Team:NCTU Formosa/project
From 2014.igem.org
(→Damage to human body) |
(→Damage to human body) |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
=====Damage to human body===== | =====Damage to human body===== | ||
| - | + | Pesticides includes substances that kill weeds (herbicides), insects (insecticides), fungus (fungicides), rodents (rodenticides), and others.The use of toxic pesticides to manage pest problems has become a common practice around the world. Pesticides are used almost everywhere, causing human health hazards, ranging from short-term impacts such as headaches and nausea to chronic impacts like cancer and reproductive harm.There is also mounting evidence that exposure to pesticides disrupts the endocrine system, wreaking havoc with the complex regulation of hormones, the reproductive system, and embryonic development.</p> | |
=====Damage to the environment===== | =====Damage to the environment===== | ||
Revision as of 14:53, 29 September 2014
- Overview
- PBAN
- Biobrick
-
Overview
Insect damage have been a serious problem for a long time over the whole world and it is difficult to be solved. People take several methods to kill these harmful insects, but the methods have cause other problems to the environment. In order to solve the troublesome problem and not to have the bad side effect, we established an alternative way to solve it in an eco-friendly manner.
-
PBAN
PBAN (Pheromone Biosynthesis Activating Neuropeptide) is a simple, short peptide. When it binds with a receptor on the pheromone gland of an insect, it will activates pheromone synthesis. Just like the pheromones, PBAN is species-specific, so we can use one kind of PBAN to enhance pheromone biosynthesis on the kind of insect that we are targeting.
-
Brobrick
In our basic design, we want to express PBAN in an easier way than the original complex process. To make it more convenient to observe and model, we ligate the reporter gene BFP into our biobrick.
Contents |
Overview
Impact of pest
From ancient times to the present, harmful insects always play roles in our life, and we don’t have any appropriate solution to these annoying pest. Every year, harmful insect cause a great amount of loss to our agriculture, and it seriously disturbs our people livelihood and economy.
In order to make our discuss more trustworthy ,we find some data to support our opion. We take the Brazil for example. We can find several crucial economic crop such as coconut ,coffee, and Sugarcan are damaged by harmful insect. The total loss of crop in the Brazil is about 11 billion US dollars. In addition, we can also find that people spend nearly 1.4 billion controling to the number of these annoying pest. What is more? They use a great number of insecticides which have some toxic substance. Therefore, this method will make our people expose to horrible situation.
loss caused by Pest in BrazilThere are many factors that cause the loss. Losses caused by pests on crops include direct damage, drug costs and the experimental costs, The loss which is most difficult to estimate is the consumption of medical resources on human health hazards caused by pesticides.
chemical control method
Because of the hazard of insects, human beings to come out lots of ideas to kill these harmful insects. In 15th century,people used heavy metals to kill harmful insects, such as Arsenic, Mercury and Plumbum, which caused a catastrophe to the environment. Pesticides become more powerful along with the technology, in 20th century,the agriculture develops rapidly just because of the evolution of pesticide. But the pesticides are not only harmful to the insects but also harmful to the human beings. People found this problem after several decades. The toxin of the pesticides will be kept in creatures by the food chain ,and finally go into human's body. However, it's not too late to improve this situation. We can create an evolution of agriculture by a new method, and it is what we do!
Damage to human body
Pesticides includes substances that kill weeds (herbicides), insects (insecticides), fungus (fungicides), rodents (rodenticides), and others.The use of toxic pesticides to manage pest problems has become a common practice around the world. Pesticides are used almost everywhere, causing human health hazards, ranging from short-term impacts such as headaches and nausea to chronic impacts like cancer and reproductive harm.There is also mounting evidence that exposure to pesticides disrupts the endocrine system, wreaking havoc with the complex regulation of hormones, the reproductive system, and embryonic development.Damage to the environment
Pesticides wreak havoc on the environment, threatening biodiversity and weakening the natural systems upon which human survival depends.Pesticides have led to abnormal mass mortality of America's honeybees.The populations of bees have dropped by 29% to 36% each year since 2006. To our astonishment, fully 1/3 of the food we eat depends on bees for pollination!
Secondly, some scientists believe that amphibians and bats have become more susceptible to deadly disease because their immune systems are weakened by pesticides.What's more,one kind of pesticides called herbicide, which can give a male frog a sex change . Genetically, the frogs are still males, but morphologically they are completely female and they can even mate successfully with other males and lay viable eggs. Pesticides have also contaminated waterways and endangered fish and birds, causing ecological damage.
