Team:Austin Texas/kit
From 2014.igem.org
| Line 207: | Line 207: | ||
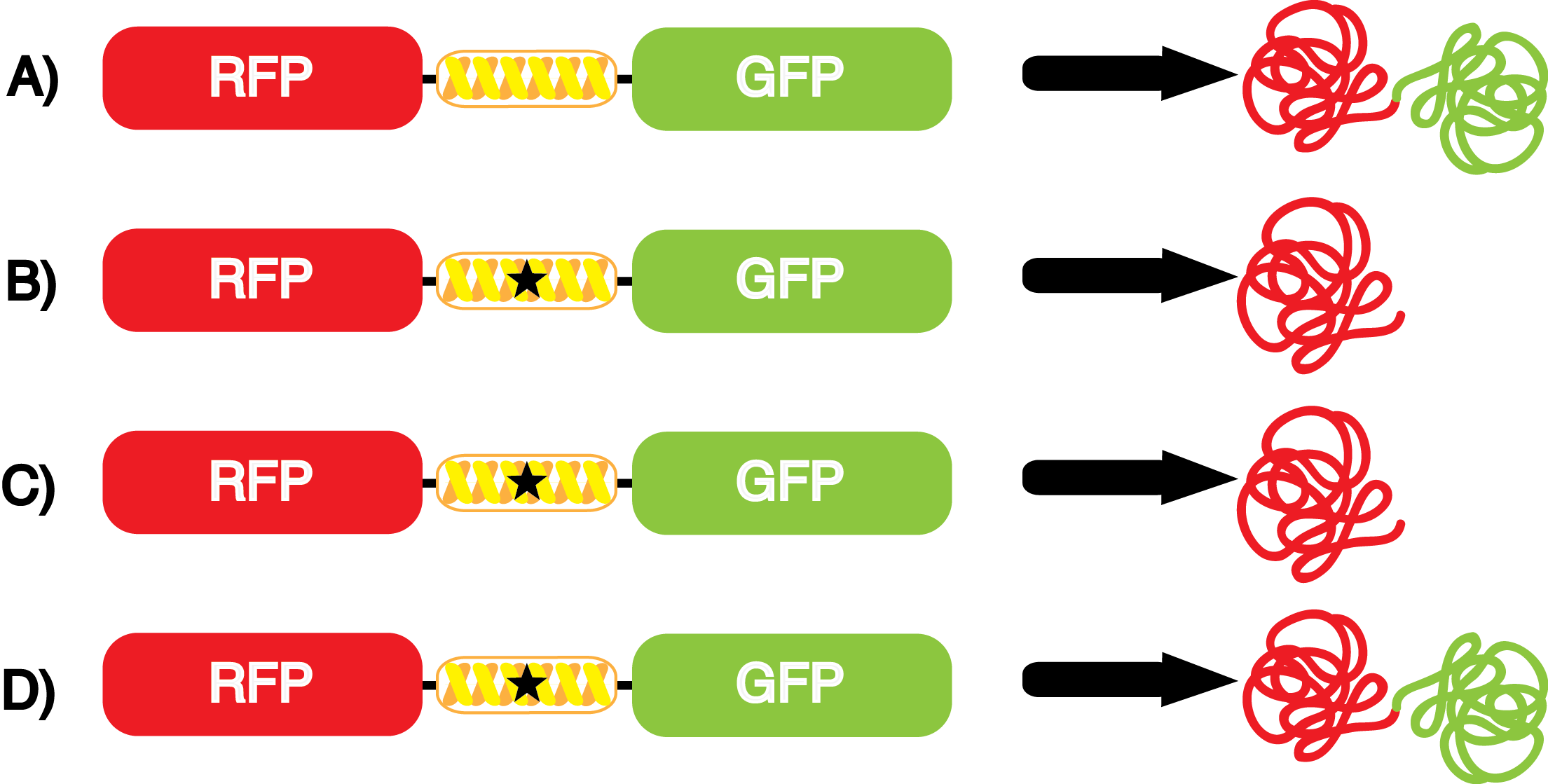
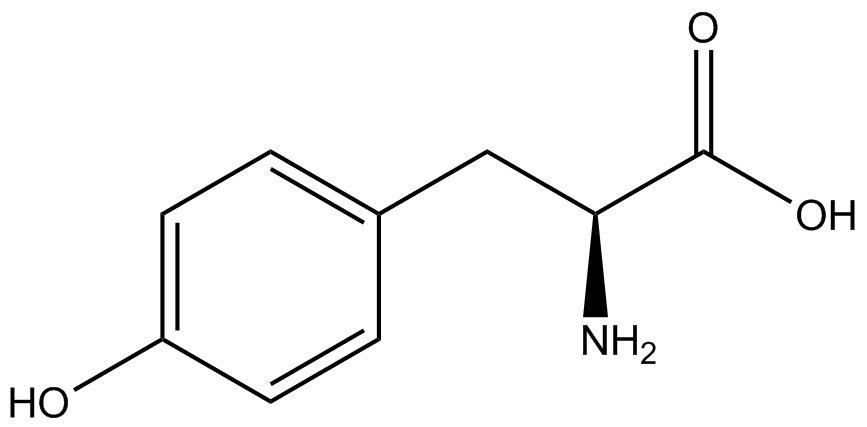
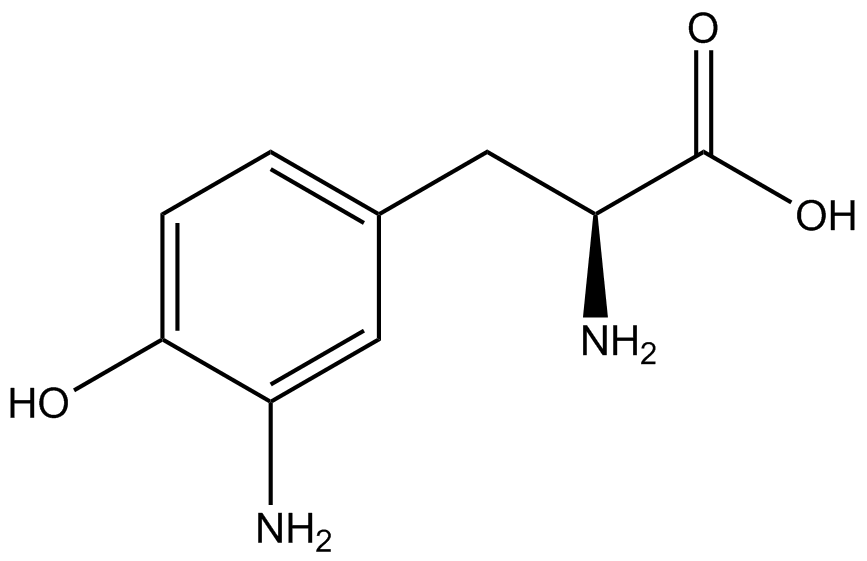
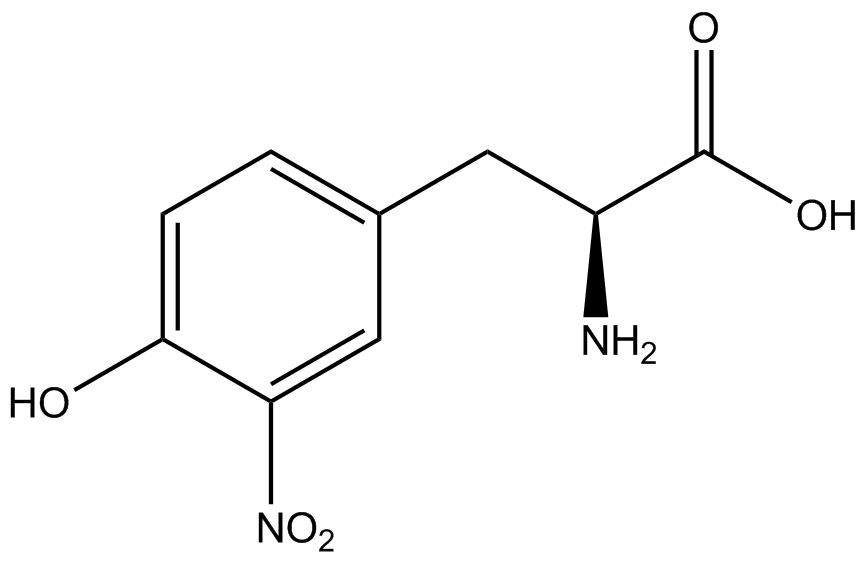
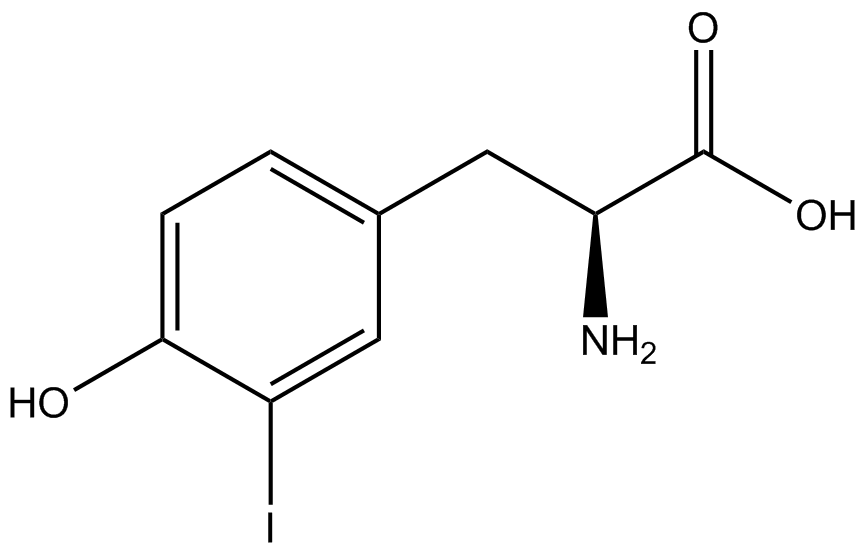
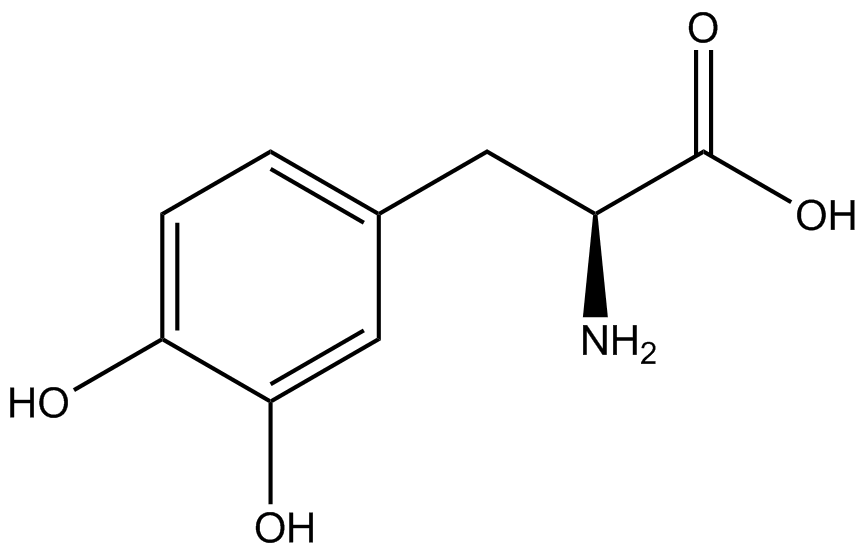
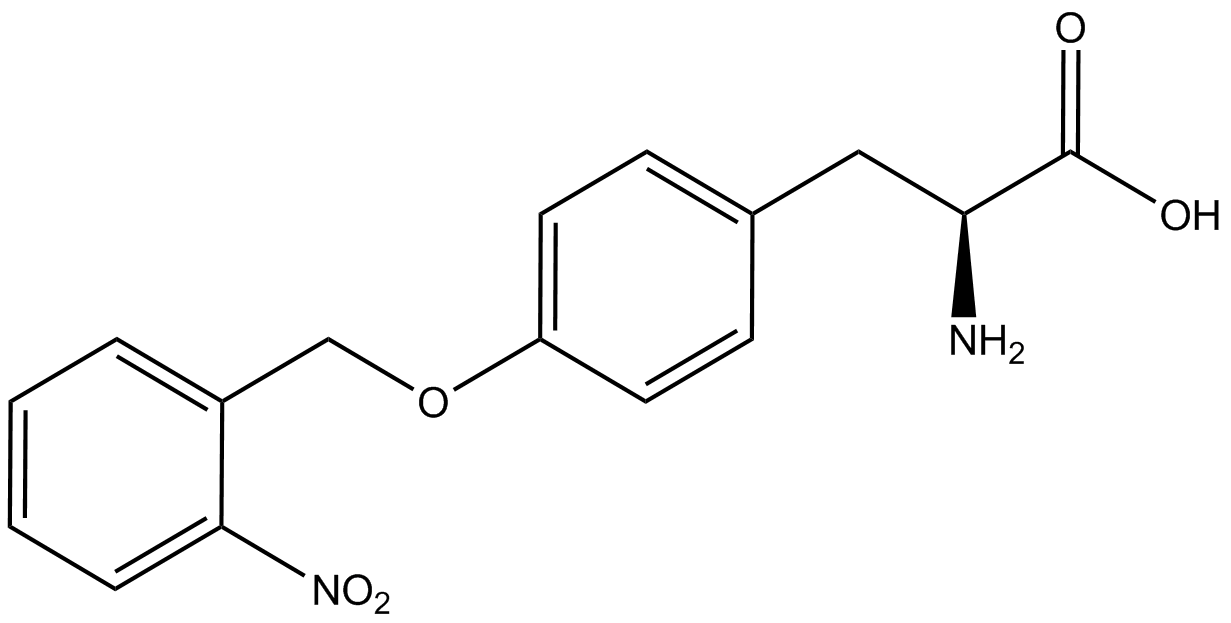
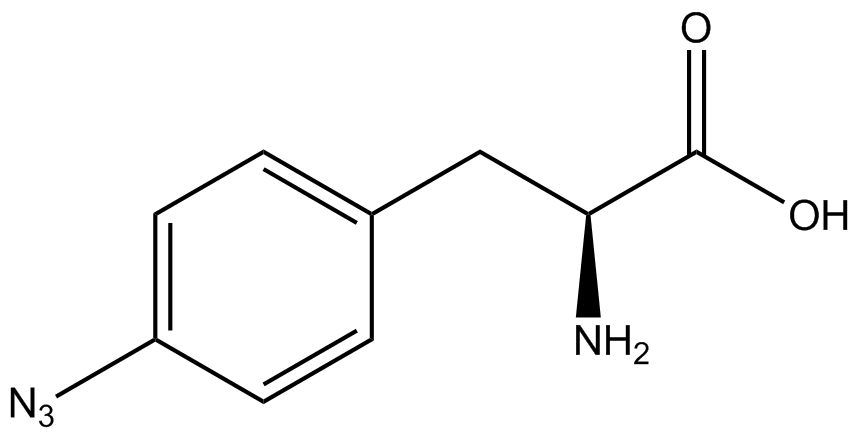
| - | When these values were graphed (Figure 4), some synthetase/tRNA pairs such as 4-azidophenylalanine, 3-nitrotyrosine, 3-iodotyrosine, and ortho-nitrobenzyltyrosine resulted in higher GFP fluorescence in the presence of ncAA than in the absence of ncAA, which suggests that those synthetases only incorporated an amino acid if their specific amino acid was present, meaning that they have a high fidelity. However, the other synthetase/tRNA pairs (3-aminotyrosine, L-DOPA, and cyanophenylalanine) did not show a difference in GFP fluorescence normalized to RFP fluorescence dependent on the presence of ncAA, indicating that these pairs incorporated other amino acids at the amber codon when their specific ncAA was not present (and perhaps even when it was), and thus have a low fidelity. | + | When these values were graphed (Figure 4), some synthetase/tRNA pairs such as 4-azidophenylalanine (AzF), 3-nitrotyrosine, 3-iodotyrosine, and ortho-nitrobenzyltyrosine (ONBY) resulted in higher GFP fluorescence in the presence of ncAA than in the absence of ncAA, which suggests that those synthetases only incorporated an amino acid if their specific amino acid was present, meaning that they have a high fidelity. However, the other synthetase/tRNA pairs (3-aminotyrosine, L-DOPA, and cyanophenylalanine (CNF)) did not show a difference in GFP