Team:Freiburg/Content/Results/Vector
From 2014.igem.org
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<div class="col-sm-6"> | <div class="col-sm-6"> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/3/38/Freiburg2014-10-03_Results_Vector_skizze.JPG"> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/3/38/Freiburg2014-10-03_Results_Vector_skizze.JPG"> <!-- ORGINAL --> |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/3/38/Freiburg2014-10-03_Results_Vector_skizze.JPG"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">Test</p> | <p class="header">Test</p> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 49: | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/c/c9/Freiburg2014-09-06_stable_EGPF_integration_diagram_and_facs.png"> <!-- ORGINAL --> | |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/c/c9/Freiburg2014-09-06_stable_EGPF_integration_diagram_and_facs.png"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header"></p> | <p class="header"></p> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 67: | ||
<div class="col-sm-6"> | <div class="col-sm-6"> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/9/95/Freiburg2014-10-08_Integration_time.png"> <!-- ORGINAL --> | |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/9/95/Freiburg2014-10-08_Integration_time.png"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">Fig.: Integration time of our viral vector into murine cells.</p> | <p class="header">Fig.: Integration time of our viral vector into murine cells.</p> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 83: | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/b/b2/Freiburg2014-10-02_plasmid_map_pMIG_constructs_skizze.JPG"> <!-- ORGINAL --> | |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/b/b2/Freiburg2014-10-02_plasmid_map_pMIG_constructs_skizze.JPG"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">Fig.: pMIG constructs</p> | <p class="header">Fig.: pMIG constructs</p> | ||
| Line 85: | Line 93: | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/20/Freiburg2014-10-02_pMIG_different_consctructs.JPG"> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/20/Freiburg2014-10-02_pMIG_different_consctructs.JPG"> <!-- ORGINAL --> |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/2/20/Freiburg2014-10-02_pMIG_different_consctructs.JPG"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">Fig.: Transduction efficiency of the viral vector in mouse cells.</p> | <p class="header">Fig.: Transduction efficiency of the viral vector in mouse cells.</p> | ||
| Line 102: | Line 112: | ||
<div class="col-sm-6"> | <div class="col-sm-6"> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/0/0d/Freiburg2014-10-02_transduction_efficiency_in_pictures.JPG"> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/0/0d/Freiburg2014-10-02_transduction_efficiency_in_pictures.JPG"> <!-- ORGINAL --> |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/0/0d/Freiburg2014-10-02_transduction_efficiency_in_pictures.JPG"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">Fig.: nice pictures of nice cells.</p> | <p class="header">Fig.: nice pictures of nice cells.</p> | ||
| Line 109: | Line 121: | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/4/44/Freiburg2014-10-02_transduction_efficiency_before_and_after.JPG"> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/4/44/Freiburg2014-10-02_transduction_efficiency_before_and_after.JPG"> <!-- ORGINAL --> |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/4/44/Freiburg2014-10-02_transduction_efficiency_before_and_after.JPG"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">Fig.: Transduction efficiency of the viral vector in mouse cells.</p> | <p class="header">Fig.: Transduction efficiency of the viral vector in mouse cells.</p> | ||
| Line 117: | Line 131: | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/b/bc/Freiburg2014-10-08_HWZ.png"> <!-- ORGINAL --> | |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/b/bc/Freiburg2014-10-08_HWZ.png"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">grüne balken</p> | <p class="header">grüne balken</p> | ||