By the way, pesticide resistance makes insecticides ineffective. Other factors in the speed with which a species evolves resistance are generation time and fecundity, that is , causing shorter generations and more offspring lead to resistance more quickly.
Biological control method
Since most chemical control methods are poisonous to environment, human begins to look for other alternative ways. One of the most well known example is bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), with its crystal proteins, it can efficiently kill insects. However, recent researches show that more and more insects are resistant to this kind of protein. It's time to find another better solution.
Solution to both questions
People invent pesticides to eliminate the pests, but the use of pesticides will hurt the environment and cause harm to humans. Thus there have been conflicting issues, and have remained to be settled. In order to solve the above-mentioned problems, we came up with a practical, inexpensive way.

|
 |
 |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reference
-
1.Pogue, Michael. "A review of selected species of Lymantria Huber [1819]". Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team. Retrieved September 14, 2012.
2.Eliminate Cutworms Using Natural Pest Control By Susan Glaese March/April 1987
3. Laurence Mousson, Catherine Dauga, Thomas Garrigues, Francis Schaffner, Marie Vazeille & Anna-Bella Failloux (August 2005). "Phylogeography of Aedes (Stegomyia) aegypti (L.) and Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus (Skuse) (Diptera: Culicidae) based on mitochondrial DNA variations". Genetics Research
4. NPIC is a cooperative agreement between Oregon State University
5.M. S. Ascunce et al., “Global Invasion History of the Fire Ant Solenopsis invicta”, Science, vol. 331, no. 6020, pp. 1066 - 1068, 2011
6.organicgardening.com/learn-and-grow/fire-ant-control
7.Scientists suggest fighting fire ants with ice By Chiu Yu-Tzu / STAFF REPORTER
8.Capinera, J.L. 1999. Fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Noctuidae
9.Helicoverpa Diapause Induction and Emergence Tool Introduction to the Helicoverpa armigera Genome Project Helicoverpa armigera Genome Project updates on InsectaCentral Helicoverpa Genome Project database on-line Lepiforum Funet Taxonomy Fauna Europaea
UC IPM Pest Management Guidelines: Cotton UC ANR Publication 3444
10. "Interesting (To Us) Photos From The Garden". Meades.org. Retrieved 2011-08-11.RXwildlife Sightings » Blog Archive » More Emergence". Rxwildlife.org.uk. 2009-06-03. Retrieved 2011-08-11.Cabbage Moth - Caterpillar". Habitas.org.uk. Retrieved 2014-08-11.
11.Authored by W. H. Reissig. Published by the New York State Agricultural Experiment Station, Geneva, A Division of the New York State College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, A Statutory College of the State University, Cornell University, Ithaca. Funded in part by an Extension Service-USDA, IPM Grant.
PBAN(Pheromone Biosynthesis Activating Neuropeptide)
Introduction of Pheromones
A pheromone is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting outside the body of the secreting individual to impact the behavior of the receiving individual.
There are many kinds of pheromone such as alarm pheromones, food trail pheromones, sex pheromones, and many others that affect behavior or physiology.
Our project : Operation Debug aims to use different PBANs from different moths and other insects to induce them to make their own sex pheromone .
Sex pheromones, which are an important factor in finding a mating partner. When a female releases chemicals, the mate search is initiated, and the male moths begin their upwind motion toward their potential partner. Sex pheromones in particular are associated with long-range chemical communication of sex substances used in signaling a mating partner. Mate finding in moths involve sex pheromones that have the ability to propel long-distances and are emitted by the females abdominal glands in most cases.
Ways to make pheromones
There are 2 main ways to make pheromones. One is chemical synthesis, the other one is biosynthesis approach.
1. Chemical synthesis approach:
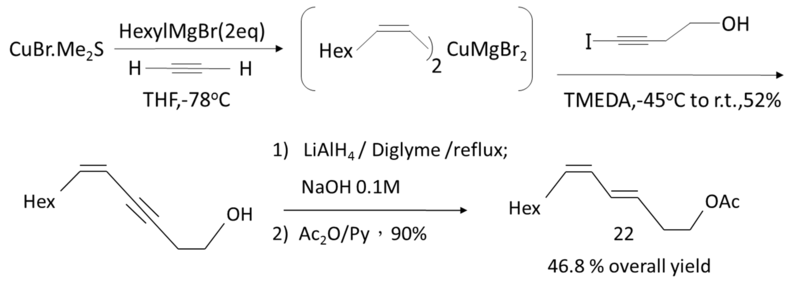
It is difficult to make pheromone by chemical synthesis approach. This approach needs to use many kinds of chemical compound which may cause some pollution to the environment. Furthermore, chemical approach needs to control the condition of reaction that may consume a lot of energy.An example of chemical synthesis approach:
leafroller moth, Bonagota cranaodes
2.Biosynthesis approach:
Biosynthesis approach needs lots of enzymes to catalyzed , which is too complicated for E.coli to carry out .In addition, E.coli is lack of Glycoproteins that can do posttranslational modification. Therefore, it is nearly impossible for E.coli to produce pheromones in normal way. An example of Biosynthesis approach: Gypsy moth, Lymantria dispar.