fluorescence normalized to RFP fluorescence dependent on the presence of ncAA, indicating that these pairs incorporated other amino acids at the amber codon when their specific ncAA was not present (and perhaps even when it was), and thus have a low fidelity. |
<h2>Synthetase Efficiency</h2> | <h2>Synthetase Efficiency</h2> | ||
| Line 214: | Line 214: | ||
| - | For our results (Figure 4), two synthesase/tRNA pairs stood out as relatively inefficient: 3-nitrotyrosine and | + | For our results (Figure 4), two synthesase/tRNA pairs stood out as relatively inefficient: 3-nitrotyrosine and ONBY. Both of these synthetase/tRNA pairs showed a significantly smaller normalized GFP to RFP fluorescence when the ncAA was present with the pFRY construct. While both synthetase/tRNA pairs show a significant increase in normalized GFP to RFP fluorescence when the amino acid was present compared to when it was absent, which indicates a high fidelity, the actual GFP fluorescence relative to the RFP fluorescence was only around 50% for 3-nitrotyrosine and 20% for ONBY. These results suggest that, these synthetase/tRNA pairs do not always incorporate their ncAA at the amber stop codon. It is important to note that this could partly result for ncAA-related toxicity, and such an effect was repeatedly observed for ONBY. |
<h2>Incorporation Value</h2> | <h2>Incorporation Value</h2> | ||
| - | [[File:UT_Austin_2014_Kit_Incorporation_Value_Graph.png|600px|thumb|'''Figure 5.''' | + | [[File:UT_Austin_2014_Kit_Incorporation_Value_Graph.png|600px|thumb|'''Figure 5.''' Incorporation values for each synthetase/tRNA pair. Dash line equals an incorporation value of 1. Values greater than 1 are desirable. The GFP:RFP relative fluorescence values in