Team:ETH Zurich/expresults/qs
From 2014.igem.org
(→Quorum Sensing) |
(→How to read the matrices below.) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
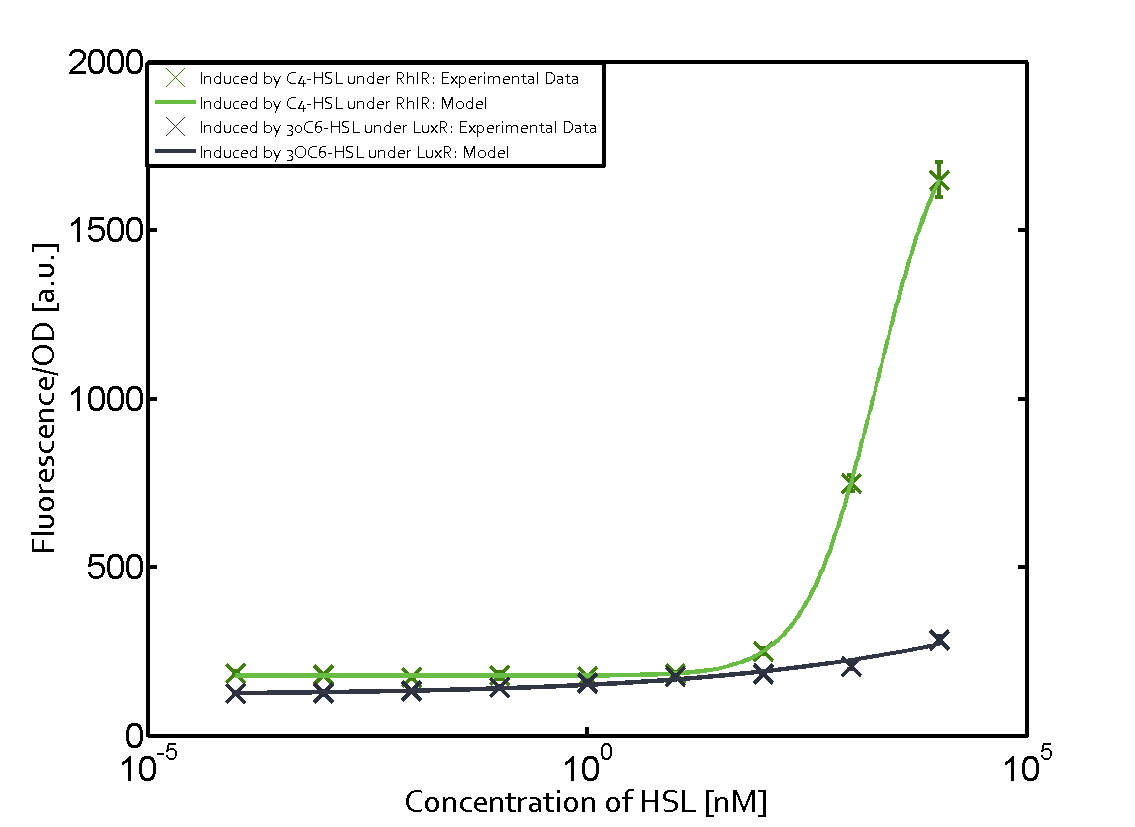
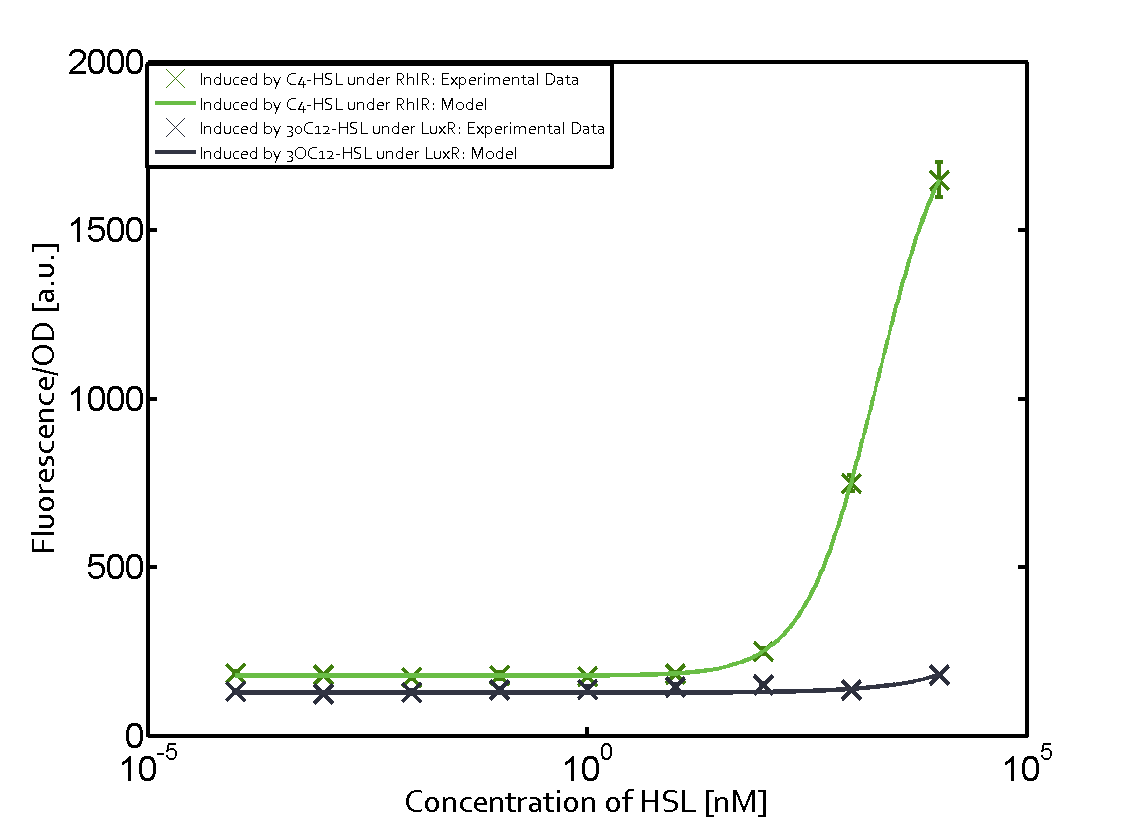
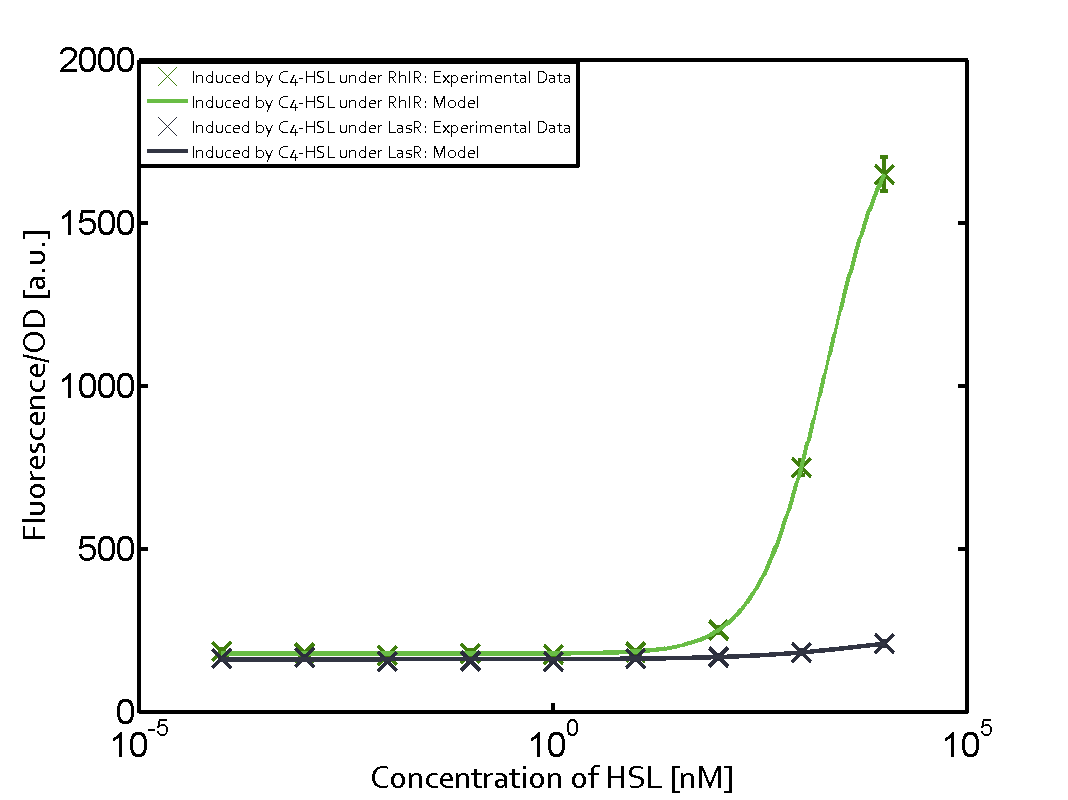
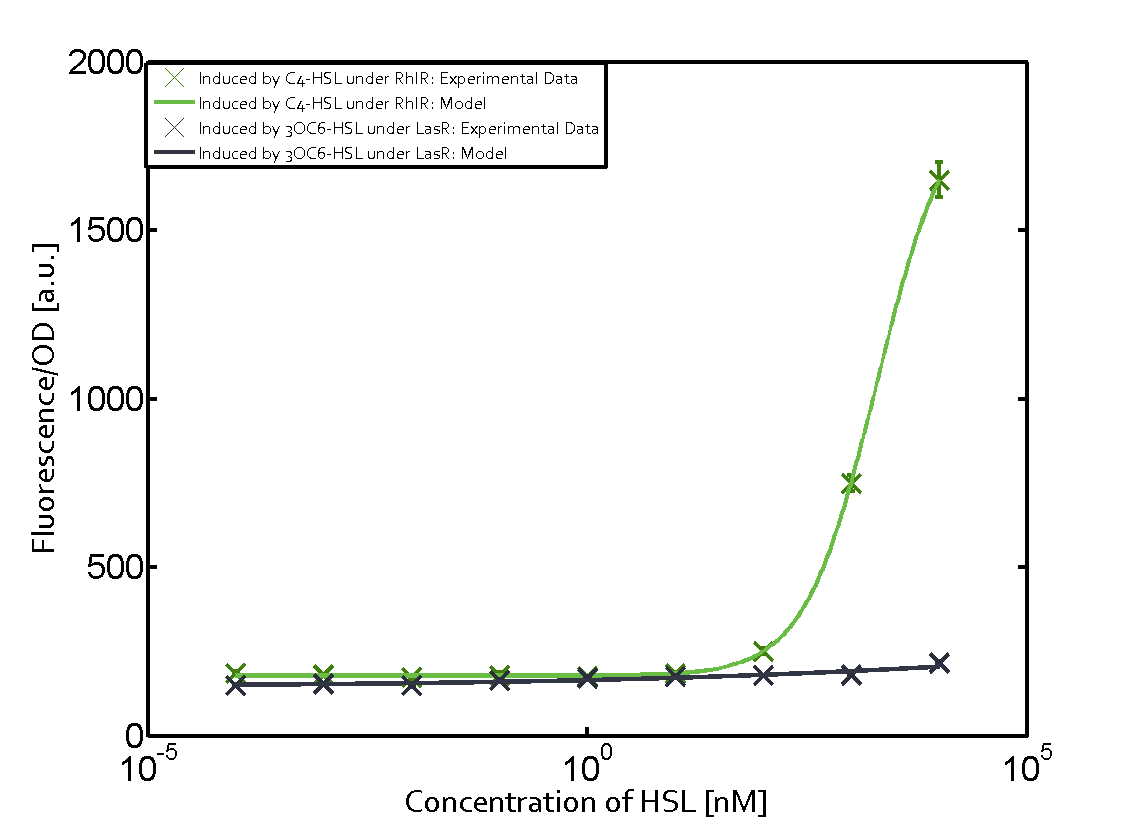
| - | In this matrix the results of experiments with the promoter pRhl are summarized. In the top left corner we see the pRhl induced by the corresponding C4-HSL bound to RhlR. Transition occurs at a concentration of 1 micromolar of CS4-HSL. | + | In this matrix the results of experiments with the promoter pRhl are summarized. The solid green line shows the modeling data whereas the cross represent experimental data. |
| - | When observing pRhl see cross-talk when inducing the promoter with 3OC6-HSL binding to RhlR for induction of pRhl | + | In the top left corner we see the pRhl induced by the corresponding C4-HSL bound to RhlR. Transition occurs at a concentration of 1 micromolar of CS4-HSL. |