Introduction of PBAN
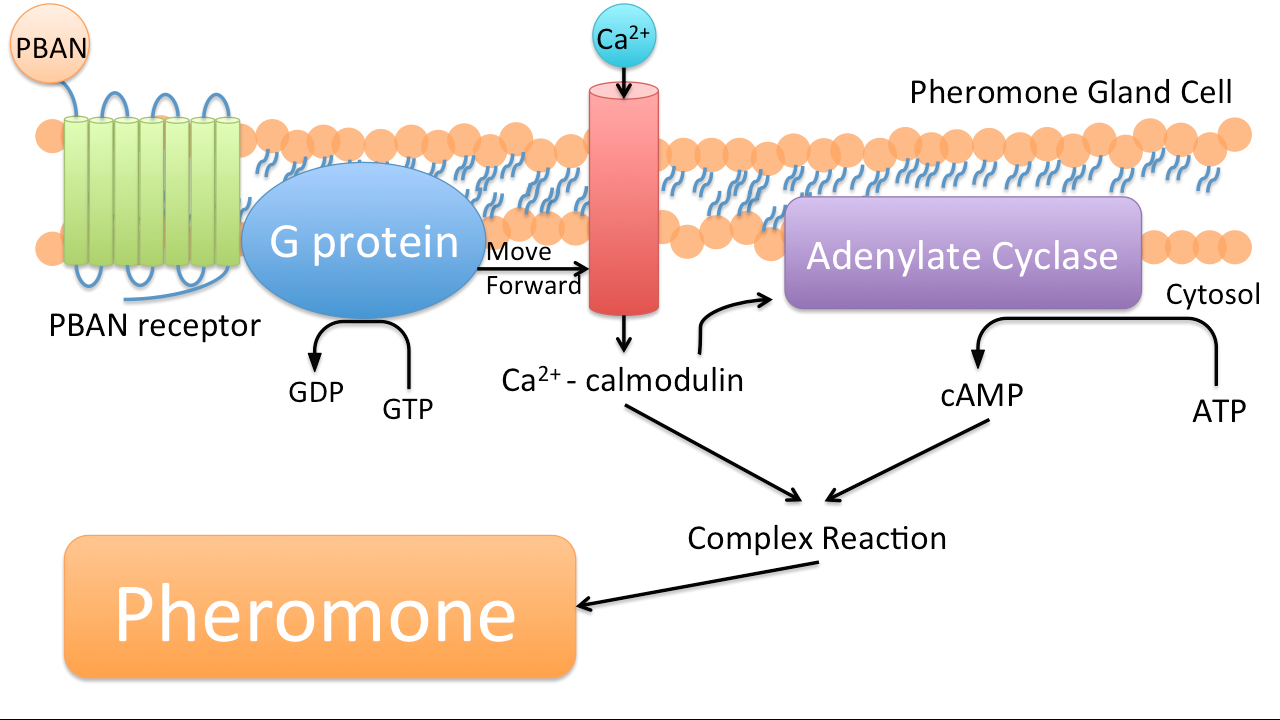
PBAN(Pheromone Biosynthesis Activating Neuropeptide) is one kind of peptides that can activate biosynthesis of pheromones of many kinds of insects. Once a PBAN binds with the G-protein coupled receptor on an insect’s pheromone gland, the signal send by the G-protein coupled receptor activates the kinase and phosphatase, and then kinase and phosphatase can activate enzymes that participate in the biosynthesis of insect pheromone, which will be emitted.
In nature, female insects such as moths release PBAN during mating to stimulate the synthesis of pheromones in order to attract their male counterparts. PBAN can also facilitate the release of non-sex pheromones such as trail pheromones for ants.
