Team:Nagahama project
From 2014.igem.org
(→Reference) |
(→SDS PAGE) |
||
| Line 322: | Line 322: | ||
===SDS PAGE=== | ===SDS PAGE=== | ||
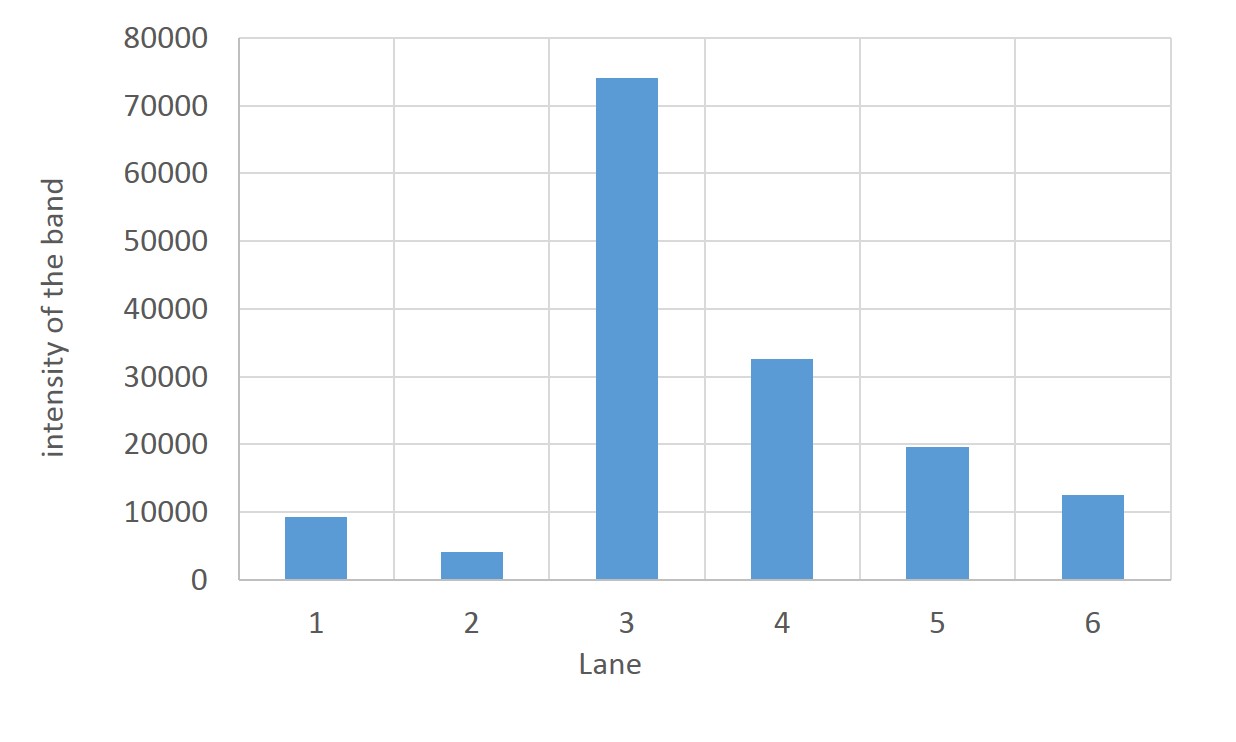
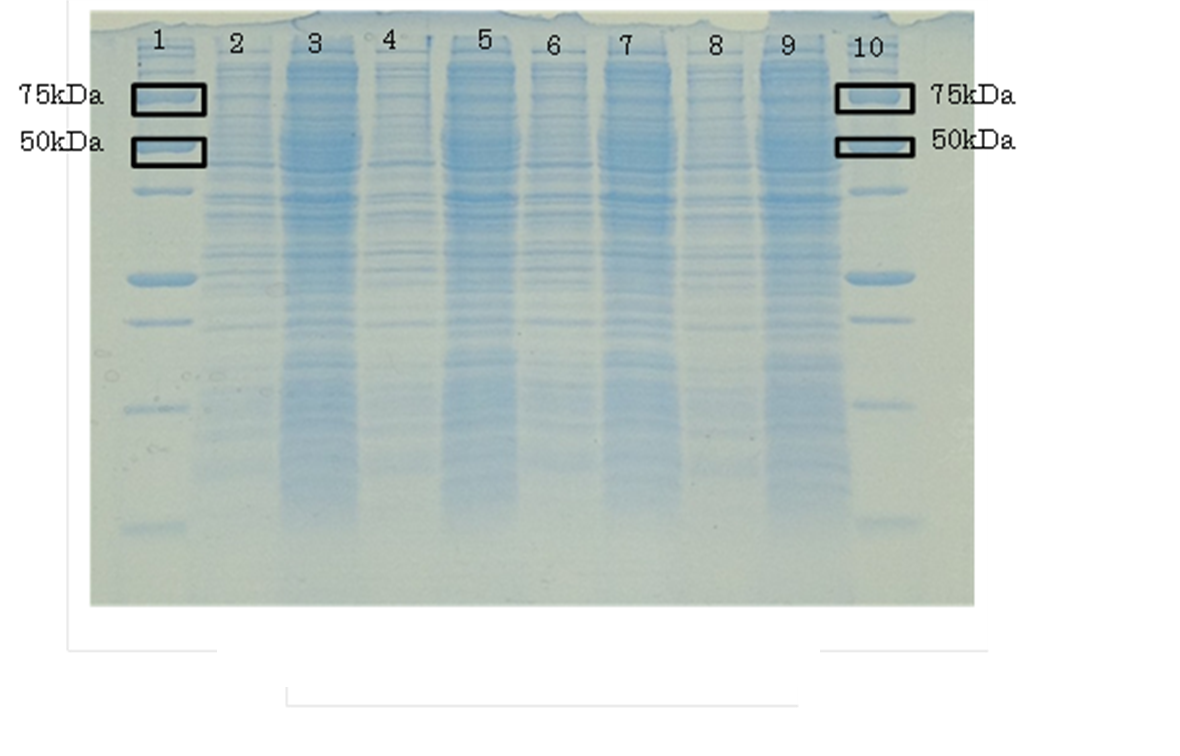
| - | [[File:PAGE1.jpg|500px|thumb|Analyzed aspartase by ''E. coli'' JM109 and ''E. coli'' JM109/[http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K1342001 BBa_K1342001] by SDS-PAGE Lane:1,10 Protein Marker(Precision Plus Protein Standards (BIO-RAD)) | + | [[File:PAGE1.jpg|500px|thumb|Analyzed