| + | When observing pRhl we see cross-talk when inducing the promoter with 3OC6-HSL binding to RhlR for induction of pRhl. In this case the switching behaviour is observable at a concentration of 1 micro molar of 3OC6-HSL. The other observed cross-talk is the binding of 3OC12-HSL to LasR with subsequent induction of the promoter pRhl with a transition at 1nM of 3OC12-HSL. | ||
====Conclusion of cross-talk experiments==== | ====Conclusion of cross-talk experiments==== | ||
As shown in the graphs in the matrices above, we found and quantitatively characterized all three levels of cross-talk described previously. Unspecific inducer binding to the regulators as well as unspecific binding of the regulator to the promoter occurred in almost all possible combinations. To conclude, we were not able to find an orthogonal quorum-sensing pair due to inevitable cross-talk between the systems employing LuxI/LuxR, LasI/LasR, or RhlI/RhlR. | As shown in the graphs in the matrices above, we found and quantitatively characterized all three levels of cross-talk described previously. Unspecific inducer binding to the regulators as well as unspecific binding of the regulator to the promoter occurred in almost all possible combinations. To conclude, we were not able to find an orthogonal quorum-sensing pair due to inevitable cross-talk between the systems employing LuxI/LuxR, LasI/LasR, or RhlI/RhlR. | ||
Revision as of 17:43, 17 October 2014
Quorum Sensing
For our Mosiacoli project, we were looking for molecular systems that allow orthogonal cell-to-cell communication in order to implement connected XOR logic gates. We decided to exploit the quorum-sensing systems LuxI/LuxR, LasI/LasR, and RhlI/RhlR in order to achieve the required orthogonal cell-to-cell communication. Even though the corresponding inducer molecules are commercially available and the systems often used, in particular in iGEM projects (e.g. [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 pLux (BBa_R0062)], '[http://parts.igem.org/Frequently_Used_Parts Top 10 Most used promoters]' with 246 uses), potential cross-talk activity between the different systems may be a severe problem (ref).
In order to address that challenge, we measured a) a given promoter with its corresponding regulator and a different inducer molecule, b) a given promoter with an unspecific regulator and a particular inducer, c) a given promoter with both regulator and inducer being unspecific, and always included the correct combination of inducer molecule, regulator and promoter as a positive control. This gives in total 27 possible combinations. The output was assessed via sfGFP and measured in terms of fluorescence on microtiter-plate scale.
How to read the matrices below.