Features of PBAN
1. PBAN is species-specific just like pheromones, that means every kinds of insects which can produce pheromone have it's specific PBAN,which can only bind with it's specific receptor and only stimulate the biosynthesis of a specific pheromone.
2. The coding sequence for a PBAN is usually around 100 base pairs. Thus, it is easy for E.coli to express. We can even combine several different PBAN sequences into one BioBrick assembly or even make different regulation for different PBANs.
Effect Testing of PBAN from Reference
Because we regard PBAN as a leading character in our project, we have to realize what kind of problem we would meet with if we want to make use of PBAN. First, we had to confirm that whether PBAN can work when getting in the moth’s body from outside, we got a paper titled “Pheromonotropic Activity of Naturally Occurring Pyrokinin Insect Neuropeptides (FXPRLamide) in Helicoverpa zea” from ELSEVIER, experiments of the research were conducted with Helicoverpa zea(corn earworm) in this research, researchers injected different amount(from 0.05 pmol to 200 pmol) of PBAN of Helicoverpa zea (named Hez-PBAN )into their bodies directly, and then measured the amount of pheromone produced, the result (fig.1-2-4)showed that PBAN has function as long as it gets in moth’s body, and the 2 pmol dose of Hez-PBAN was the minimum dose required to stimulate production of the maximum amount of pheromone, that revealed we are able to stimulate the production of pheromone with only little amount of PBAN which gets in moth’s body, whether we fed or injected PBAN.
Difficulty of Natural PBAN about Peptidase Degradation
But we still had the second problem,we had known that peptidase in the insect’s body can degrade peptides including PBAN, so the effect of PBAN can’t continue for a long time. In order to solve this problem, we search some former papers and we found another paper from ELSEVIER, it was titled “Enhanced oral availability/pheromonotropic activity of peptidase-resistanttopical amphiphilic analogs of pyrokinin/PBAN insect neuropeptides”, Heliothis virescens was used in this research, researchers produced amphiphilic analogs of pyrokinin/PBAN with chemical synthesis method, they used hydroxyproline (Hyp) and octahydroindole-2-carboxyl (Oic) to replace the Proline(Pro) of the PBAN C-terminal penpapeptides(Phe-Thr-Pro-Arg-Leu-NH2), that made PBAN be able to resist peptidase, they compared the stability of the natural pyrokinin/PBAN analog LPK, and the peptidase-resistant pyrokinin/PBAN analogs(5 nmol was used), we can see that natural PBAN will be reduced over time in the moth’s body (fig.1-2-5).

Our New Idea of using PBAN
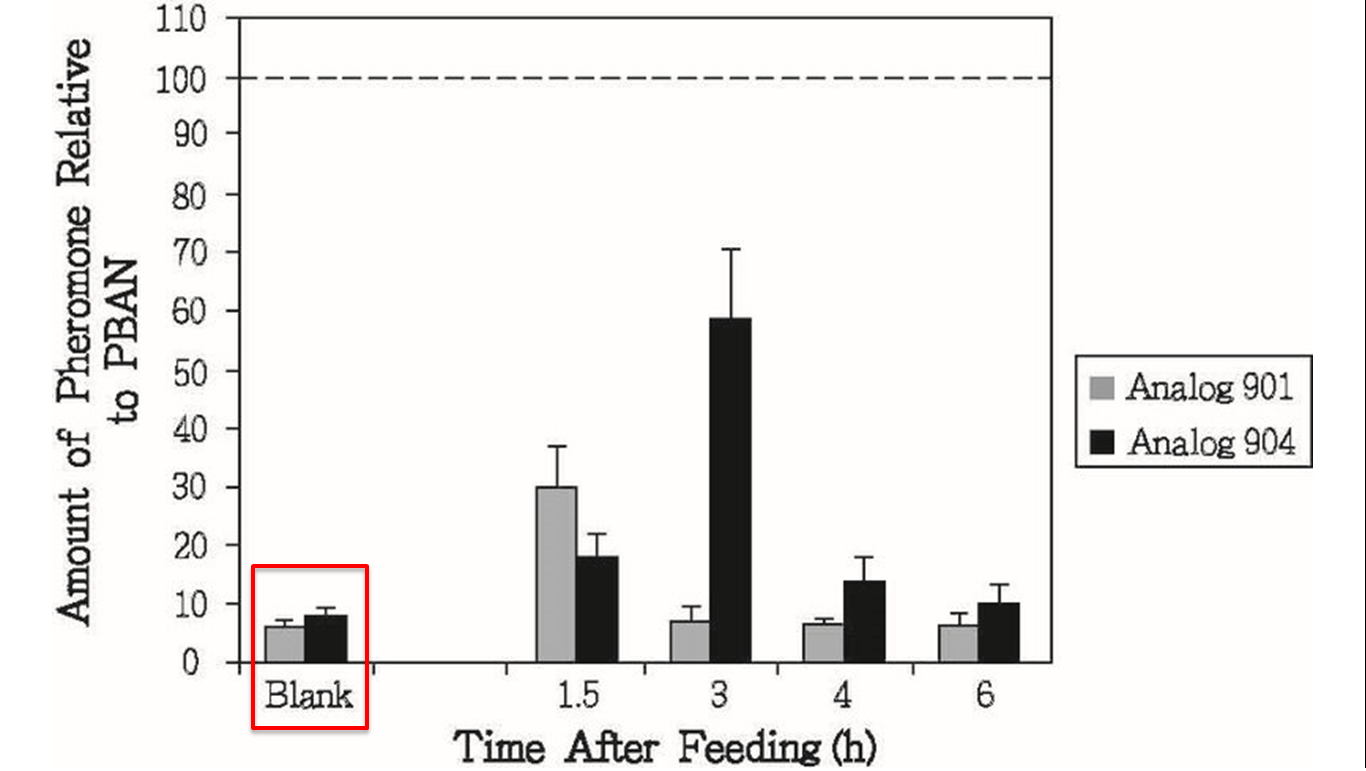
This results above sounded not good for us, but there was other experiment interested us in the same research, researchers also conducted oral test with their PBANs (fig.1-2-6), in this experiment, they fed moths with sugar solution which contained their PBAN analogs , and measure the amount of pheromone produced over time, that gave us inspiration, although natural PBAN can’t be maintained for a long time in moth’s body, we could solve this problem by feeding moths with PBAN continually, after combining this thought with the method of the oral experiment, we figured out an idea, in stead of killing all of the moths.