| Line 138: | Line 154: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/0/0e/Freiburg2014-10-06_dilution_concentration_virus.png"> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/0/0e/Freiburg2014-10-06_dilution_concentration_virus.png"> <!-- ORGINAL --> |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/0/0e/Freiburg2014-10-06_dilution_concentration_virus.png"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">Fig.: Concentrated virus</p> | <p class="header">Fig.: Concentrated virus</p> | ||
| Line 166: | Line 184: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/f/ff/Freiburg2014-10-02_results_skizze_specificity.JPG"> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/f/ff/Freiburg2014-10-02_results_skizze_specificity.JPG"> <!-- ORGINAL --> |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/f/ff/Freiburg2014-10-02_results_skizze_specificity.JPG"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">Fig.1: Description of the experiment (as picture)</p> | <p class="header">Fig.1: Description of the experiment (as picture)</p> | ||
| Line 175: | Line 195: | ||
<div class="col-sm-6"> | <div class="col-sm-6"> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/4/45/Freiburg2014-09-10_FACS-specificity-HEK-MOUSE.png"> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/4/45/Freiburg2014-09-10_FACS-specificity-HEK-MOUSE.png"> <!-- ORGINAL --> |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/4/45/Freiburg2014-09-10_FACS-specificity-HEK-MOUSE.png"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">Fig.X: FACS analysis of different cell lines incubated with the CAT-1 specific viral vector</p> | <p class="header">Fig.X: FACS analysis of different cell lines incubated with the CAT-1 specific viral vector</p> | ||
| Line 184: | Line 206: | ||
<div class="col-sm-6"> | <div class="col-sm-6"> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/5/5a/Freiburg2014-09-10_cell-line-specificity.png"> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/5/5a/Freiburg2014-09-10_cell-line-specificity.png"> <!-- ORGINAL --> |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/5/5a/Freiburg2014-09-10_cell-line-specificity.png"> <!-- Thumbnail --> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p class="header">Fig.1: Infection of different cell lines with the viral vector derived from the murine leukemia virus.</p> | <p class="header">Fig.1: Infection of different cell lines with the viral vector derived from the murine leukemia virus.</p> | ||
| Line 195: | Line 219: | ||
<blockquote><strong>The vector derived from the murine leukemia virus is specific for the murine CAT-1 receptor. Therefore it is not able to infect human cell lines!</blockquote> | <blockquote><strong>The vector derived from the murine leukemia virus is specific for the murine CAT-1 receptor. Therefore it is not able to infect human cell lines!</blockquote> | ||
</section> | </section> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Revision as of 22:15, 8 October 2014
The Vector
Introduction
We succeed to stably integrate our gene of interest into the genome of target cells by using a viral vector derived from the murine leukemia virus. The advantages of this vector are: its specificity for murine cells, making the viral work safe and easy; a very high efficiency for infection; and the ability of stable gene transfer into the genomes of target cells. Here we present results on these three qualities of our viral vector and how we optimized virus production and cell infection.
Stable integration of target genes into the genome
Our viral vector derives from the murine leukemia virus and since this virus is a retrovirus, it stably integrates our gene of interest into the target genomes. Hereby, any gene of interest can be delivered. So as to demonstrate this we transferred different genes for fluorescence proteins into murine cell lines.

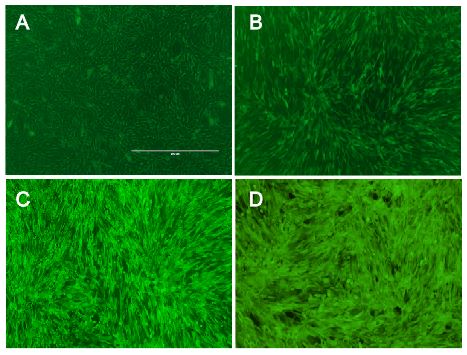
Fig.: Murine cells infected with our viral vector containing different fluorescence markers; (left) EGFP, (middle) mKate, (right) mKO.
In addition, we demonstrated the capability of stable gene integration by creating an EGFP cell line by infecting murine cells with our viral vector. Two days after virus infection, we selected for cells displaying green fluorescence by a cell sorter. Afterwards, we analyzed the EGFP cell line for several weeks by flow cytometry. Sustained expression of EGFP indicates stable integration into the genome of the original cell line.