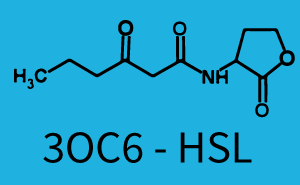
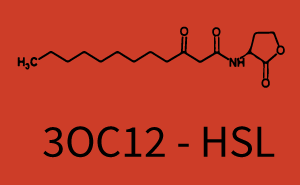
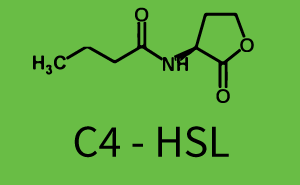
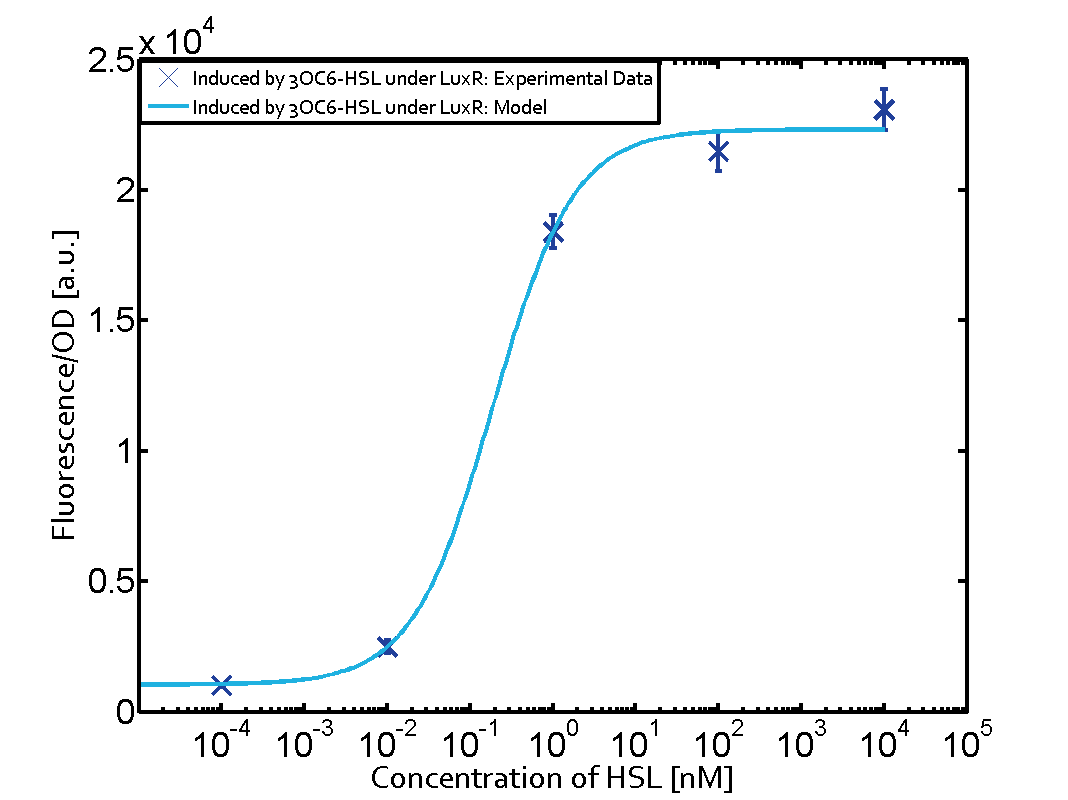
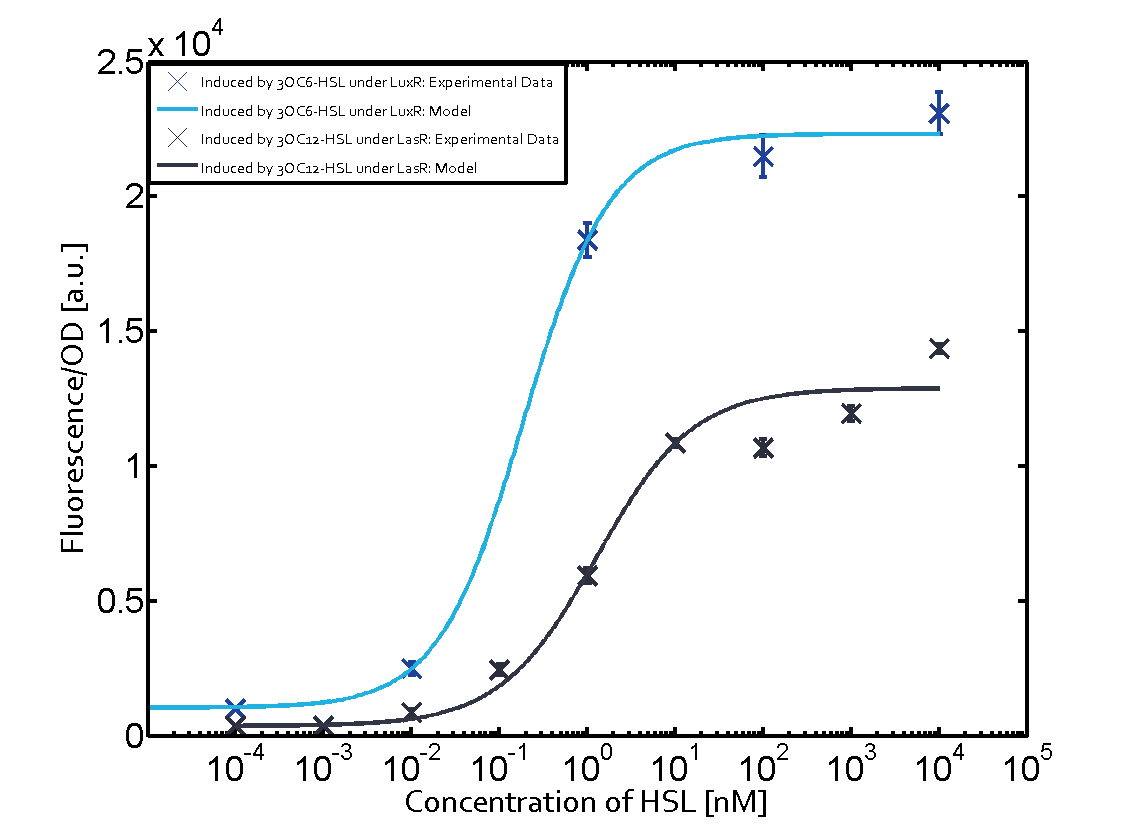