aspartase by ''E. coli'' JM109 and ''E. coli'' JM109/[http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K1342001 BBa_K1342001] by SDS-PAGE ,37℃ for 0,6 hr |
| - | + | Lane:1,10 Protein Marker(Precision Plus Protein Standards (BIO-RAD)) | |
Lane:2,3 ''E. coli'' JM109 | Lane:2,3 ''E. coli'' JM109 | ||
Lane:4,5 ''E. coli'' JM109/BBa_K1342001 ) | Lane:4,5 ''E. coli'' JM109/BBa_K1342001 ) | ||
Revision as of 23:30, 17 October 2014
| ||||||||||||||
Contents |
Our Project
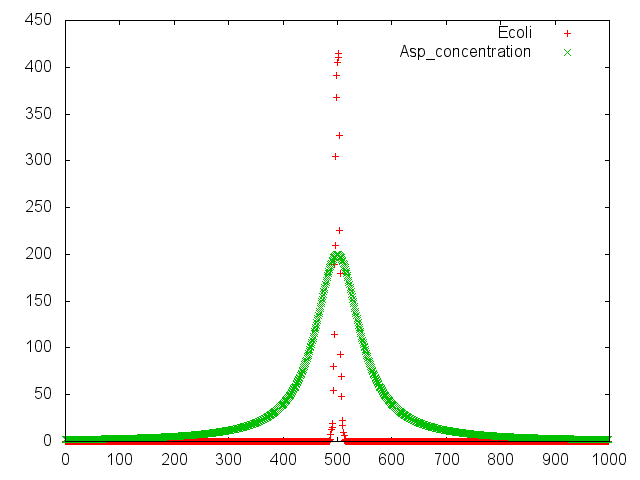
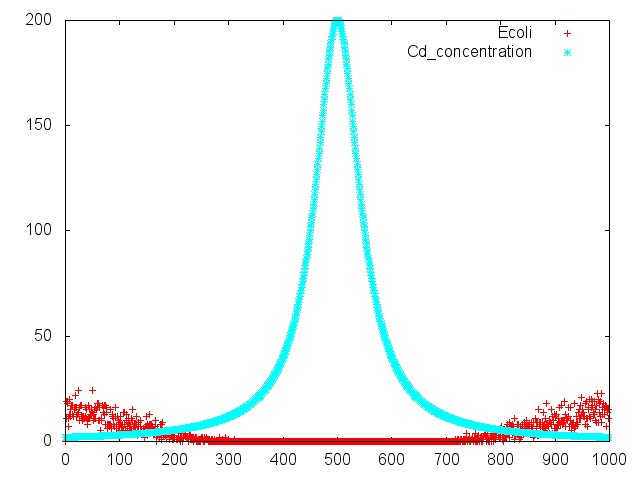
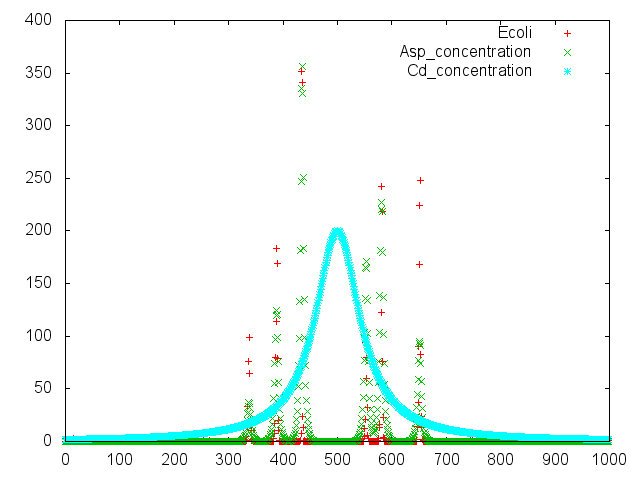
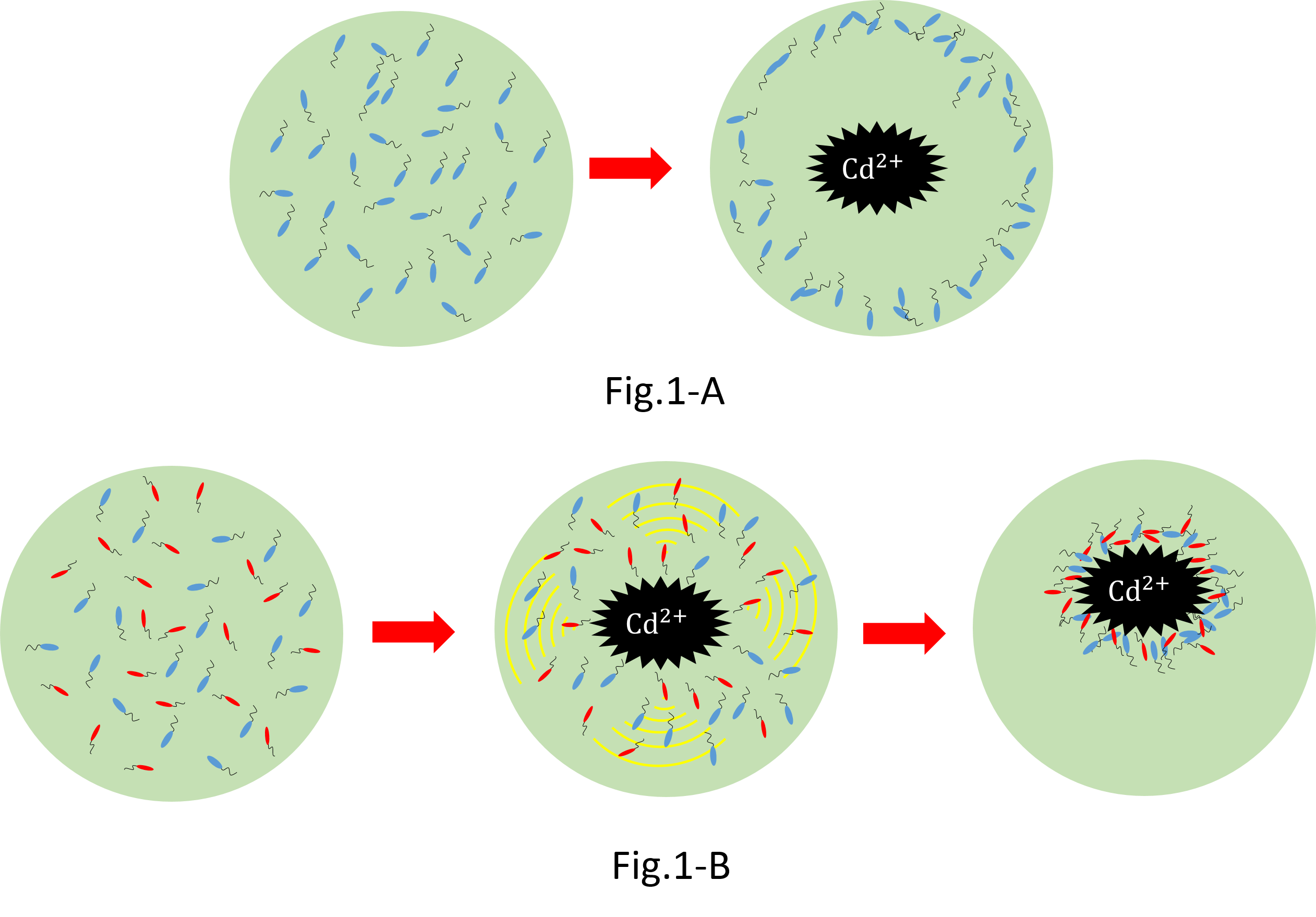
We make various systems by cell-cell communication. We keep one function in one E. coli. This means to make simple plasmid. The following is one example. We’d like to collect cadmium in water. Therefore we use two kinds of E.coli. One catches Cadmium. The other attracts all E.coli by using chemoattractant. Catches E.coli displays metallothionein a protein combines a heavy metal. Cadmium is a kind of heavy metal. The other synthesizes aspartic acid (Asp) one kind of chemoattractant. All E.coli gather in the E. coli synthesizes Asp. To use these E.coli, finally cadmium will be caught.

Modeling
We consigned modeling of our project to
UT-Tokyo.They readily compiled with our requests. Their model is ideal.We really appreciate their jobs We wish a friendly relationship with UT-Tokyo.Thank you so much!! The detail of their jobs are lists below!!