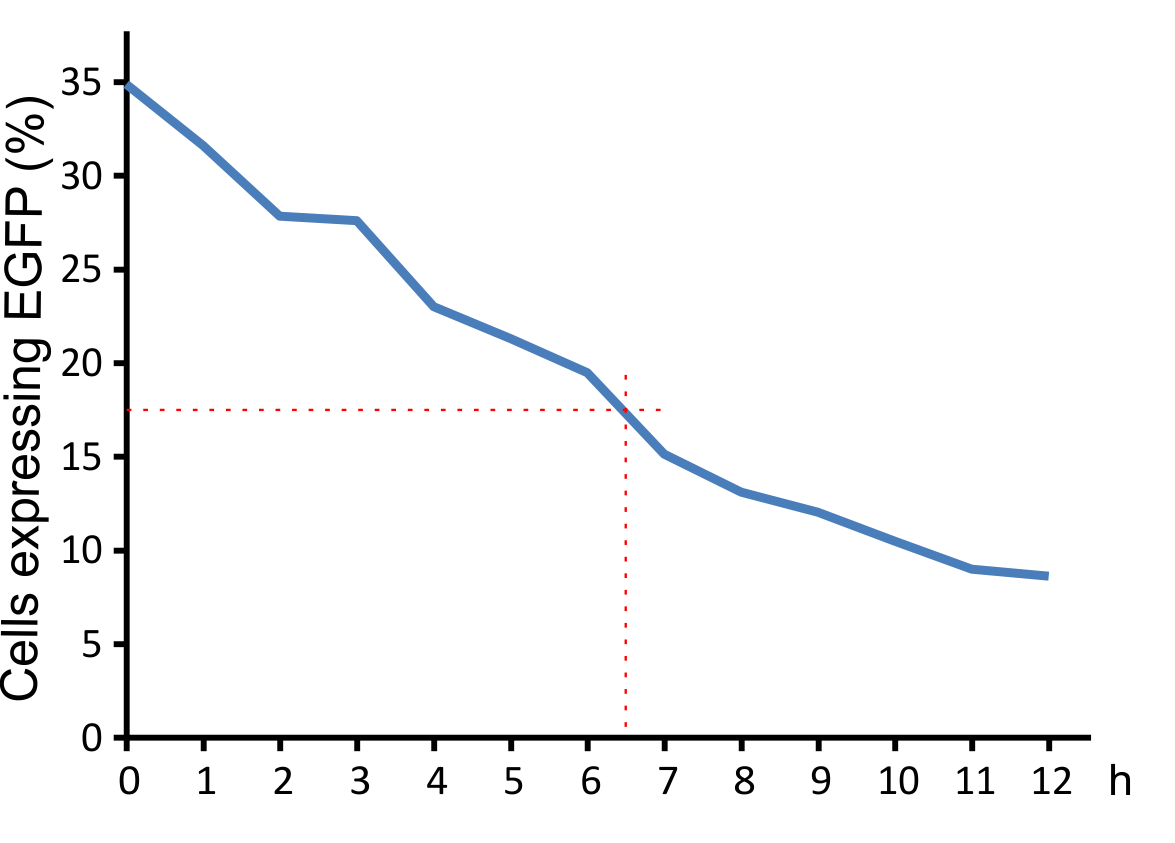
For optimal integration of the target gene, it was tested how long the viral vector need for transducing murine cells. The results indicate that a high infection rate was already reached after incubating the cells for five hours with the viral particles
In order to sort the cells stable integrated the gene of interest into the genome, the viral vector contains a marker like the gene for a fluorophore. We tested the expression rate of EGFP in pMIG constructs containing only the marker in comparison to constructs containing the stably transferred target gene in combination with the marker. In the construct combining the target gene with the marker, EGFP expression is apparently lower explainable by the lower binding capacity of the internal ribosomal entry site (IRES).

Fig.: pMIG constructs

Fig.: Transduction efficiency of the viral vector in mouse cells.