It is very possible that the PBANs in the food will penetrate into moths’ body from the digestive system. Thus, if female moths suck the food, the PBAN in the moths’ body will be replenished, that solves the problem that PBAN can not maintain for a long time in the moths’body. As to how we produce PBAN and apply our concept to capture wanted harmful insects, we will explain in the following.
How are we going to use PBAN?
In our project, we will biologically synthesize PBAN with our E.coli. We store the PBAN inside a trapping device (check this out at our Device page). In the device, there will be appropriate lighting and nutrient sources that will attract insects.
Once an insect is attracted into our device and ingests the nutrient sources we provide, it will also inevitably come in contact with our PBAN, which is evenly mixed with the nutrient sources. As the PBAN works its magic and activates the pheromone synthesis of the attracted insect, more of this species of insect’s counterparts will be attracted and later captured.
Owing to the first feature mentioned above, PBANs are species-specific, which means that it doesn't matter if other kind of insect fly into our device and eat PBANs, because the insects we don't want to catch will not be stimulated by PBANs to produce pheromone; our PBANs are only for what we want to catch, we are sure that our method won't affect other kinds of insects.
Reference
- Miriam Altstein, Role of neuropeptides in sex pheromone production in moths, ELSEVIER, Peptides 25 (2004) 1491–1501.
- Ada Rafaeli, Pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide (PBAN): Regulatory role and mode of action, General and Comparative Endocrinology 162 (2009) 69–78
- Ronald J. Nachmana, Peter E.A. Teal, Allison Strey, Enhanced oral availability/pheromonotropic activity of peptidase-resistant topical amphiphilic analogs of pyrokinin/PBAN insect neuropeptides, ELSEVIER, Peptides 23 (2002) 2035–2043 +
- Russell Jurenka1 and Ada Rafaeli, Regulatory role of PBAN in sex pheromone biosynthesis of heliothine moths, frontiers in ENDOCRINOLOGY, published: 10 October 2011 doi: 10.3389/fendo.2011.00046
- Dr. Ashok K. Raina andJulius J. Menn, Pheromone biosynthesis activating neuropeptide: From discovery to current status, Issue Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, Article first published online: 7 FEB 2005 DOI: 10.1002/arch.940220112
- Man-Yeon Choi and Robert K. Vander Meer, Ant Trail Pheromone Biosynthesis Is Triggered by a Neuropeptide Hormone, PLoS Onev.7(11); 2012PMC3511524
- RELLA L. ABERNATHY, RONALD J. NACHMAN, PETER E. A. TEAL, OKITSUGU YAMASHITAS AND JAMES H. TUMLINSON, Pheromonotropic Activity of Naturally Occurring Pyrokinin Insect Neuropeptides (FXPRLamide) in Helicoverpa zea, ELSEVIER, Peptides Volume 16, Issue 2, 1995, Pages 215–219
Design
Biobrick Design
We searched the DNA sequences of the PBANs from many kinds of insects on NCBI, then contrasted to the amino sequences from papers so that we can selected the DNA fragments which directly correspond to gland-stimulating function, By ligating the constitutive promoter(J23101), Ribosome binding site(B0034) and PBAN DNA sequence with a terminator(J61048) at the last, we were able to make E.coli directly produce these PBANs continusely instead of the original complex process of PBAN biosynthesis in insects.
