein expression (Chou et al. 2010). The light-activatable T7 RNAP was created by mutating a tyrosine codon at position 639 of a domain crucial for the polymerization of RNA during transcription. Y639 was mutated to an amber codon, allowing us to incorporate a ncAA at this position. We used ortho-nitrobenzyl tyrosine (ONBY), which is a "photocaged" ncAA ('''Figure 1'''). Thus, if our synthetase/tRNA pair works, position 639 should contain ONBY in place of tyrosine. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | When the photocaged ONBY is incorporated at position 639, RNAP activity is inhibited. The polymerase can become activated only upon | + | |
| + | When the photocaged ONBY is incorporated at position 639, RNAP activity is inhibited. The polymerase can become activated only upon decaging of the ONB group from the ONBY. This is accomplished by exposing the cells to 365 nm light. When exposed to 365 nm light, the ONB group is released, resulting in a normal tyrosine amino acid at position 639. T7 RNAP was selected because of its orthogonal nature, which allows us to selectively induce the expression of specific genes that are preceded by the T7 RNAP promoter. Because T7 promoters are not natively found in ''E. coli'', a gene downstream of a T7 promoter may be exclusively expressed through the introduction of 365 nm light. | ||
<h1>Background</h1> | <h1>Background</h1> | ||
| - | Tyrosine residue 639 (Y639) was specifically targeted because it lies on a crucial position on the O-helix domain of T7 RNAP and has been proven to be essential for polymerization | + | Tyrosine residue 639 (Y639) was specifically targeted because it lies on a crucial position on the O-helix domain of T7 RNAP and has been proven to be essential for polymerization (Chou et al. 2010). The Y639 residue in the O-helix is responsible for two major roles in the elongation stage of DNA polymerization. First, this tyrosine residue discriminates between deoxyribose and ribose substrates using the Tyrosyl-OH (Temiakov et al. 2004). Second, Y639 is responsible for moving newly synthesized RNA out of the catalytic site and preparing for the next NTP to be inserted (Achenbach 2004). These functions of the O-helix were shown to be essential through mutational analysis (Osumidavis 1994). Introducing a bulky group such as ONBY in place of tyrosine renders the enzyme nonfunctional in several ways. First, the native tyrosine-OH is not there anymore to coordinate Mg<sup>2+</sup>, which plays an essential role in discriminating between deoxyribose and ribose substrates. Additionally, because of the sterics of the ONBY molecule itself, it blocks incoming nucleotides from entering the active site. Because the loss of this tyrosine residue in the active site leads to a non-functional polymerase, Y639 proved to be a good candidate for incorporating a photocaged amino acid (Chou et al. 2010). |
[[Image:Uncaging_of_ONBY.jpg | 300px|left|thumb| '''Figure 2.''' The caged T7 RNAP is decaged via exposure to 365 nm light. Figure reproduced from '''Chou et al. 2010'''.]] | [[Image:Uncaging_of_ONBY.jpg | 300px|left|thumb| '''Figure 2.''' The caged T7 RNAP is decaged via exposure to 365 nm light. Figure reproduced from '''Chou et al. 2010'''.]] | ||
| - | Incorporation of ONBY at position 639 of T7 RNAP halts activity because of the bulky nature of ONBY (Chou et al. 2010). This ONB side group effectively renders T7 RNAP inactive. However, the bulky ONB group is able to be removed through irradiation with 365 nm light. The wavelength of light used to | + | Incorporation of ONBY at position 639 of T7 RNAP halts activity because of the bulky nature of ONBY (Chou et al. 2010). This ONB side group effectively renders T7 RNAP inactive. However, the bulky ONB group is able to be removed through irradiation with 365 nm light. The wavelength of light used to decage the amino acid proved to be another advantage of this system because 365 nm light is not toxic to the cell (Chou et al 2010). Once the ONB group is removed, a normal tyrosine residue is left in its place, restoring T7 RNA polymerase activity ('''Figure 2'''). |
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
<h1>Experimental Methods</h1> | <h1>Experimental Methods</h1> | ||
| - | In order to create an in vivo light-activated GFP expression system, two plasmids were constructed and transformed into amberless E.coli cells. The first plasmid contains the tRNA and synthetase pair, which is necessary to incorporate ONBY into the amber stop codon of the T7 RNAP. The second plasmid contains the coding sequence for T7 RNAP, which has a mutation on the Tyrosine 639 residue, and a GFP coding sequence bound to an upstream T7 promoter. The T7 RNAP coding sequence was taken from the BioBrick part [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K145001 BBa_K145001] and mutated to construct our desired plasmid. Once these components were assembled by Gibson Assembly, the two plasmids were transformed via electroporation into aliquots of | + | In order to create an in vivo light-activated GFP expression system, two plasmids were constructed and transformed into amberless ''E. coli'' cells. The first plasmid contains the tRNA and synthetase pair, which is necessary to incorporate ONBY into the amber stop codon of the T7 RNAP. The second plasmid contains the coding sequence for T7 RNAP, which has a mutation on the Tyrosine 639 residue, and a GFP coding sequence bound to an upstream T7 promoter. The T7 RNAP coding sequence was taken from the BioBrick part [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K145001 BBa_K145001] and mutated to construct our desired plasmid. Once these components were assembled by Gibson Assembly, the two plasmids were transformed via electroporation into aliquots of amberless ''E. coli''. |
| - | For this experiment, there were also other necessary control strains to test alongside the experimental strain. These controls included a T7-GFP construct with no amber stop codon in the O-helix (to serve as a positive control for expression with T7 polymerase), sfGFP amberless E.coli (to observe the expression of GFP by native polymerase), amberless E.coli (to serve as a cell background control), and LB supplemented with ncAA (to serve as a media background control). | + | For this experiment, there were also other necessary control strains to test alongside the experimental strain. These controls included a T7-GFP construct with no amber stop codon in the O-helix (to serve as a positive control for expression with T7 polymerase), sfGFP amberless ''E. coli'' (to observe the expression of GFP by native polymerase), amberless ''E. coli'' (to serve as a cell background control), and LB supplemented with ncAA (to serve as a media background control). |