the presence and absence of ncAA (see Figure 4) were used to calculate incorporation values. Values were determined by dividing the GFP:RFP relative fluorescence in the presence of ncAA by the GFP:RFP relative fluorescence in the absence of ncAA. This value does not correct for ncAA-related effects on translation, which can occasionally be seen with the pFRYC controls.]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | The incorporation value is a single number that measure the relative efficiency and fidelity of a ncAA tRNA synthetase/tRNA pair. A value of 1 or lower indicates no significant incorporation dependent on the presence of ncAA in the culture. The higher the value, the higher the fidelity and/or efficiency of the synthetase/tRNA pair. It is important to note that ncAA-related effects on growth and translation can reduce the incorporation value of a synthetase/tRNA pair. At this time, we believe this is the most telling form of an incorporation value. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | The synthetase/tRNA pairs that showed the highest incorporation values include | + | The synthetase/tRNA pairs that showed the highest incorporation values include AzF, 3-nitrotyrosine, ONBY, and 3-iodotyrosine in decreasing order. Among the ncAAs tested, ONBY consistently slowed the growth rate of the culture significantly (as seen by OD600 readings, data not shown) suggesting possible toxicity to the cell. However, ncAA incorporation remained relatively high, resulting in a good incorporation value. Synthetase/tRNA pairs that showed the lowest levels of ncAA incorporation include 3-aminotyrosine, <small>L</small>-DOPA, and CNF. |
| Line 232: | Line 229: | ||
<h1>Discussion</h1> | <h1>Discussion</h1> | ||