Reference
- Torsten Waldminghaus, Nadja Heidrich, Sabine Brantl and Franz Narberhaus .(2007). FourU: a novel type of RNA thermometer in Salmonella . Molecular Microbiology , 65(2): 413–424 DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05794.x
- part BBa_K115002;TUDelft Registry of Standard Biological Parts
Device
Introduction
Since insects react widely different to the gravity force, we design a device which could catch specific kind of insect species that we want. For example, Agrotis ypsilon Rottemberg and Spodoptera litura falls into the kind of moth that have geotaxis. So we made a trap with accessible pathway in the bottom. Once an insect enters the device, it could only goes up and be trapped inside the pyramid. However, after field investigation, we found some insects still escape from the device. Then we came out with a new version trap with doubled layers.
Mechanism
First, we divide our design chart into two parts-exterior and interior. The exterior is just like the appearance of Pyramid ,and the interior is used to equip PBANs and bag for pests. When the harmful insects we want to catch eat our PBANs, they will release pheromone, and attract the same species. We can use blue light or the smell of pheromone to attract insect at first. After they go into our device, the design of our device will take advantages of their characteristic that insects always fly high to escape and make them stuck in our device. When we take away the outer shield ,the hock on the outer shield will close the bag ,and the insects will be caught. In addition, the four tenons at the corner can firm up our device.
To get more professional suggestions, we went to the National Chung Hsing university,and visited the professor Hau You Tzeng who major in mosquito. This tour benefited us very much. We got some knowledge about how to design breeding cage. With this experience, we finally designed our own breeding cage.
Design
For the materials of our device, We use Acrylic Sheet or balsa. The fomer is transparent and safer than glass. The latter is cheap, light, and easy to cut. For the process , We google some informations of our factories, and use Colddraw to hand out the design chart. We also go everywhere to buy what we need for our device. For example, the tool for cutting wood and LED light were just named a few.
Table below shows the exploded view of a complete device:
| Introduction | Function | schematic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outer shell | We shaped the device into a pyramid. Its special layout also enriches the device with mysterious colors. |
1. Outer shell is composed of 4 triangular acrylic planes which has a trapezoid entrance to let bugs in and release the smell of PBAN. 2.There is a hook installed on the outer plane which attaches to the collecting bag inside. When we pull up the outer shell, the bag inside would also be sealed simultaneously so the bugs won’t escape. |
|
| Inner shell | Similar to the outer one, inner shell are also composed of 4 trapezoid planes and removable from the base. The only different part is that its top is not sealed in order to contain the collecting bag. |
1. The inner space can contain a purse-string bag to collect insects we want. 2. 4 rods are assembled like a pound sign on the top to sustain the bag. 3. There would be a culture dish placed on the bottom. 4. A blue LED light bulb will be installed around the top of the inner shell plane to attract the first female insect. |
|
| Tenon | A part to stabilize the pyramid. |
1. Stabilize 4 corners of the bottom. 2. To make sure the outer shell can combine with the inner one tightly. |
Advantages
1. We successfully apply the geotaxis of targeted female moth to trap them in our device, forcing them releasing sex pheromone by our PBAN to attract more same-kind insects.
2. The hook attached to the purse-string bag can seal it simultaneously when we want to remove the outer shell. By doing so, no insects would flee from the bag and safety problems can also be solved.
3. Inner shell is removable so it’s easier to add new PBAN solution.
4. Compared to conventional light bulb, LED bulb is much brighter and conserves more energy. It could powered by battery so it’s also easier to establish.
5. Purse-string bag is cheap and easy to switch.
6. The PBAN system can run day and night. Its function won’t be affected by sunlight.
 "
"