All of these strains were grown overnight in LB and appropriate antibiotics. The next morning, three 100 microliters samples of each of the strains were inoculated into three different conditions. The conditions are as follows: | All of these strains were grown overnight in LB and appropriate antibiotics. The next morning, three 100 microliters samples of each of the strains were inoculated into three different conditions. The conditions are as follows: | ||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
Each of the conditions were in sterile test tubes and contained 1 mL of media and appropriate antibiotics. These cultures were allowed to grow for 2 hours. After 2 hours of growth, IPTG was added to all (+)IPTG condition tubes. The test tubes were allowed to grow another 2-4 hours, or until the OD600 reached at least 0.3. At this point, five 100 microliter samples of each of the strains were transferred into a 96-well plate. Each of the five samples represents a time interval of light exposure. | Each of the conditions were in sterile test tubes and contained 1 mL of media and appropriate antibiotics. These cultures were allowed to grow for 2 hours. After 2 hours of growth, IPTG was added to all (+)IPTG condition tubes. The test tubes were allowed to grow another 2-4 hours, or until the OD600 reached at least 0.3. At this point, five 100 microliter samples of each of the strains were transferred into a 96-well plate. Each of the five samples represents a time interval of light exposure. | ||
| - | Next, the 96-well plate was covered in foil such that only the first column (which only contained samples that are to be exposed to 365 nm light for 30 minutes) was exposed. The handheld UV light was held | + | Next, the 96-well plate was covered in foil such that only the first column (which only contained samples that are to be exposed to 365 nm light for 30 minutes) was exposed. The handheld UV light was held 5 cm over the 96-well plate and the first column was exposed to the 365 nm light for 15 minutes. After 15 minutes of exposure, the foil was removed to reveal the second column of cultures. Then, after another 10 minutes of exposure, the foil was removed to exposed the third column. After another 4 minutes, the fourth column was exposed. Finally, after the final 1 minute of exposure, the plate was re-covered with foil. After all of the sample were irradiated, an initial measurement of GFP expression was taken by the fluorometer. The purpose of the initial reading was to see what the initial effects of irradiation on the cultures were. |
| - | Once the initial readings were recorded, the 100 microliters samples in the black 96 well plate were transferred into a deep 96 well plate, covered, and allowed to grow overnight at | + | Once the initial readings were recorded, the 100 microliters samples in the black 96 well plate were transferred into a deep 96-well plate, covered, and allowed to grow overnight at 37°C and 225 RPM. |
| - | The cultures were allowed 16 hours of growth so that the decaged T7 RNA polymerase would have time to polymerize mRNA transcripts of the GFP, which is downstream of a T7 promoter. After 16 hours of growth, cultures were transferred back to a black 96 well plate and the fluorescence was measured. | + | The cultures were allowed 16 hours of growth so that the decaged T7 RNA polymerase would have time to polymerize mRNA transcripts of the GFP, which is downstream of a T7 promoter. After 16 hours of growth, cultures were transferred back to a black 96-well plate and the fluorescence was measured. |
| Line 151: | Line 151: | ||
| - | Although the increases in fluorescence are clearly present, there are still a few problems regarding the system. For one, the level of background expression of the | + | Although the increases in fluorescence are clearly present, there are still a few problems regarding the system. For one, the level of background expression of the uninduced T7 RNAP is relatively high. The uninduced caged T7 RNAP has roughly 25 times more expression compared to the negative control. The relatively high level of fluorescence may be explained by the efficient nature of T7 RNAP. Even if a few polymerases were decaged by spurious light during the initial making of the culture or during transfers, the decaged T7 RNAP would have 16 hours to transcribe the RNA the GFP gene. |
| Line 158: | Line 158: | ||
A third potential solution would be to redesign the entire plasmid containing the T7 RNAP to reduce the amount of T7 RNAP that is made by the cell. This could be through a lower copy number plasmid or choosing a different promoter sequence for the purpose of slowing down gene expression. | A third potential solution would be to redesign the entire plasmid containing the T7 RNAP to reduce the amount of T7 RNAP that is made by the cell. This could be through a lower copy number plasmid or choosing a different promoter sequence for the purpose of slowing down gene expression. | ||
| - | The recreation of this light-activatible gene expression system provides a potential foundation for future iGEM projects that wish to use light to control gene expression. By replacing the GFP reporter with coding sequences for other proteins, we will be able to explore novel applications of light-activated protein expression. | + | The recreation of this light-activatible gene expression system provides a potential foundation for future iGEM projects that wish to use light to control gene expression. By replacing the GFP reporter with coding sequences for other proteins, we will be able to explore novel applications of light-activated protein expression. Photodecaging of ONBY can also be used to activate other types of proteins that include important tyrosine residues. |
<h1>References</h1> | <h1>References</h1> | ||
Revision as of 01:31, 18 October 2014
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"