Method
Medium
Trypton broth
Trypton 10g/L
NaCl 10g/L
H2O 1L
Wash medium
Potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), 10⁻²M
MgSO₄, 10⁻³M
potassium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA), 10⁻⁴M
Chemotaxis medium
Potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), 10⁻²M
potassium EDTA, 10⁻⁴M
L-methionine 10⁻⁶M
Synthesis medium
Sodium hydrogen fumarate 46g/L
Ammonium chloride 17.8g/L
Magnesium sulfate 7 hydrate 0.25g/L
H₂O 1L
Ph8.5with sodium hydrogen
LB medium
Tryptone 10g/L
Yeast extract 5g/L
NaCl 10g/L
(agar 15g/L)
H₂O 1L
2×YT medium
Tripton 16g/L
Yeast extract 10g/L
NaCl 5g/L
(agar 15g/L)
H₂O 1L
M9 swarming agar
M9 salt
1.25 % (v/v) glycerol
0.3 % (w/v) agar
0.1 % (w/v) CaCl₂ solution (after autoclave)
0.1 % (w/v) MgSO₄ solution (after autoclave)
0.03 % (w/v) thiamine (after autoclave)
5 × M9 stock solution
6.4 % (w/v) Na2HPO4
1.5 % (w/v) KH2PO4
0.25 % (w/v) NaCl
0.5 % (w/v) NH4Cl
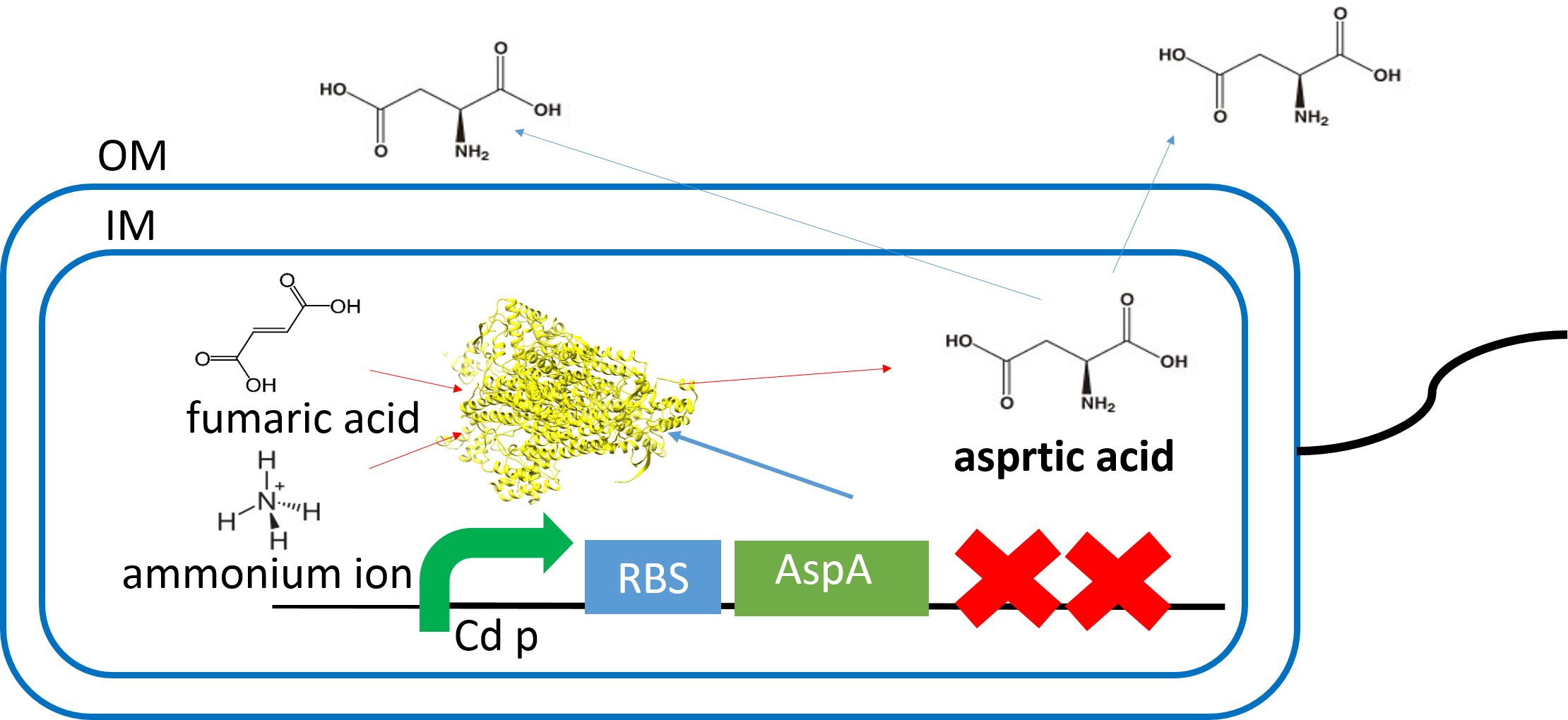
Aspartate synthesis
E.coli K12 transformed with CdP-R.B.S-AspA-d.Ter (BBa_K1342001) previous cultured with cadmium in LB medium (250μM) in 37℃ for 12hr at 120rpm. Adjust Cell mass (OD1.0) and therefor centrifuged 4000rpm for 20 min. Cell pellets ware activated in synthesis medium in 37℃ for 2hr at 120rpm/min.