| - | |||
| + | Our ncAA measurement kit was able to successfully compare the fidelity and efficiency of seven different synthetase/tRNA pairs. We were able to confidently say that one synthetase/tRNA pair had a higher fidelity than another. We saw clear evidence that three of our tRNA synthetase/tRNA pairs seemed incapable of discriminating between their ncAA and the 20 canonical amino acids present in media: 3-aminotyrosine, <small>L</small>-DOPA, and CNF. We were able to test triplicate cultures of seven different ncAAs and tyrosine (eight total synthetase/tRNA pairs) in one day, generating results that immediately told us which ncAAs worked best in our system both in terms of fidelity and efficiency of incorporation. This required no advanced training or access to equipment besides a shaker and a fluorometer. | ||
| - | |||
| + | While the measurements may not be perfectly accurate due to the nature of this test, the measurement kit is designed more around ease of use, cost-efficiency, and portability. The ncAA measurement kit can be used to quickly test a synthetase/tRNA pair's quality with minimal effort, as opposed to other more accurate but more intensive or expensive measures such as mass spectrometry. While mass spectrometry can give much more definitive information about a synthetase/tRNA pair, there are many different factors that could make it unreasonable for undergraduate research. It is a technique that requires a fair amount of skill to do properly, and can be very costly as well. Additionally, the sample needs to be purified from cell culture and prepped for mass spectrometry. | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | For the ncAA measurement kit, all that is necessary is to