Team:Freiburg/Content/Results/Vector
From 2014.igem.org
Mirja Harms (Talk | contribs) |
Mirja Harms (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<div class="row category-row"> | <div class="row category-row"> | ||
| - | + | <div class="col-sm-6"> | |
<p>An important aspect for the function of our system as well as for its safety is the specificity of the vector regarding infection of different | <p>An important aspect for the function of our system as well as for its safety is the specificity of the vector regarding infection of different | ||
kind of cells. The vector deriving from the murine leukemia virus is specific for cells carrying the mouse specific CAT-1. Cells that do not have | kind of cells. The vector deriving from the murine leukemia virus is specific for cells carrying the mouse specific CAT-1. Cells that do not have | ||
this specific receptor are not targeted by the vector. In order to test the specificity of the system, different kind of cells were incubated with | this specific receptor are not targeted by the vector. In order to test the specificity of the system, different kind of cells were incubated with | ||
the vector containing EGFP. Since EGFP is stable integrated by the system, infected cells are identified by a green fluorescence that was analysed | the vector containing EGFP. Since EGFP is stable integrated by the system, infected cells are identified by a green fluorescence that was analysed | ||
| - | via flow cytometry (figure 1). We tested two human cell lines, human embryonic kidney cells as well as human lung epithel carcinoma cells, for their | + | via flow cytometry (figure 1). |
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="col-sm-6"> | ||
| + | <p>We tested two human cell lines, human embryonic kidney cells as well as human lung epithel carcinoma cells, for their | ||
capability of being targeted by the vector. In addition, mouse fibroblasts that express the mouse specific CAT-1 receptor were tested for a positive | capability of being targeted by the vector. In addition, mouse fibroblasts that express the mouse specific CAT-1 receptor were tested for a positive | ||
control. As shown in figure 1 both human cell lines did not express EGFP after incubation with the vector indicating that they were not targeted. However, | control. As shown in figure 1 both human cell lines did not express EGFP after incubation with the vector indicating that they were not targeted. However, | ||
many cells of the mouse cell line were expressing EGFP after infection. | many cells of the mouse cell line were expressing EGFP after infection. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| - | + | </div> | |
| - | + | </div> | |
| - | <div | + | |
| - | + | ||
| + | <figure> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/f/ff/Freiburg2014-10-02_results_skizze_specificity.JPG"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/f/ff/Freiburg2014-10-02_results_skizze_specificity.JPG"> | ||
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 35: | ||
</figcaption> | </figcaption> | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="row category-row"> | ||
| + | <div class="col-sm-6"> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/4/45/Freiburg2014-09-10_FACS-specificity-HEK-MOUSE.png"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/4/45/Freiburg2014-09-10_FACS-specificity-HEK-MOUSE.png"> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 48: | ||
</figcaption> | </figcaption> | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| - | + | </div> | |
| + | <div class="col-sm-6"> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/5/5a/Freiburg2014-09-10_cell-line-specificity.png"> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2014/5/5a/Freiburg2014-09-10_cell-line-specificity.png"> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 58: | ||
</figcaption> | </figcaption> | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
| - | + | </div> | |
| + | |||
<blockquote><strong>The vector derived from the murine leukemia virus is specific for the murine CAT-1 receptor. Therefore | <blockquote><strong>The vector derived from the murine leukemia virus is specific for the murine CAT-1 receptor. Therefore | ||
it is not able to infect human cell lines!</blockquote> | it is not able to infect human cell lines!</blockquote> | ||
Revision as of 15:03, 2 October 2014
1 The Vector
1.1 Specificity of MuLV
An important aspect for the function of our system as well as for its safety is the specificity of the vector regarding infection of different kind of cells. The vector deriving from the murine leukemia virus is specific for cells carrying the mouse specific CAT-1. Cells that do not have this specific receptor are not targeted by the vector. In order to test the specificity of the system, different kind of cells were incubated with the vector containing EGFP. Since EGFP is stable integrated by the system, infected cells are identified by a green fluorescence that was analysed via flow cytometry (figure 1).
We tested two human cell lines, human embryonic kidney cells as well as human lung epithel carcinoma cells, for their capability of being targeted by the vector. In addition, mouse fibroblasts that express the mouse specific CAT-1 receptor were tested for a positive control. As shown in figure 1 both human cell lines did not express EGFP after incubation with the vector indicating that they were not targeted. However, many cells of the mouse cell line were expressing EGFP after infection.

Fig.1: Description of the experiment (as picture)

Fig.X: FACS analysis of different cell lines incubated with the CAT-1 specific viral vector
Left: Different cell lines not incubated with the vector as negative control, Middle: different cell lines infected with MuLV IRES EGFP (50% in completed growth medium), Right: cells transfected with the mouse specific receptor CAT-1 (rz006) were infected with the viral vector. The infection efficiency is directly correlated with transfection efficiency of the receptor into the different kind of cells.
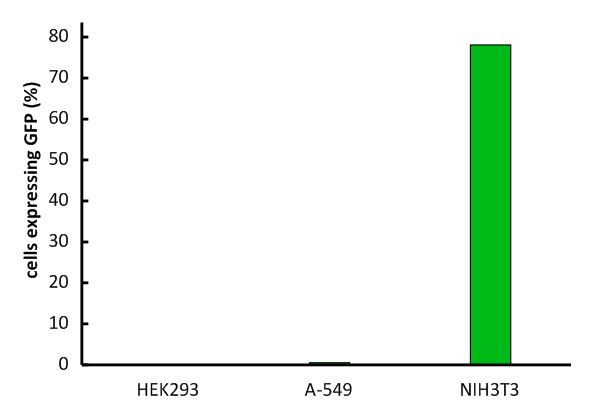
Fig.1: Infection of different cell lines with the viral vector derived from the murine leukemia virus.
In order to investigate the specificity of the viral vector, two human cell lines, human embryonic kidney cells as well as lung epithel carcinoma cells, were infected and the percentage of cells expressing EGFP was analyzed by flow cytometry.
The vector derived from the murine leukemia virus is specific for the murine CAT-1 receptor. Therefore it is not able to infect human cell lines!
1.2 Optimization of transduction
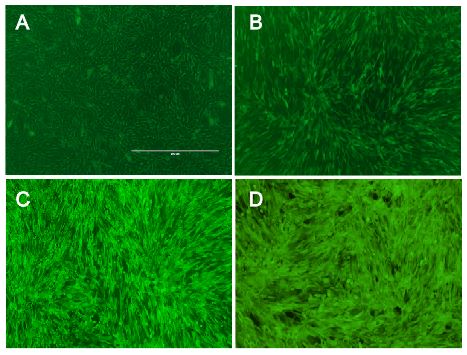
Fig.: Transduction efficiency of the viral vector in mouse cells.

Fig.: Transduction efficiency of the viral vector in mouse cells.
 "
"