SDS PAGE
・E. coli JM109 containing CdP-R.B.S-AspA-d.Ter (BBa_K1342001) or normal E. coli was precultured at 37 ℃ for 24 hr with shaking.
・The culture (OD600 0.6-1.0) was used for induction of protein expression by isopropylthio-β-D-galactoside 1mM and Cd2+ 100µM soln. 37℃、o hr, 0.5 hr, 2hr, 6 hr, 24hr.
・200 μl of the induced culture was centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 1 min at 4 ℃.
・The supernatant was discarded and the pellet was stored at -20 ℃.
・The stored pellet was resuspended in 1 x sample buffer (100 μL), followed by heating at 98 °C for 5 min.
・The lysate was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min. at 4℃.
・The supernatant was collected into a new microcentrifuge tube.
・20 μL of the supernatant was analyzed by SDS-PAGE.
TLC assay
We analyzed L-aspartate by thin-layer chromatography (TLC). The equal volume of the supernatant of synthesis medium was added with 7 mg/mL 5-Dimethylamino naphthalene-1-sulfonyl Chloride (dissolved in acetone) and was incubated for more than 30 min at room temperature. Two microliters of the reactant was spotted on a TLC silica plate, and was developed in a mixture of ethyl acetate, pyridine, water, and acetic acid(162:21:11:6 v/v).
Chemotaxis Assay
Introduction
Chemotaxis of E. coli against aspartic acis was assayed by two methods. One was "swarming assay", and the other was capillary assay. In "swarming assay", we have used "sawarming plate", a solid culture plate containing lower concentration of agar, on that plate, E. coli can swim. We have used capillary containing aspartic acid. The capillary was set in chemotaxis medium containing motile E. coli. The number of E. coli attracted to aspartic acid in capillary was determined by colony formation on LB plate.
Swarming Assay
We assayed chemotaxis of E. coli against cadmium and aspartic acid on soft agar, containing M9 synthetic medium, on that plate E. coli can swim.
Protocol
1.E. coli JM109 was cultured at 30℃ for 12 hours with shaking (50 rpm).
2. Aliquot of the culture was spotted on the center of agar plate.
3. 10 mM L-aspartic acid (40 μl) or 100 mM cadmium chloride (4 μl) was spotted on 25 mm distant from the center of the agar plate.
4. The plate was standed for 5 min at RT.
5. The plate was incubated at 30℃.
Capillary Assay
Object
Assay the chemotaxis of E. coli against aspartic acid with capillary.
Plotocol
1. Preculture E. coli in tripton broth at 30 ℃ for 12 hr with shaking (50 rpm).
2. Check the motility of E. coli by microscope (× 800).
3. Dilute the E. coli culture (200 μL) with tripton broth (20 mL).
4. Incubate at 30 ℃ with shaking (50 rpm) until log phase (OD600 = ~ 0.2).
5. Aliquote (500 μL) of the culture was centrifuged at 25℃ for 10 min at 3400 x G.
6. Dicard the supernatant.
7. Resuspend the pellets gently with wash medium (50 μL).
8. Repeat 5~7 step.
9. Resuspend the pellets gently with chemotaxis medium (500 μL).
10. Check the motility of E. coli by microscope (× 800).
11. Aliquote (100 μL) of E. coli suspended in chemotaxis medium was set into chamber apparatus.
12. Prepare aspartic acid capillary and negative control capillary that contain 1 μL of chemotaxis medium with and without 10 mM aspartic acid, respectively.