request from us the kit plasmids (pFRYC and PFRY in separate strains of amberless ''E. coli''), which we are immediately making available to anyone who requests the Expanded Genetic Code Measurement Kit. Once you receive the frozen cultures (or plasmids), transform the synthetase/tRNA pair that you wish to test into the two different cell strains, and run the experiment. Thus, if you receive the measurement kit on Monday, you could have your synthetase/tRNA pairs characterized by Friday. The kit can also be used to test how one or more synthetase/tRNA pairs work in different cells or under different conditions. However, in this case, you may need to retransform the kit plasmids into the different strain. | |
| + | We are optimistic that this measurement kit can help speed up the process of developing a new synthetase/tRNA pair, as well as characterizing large groups of synthetase/tRNA pairs, as we now have a way to quickly, cheaply, and easily do large scale characterizations. | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | Due to the nature of the Expanded Genetic Code Measurement Kit, <i>in vivo</i> influences will affect certain data and results. This knowledge is very useful by providing a broader and biological perspective of <i>in vivo</i> perspective of cellular health. In general, the presence of ncAAs slowed the growth of amberless ''E. coli'', sometimes quite significantly. This knowledge, as seen through the GFP:RFP ratio, can be very informative when assessing whether to use a ncAA tRNA synthetase/tRNA pair. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
<h1>Conclusion</h1> | <h1>Conclusion</h1> | ||
Revision as of 17:51, 17 October 2014
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"