Team:Austin Texas/photocage
From 2014.igem.org
Nathanshin (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
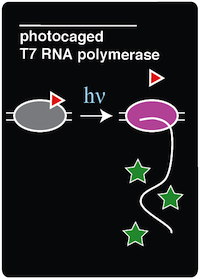
| - | In order to incorporate the ncAA into amberless E.coli (which is described '''[here]'''), a ''Methanocaldoccus jannaschii'' tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNA pair was previously mutated to selectively charge and incorporate ONBY. Six residues (Tyr 32, Leu 65, Phe 108, Gln 109, Asp 158, and Leu 162) on the original synthetase were randomized and the library was selected for its ability to charge ONBY while discriminating against other canonical amino acids. The resulting mutant ONBY synthetase contained five mutations (Deiters et al. 2006). The following are the residues that were mutated on the synthetase: Tyr32→Gly32, Leu65→Gly65, Phe108→Glu108, Asp158→Ser158, and Leu162→Glu162. The Asp158→Ser158 and Tyr32→Gly32 mutations are believed to result in the loss of hydrogen bonds with the natural substrate, which would disfavor binding to tyrosine. Additionally, the Tyr 32→Gly 32 and Leu 65→Gly 65 mutations are believed to increase the size of the substrate-binding pocket to accommodate for the size of the bulky o-nitrobenzyl group (Deiters et al. 2006). | + | In order to incorporate the ncAA into amberless E.coli (which is described '''[https://2014.igem.org/Team:Austin_Texas/kit#Background here]'''), a ''Methanocaldoccus jannaschii'' tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNA pair was previously mutated to selectively charge and incorporate ONBY. Six residues (Tyr 32, Leu 65, Phe 108, Gln 109, Asp 158, and Leu 162) on the original synthetase were randomized and the library was selected for its ability to charge ONBY while discriminating against other canonical amino acids. The resulting mutant ONBY synthetase contained five mutations (Deiters et al. 2006). The following are the residues that were mutated on the synthetase: Tyr32→Gly32, Leu65→Gly65, Phe108→Glu108, Asp158→Ser158, and Leu162→Glu162. The Asp158→Ser158 and Tyr32→Gly32 mutations are believed to result in the loss of hydrogen bonds with the natural substrate, which would disfavor binding to tyrosine. Additionally, the Tyr 32→Gly 32 and Leu 65→Gly 65 mutations are believed to increase the size of the substrate-binding pocket to accommodate for the size of the bulky o-nitrobenzyl group (Deiters et al. 2006). |
<h1>Experimental Methods</h1> | <h1>Experimental Methods</h1> | ||
Revision as of 15:23, 17 October 2014
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"