13. Both capillaries (asparate capillary and negative control capillary) were set into chamber apparatus.
14. Incubate at 30 ℃ for 90 mim.
15. The chemotaxis medium in capillary was collected in 100 μL of fresh chemotaxis medium.
16. All chemotaxis medium containing attracted E. coli was plated on LB plate.
17. Incubate at 37 ℃ for 12 hr.
18. Count the number of colony.
Result & Discussion
TLC Assay

SDS PAGE
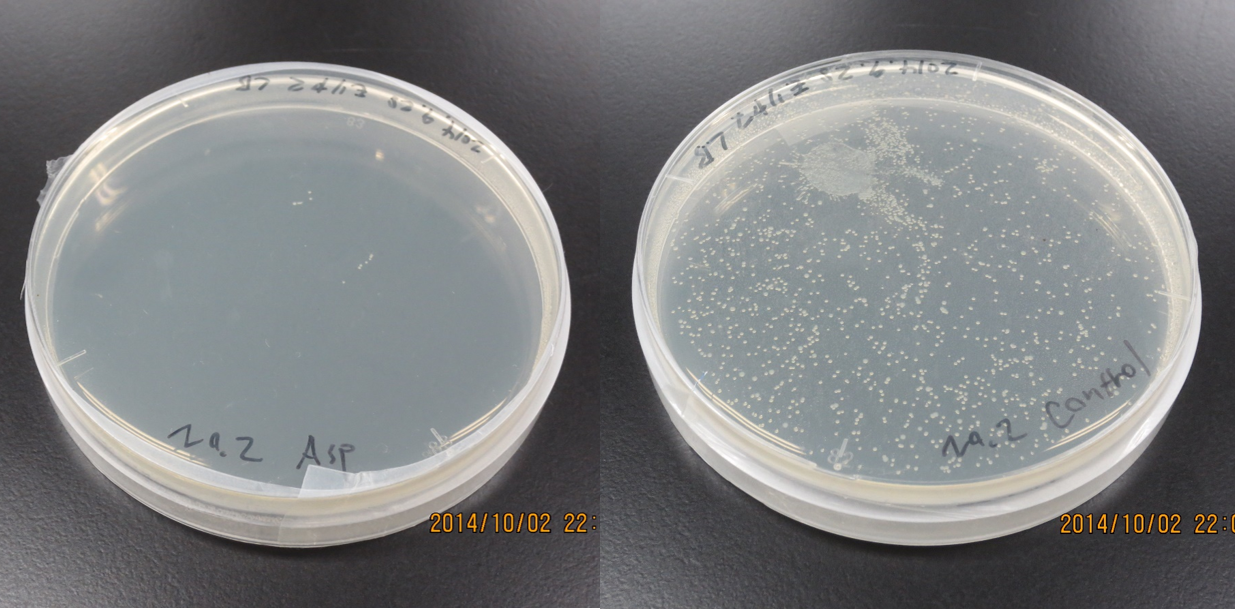
Swarming Assay
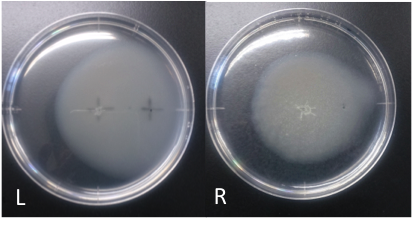
L: aspartic acid (10 mM, 40 μl) R: ddH2O (40 μl)
Incubation: 108 hours
temperature: 30 ℃
E. coli cultured was spotted on the center of agar plate, and chemotaxis was spotted on 25 mm distant from the center.
The swarming circle of aspartic acid (L) was larger than that of ddH2O (R), and the swarming area around aspartate acid (L) was more larger than that of ddH2O (R), suggesting that E. coli swarming to aspartate acid.
