Team:Austin Texas/photocage
From 2014.igem.org
Nathanshin (Talk | contribs) |
Nathanshin (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
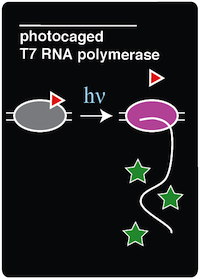
For this experiment, there were also other necessary control strains to test alongside the experimental strain. These controls included a T7-GFP construct with no amber stop codon in the O-helix (to serve as a positive control for expression with T7 polymerase), sfGFP amberless E.coli (to observe the expression of GFP by native polymerase), amberless E.coli (to serve as a cell background control), and LB supplemented with ncAA (to serve as a media background control). | For this experiment, there were also other necessary control strains to test alongside the experimental strain. These controls included a T7-GFP construct with no amber stop codon in the O-helix (to serve as a positive control for expression with T7 polymerase), sfGFP amberless E.coli (to observe the expression of GFP by native polymerase), amberless E.coli (to serve as a cell background control), and LB supplemented with ncAA (to serve as a media background control). | ||
| - | All of these strains were grown overnight in LB and appropriate antibiotics. The next morning, 100 microliters of each of the strains were | + | All of these strains were grown overnight in LB and appropriate antibiotics. The next morning, three 100 microliters samples of each of the strains were inoculated into three different conditions. The conditions are as follows: |
*(-)IPTG, (-)ONBY | *(-)IPTG, (-)ONBY | ||
*(+)IPTG, (+)ONBY | *(+)IPTG, (+)ONBY | ||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
Once the initial readings were recorded, the 100 microliters samples in the black 96 well plate were transferred into a deep 96 well plate, covered, and allowed to grow overnight at 37C and 225 RPM. | Once the initial readings were recorded, the 100 microliters samples in the black 96 well plate were transferred into a deep 96 well plate, covered, and allowed to grow overnight at 37C and 225 RPM. | ||
| - | The cultures were allowed 16 hours of growth so that the decaged T7 RNA polymerase | + | The cultures were allowed 16 hours of growth so that the decaged T7 RNA polymerase would have time to polymerize mRNA transcripts of the GFP, which is bound by an upstream T7 promoter. After 16 hours of growth, cultures were transferred back to a black 96 well plate and the fluorescence was measured. |
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
| - | Although the increases in fluorescence are clearly present, there are still a few problems regarding the system. For one, the level of background expression of the un-induced T7 RNAP is relatively high. The uninduced caged T7 RNAP has roughly 25 times more expression compared to the negative control. The relatively high level of fluorescence may be explained by the efficient nature of T7 RNAP. Even if a few polymerases were "decaged", they would have 16 hours to bind to the promoter and transcribe the RNA transcript for GFP. A potential solution to reduce the background expression of GFP would be to mutate a second amber codon into the coding sequence of T7 RNA polymerase. Adding a second stop codon would theoretically reduce the number of T7 RNA polymerases that are being transcribed. If a second amber stop codon were to be mutated into the coding sequence of T7 RNAP, it would be beneficial to be at another active site in the enzyme. Another possible location of the second amber stop codon would be at the start of the sequence. | + | Although the increases in fluorescence are clearly present, there are still a few problems regarding the system. For one, the level of background expression of the un-induced T7 RNAP is relatively high. The uninduced caged T7 RNAP has roughly 25 times more expression compared to the negative control. The relatively high level of fluorescence may be explained by the efficient nature of T7 RNAP. Even if a few polymerases were "decaged", they would have 16 hours to bind to the promoter and transcribe the RNA transcript for GFP. A potential solution to reduce the background expression of GFP would be to mutate a second amber stop codon into the coding sequence of T7 RNA polymerase. Adding a second stop codon would theoretically reduce the number of T7 RNA polymerases that are being transcribed. If a second amber stop codon were to be mutated into the coding sequence of T7 RNAP, it would be beneficial to be at another active site in the enzyme. Another possible location of the second amber stop codon would be at the start of the sequence. Placing an amber stop codon at the beginning of the sequence would prematurely halt the transcription of misincorporated amino acids. As a result, the background would be decreased as T7 RNAP would more effectively be "caged". |
The replication of such a system provides the foundation for potential projects for our future iGEM teams. By replacing the GFP reporter with coding sequences for other proteins, we will be able to explore novel applications of light-activated protein expression. | The replication of such a system provides the foundation for potential projects for our future iGEM teams. By replacing the GFP reporter with coding sequences for other proteins, we will be able to explore novel applications of light-activated protein expression. | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 17 October 2014
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"