Here should stand a sentence that simply present the results of this subsection
High efficiency
The vector we use transfers genes into target genomes. We increased the efficiency in cell targeting and gene transfer to reach an infection rate of over 80% in murine cell lines and high infection rates in other cell lines expressing the murine CAT-1 receptor. Protocols for virus production and target cell transduction were optimized. As producer cell line for viral particles we took Phoenix cells containing plasmids with viral genes. Before transfection with the pMIG, we split Phoenix cells several times to increase viability and bring them into the exponential growth phase during production on the viral vector. In addition, supernatant containing the vector were harvest at distinct time points optimized for optimal viral titer. Target cells were infected by viral supernatant with Polybrene which increases the probability for particle to reach their target cells. Since murine leukemia viruses only infect dividing cells, the growth phase of the target cells were adjusted to the time point of infection. Under these optimized conditions, the efficiency for infecting murine cell lines with our viral vector was over 80%. Since we had only 16% transduction efficiency at the beginning of the project, we would consider this a significant advance. To our knowledge, an optimized infection protocol with murine leukemia virus has not been published to date. The exact procedure can be found here (link).
With the viral vector used in our system transduction efficiency in murine cells was optimized to almost 100%!
blubb!
Specificity and safety of MuLV
An important aspect for the function of our system as well as for its safety is the specificity of the vector regarding infection of different kind of cells. The vector deriving from the murine leukemia virus is specific for cells carrying the mouse specific CAT-1. Cells that do not have this specific receptor are not targeted by the vector. In order to test the specificity of the system, different kind of cells were incubated with the vector containing EGFP. Since EGFP is stable integrated by the system, infected cells are identified by a green fluorescence that was analysed via flow cytometry (figure 1).
We tested two human cell lines, human embryonic kidney cells as well as human lung epithel carcinoma cells, for their capability of being targeted by the vector. In addition, mouse fibroblasts that express the mouse specific CAT-1 receptor were tested for a positive control. As shown in figure 1 both human cell lines did not express EGFP after incubation with the vector indicating that they were not targeted. However, many cells of the mouse cell line were expressing EGFP after infection.

Fig.1: Description of the experiment (as picture)

Fig.X: FACS analysis of different cell lines incubated with the CAT-1 specific viral vector
Left: Different cell lines not incubated with the vector as negative control, Middle: different cell lines infected with MuLV IRES EGFP (50% in completed growth medium), Right: cells transfected with the mouse specific receptor CAT-1 (rz006) were infected with the viral vector. The infection efficiency is directly correlated with transfection efficiency of the receptor into the different kind of cells.
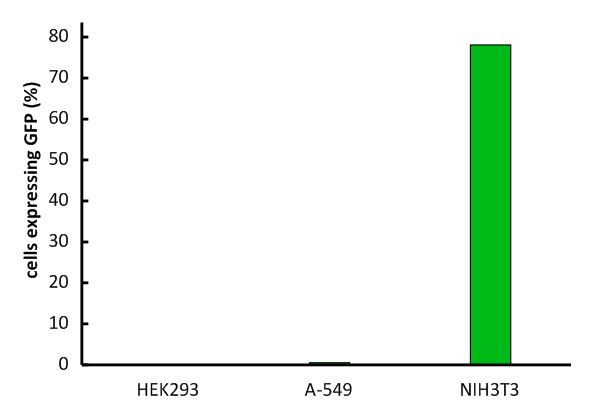
Fig.1: Infection of different cell lines with the viral vector derived from the murine leukemia virus.
In order to investigate the specificity of the viral vector, two human cell lines, human embryonic kidney cells as well as lung epithel carcinoma cells, were infected and the percentage of cells expressing EGFP was analyzed by flow cytometry.
The vector derived from the murine leukemia virus is specific for the murine CAT-1 receptor. Therefore it is not able to infect human cell lines!
 "
"