This experiment indicate that E. coli may have positive chemotaxis for aspartic acid.
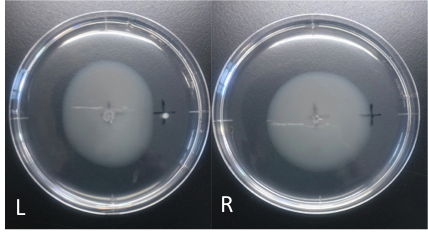
L: cadmium(100 mM, 4 μl) R: ddH2O (40 μl)
Incubation: 110 hours
temperature: 30 ℃
E. coli cultured was spotted on the center of agar plate, and chemotaxis was spotted on 25 mm distant from the center.
The swarming circle of cadmium (L) was smaller than that of ddH2O (R), and the swarming area around cadmium (L) was more smaller than that of ddH2O (R), suggesting that E. coli hate cadmium.
This experiment indicate that E. coli may have negative chemotaxis for cadmium.
Capillary Assay
Result
Discussion
At this method. We didn't assay aspartic acid cehmotaxis of E.coli. We did eleven assays.In this assay, E.coli formation will appear on aspartic acid plate more than conrol plate. But at result of Fig.1, E.coli colonies appeared control plate more than aspartic acid plate. And all result were not authenticity. There are some problems. One is heat of bacteria spreader. At plating moments. I may burn 'E.coli to death. Next is diameter of capillary. I made capillary by myself. There were various sizes of capillary. I used their capillary. So colonies formation were ununiformity. Last is the number of times of assays. In our source journal (Reference No.7), they assayed more then us.
Future work
We performed a project to collect cadmium using chemotaxis of Escherichia coli this year. But the second plasmid is still building it. We want to perform an experiment such as fig.1-B with two kinds of Escherichia coli as soon as construction is completed. In addition, the chemotactic instruction and control that we used have the applied nature to other projects very much. We want to create the new project using chemotaxis of Escherichia coli.
Reference
[1][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12480884 Ferianc, P, et al, Regulation of yodA encoding a novel cadmium-induced protein in Escherichia coli, Microbiology, vol.148, 3801–3811, (2002)]
[2]iGEM Goettingen, Homing Coli, https://2012.igem.org/Team:Goettingen/Notebook/Results, (2012)
[3][http://www.ccbi.cam.ac.uk/iGEM2006/index.php/Protocols#Autoclaving_stock_solutions_or_glassware_.28sterilisation.29 iGEM University Of Cambridge, Making swimming Agar, http://www.ccbi.cam.ac.uk/iGEM2006/index.php/Protocols#Autoclaving_stock_solutions_or_glassware_.28sterilisation.29, (2006)]
[4]iGEM UT-Tokyo, L-aspartate chemotaxis assay, https://2011.igem.org/Team:UT-Tokyo/Data/Method, (2011)
[5][http://ecocyc.org/ Keseler et al, EcoCyc, http://ecocyc.org/, (2013)]
[6][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17650676 Chmiel, A, Selection and activation of Escherichia coli strains for L-aspartic acid biosynthesis, Polish J. Microbiol, Vol.56, 71-76, (2007)]
[7][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4632978 ADLER, J, A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli, Polish J. General Microbiol, Vol.74, 77-91, (1973)]
[8][http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC106306/ Sternberg, C, et al, New Unstable Variants of Green Fluorescent Protein for Studies of Transient Gene Expression in Bacteria, Polish J. Microbiol, Vol.64, 2240–2246, (1998)]
[9]iGEM UPO-SEVILLA, Bacterial crowding, https://2010.igem.org/Team:UPO-Sevilla/Project/Assays, (2010)
 "
"