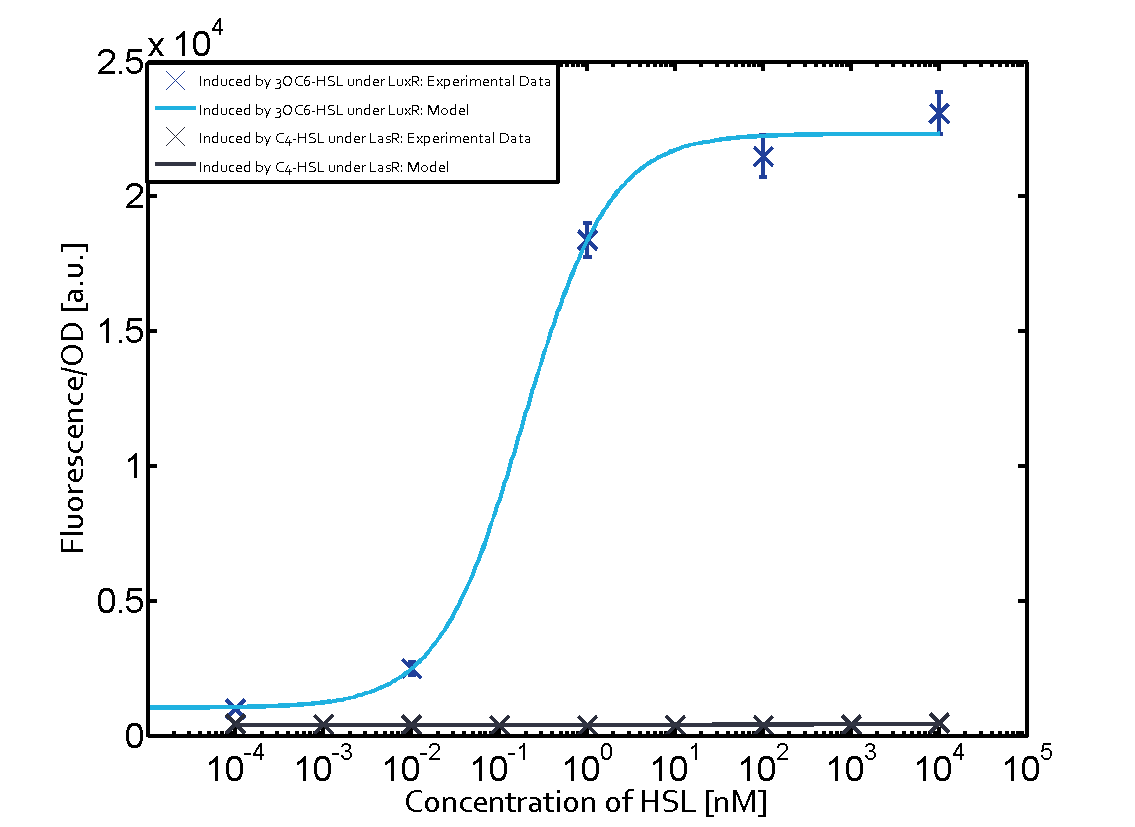
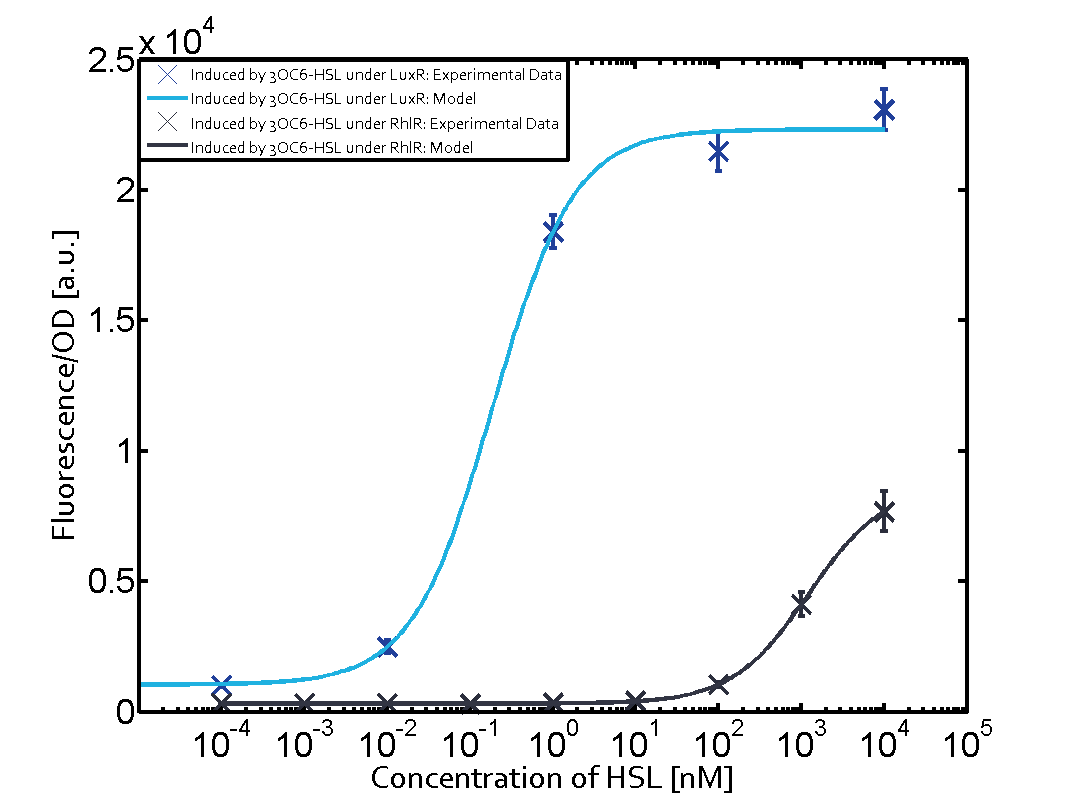
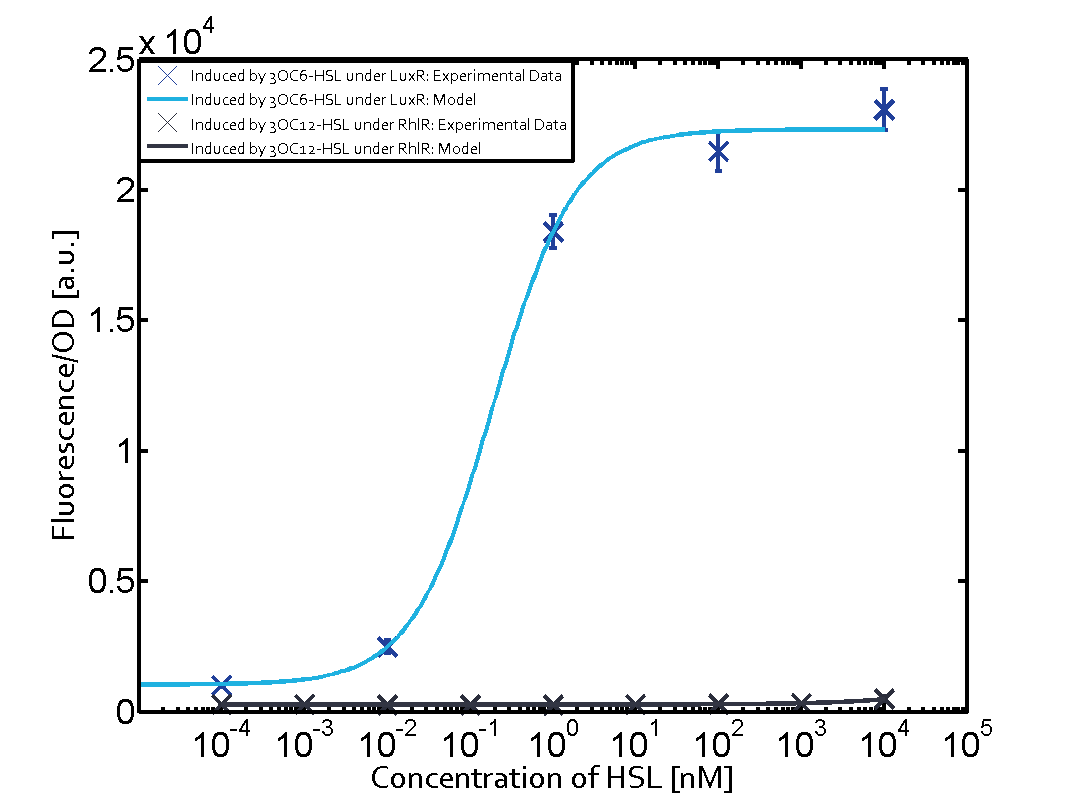
The following matrices serve as on overview summarizing the results of our experiments to characterize cross-talk on different levels. On the horizontal top row we see the three different inducer molecules (3OC12-HSL, 3OC6-HSL, C4-HSL). On the vertical axis we see the three regulators (LuxR, LasR, RhlR). These matrices aim at giving an overview of the experimental results conducted in relation with quorum-sensing and cross-talk. The graph shown in each matrix on the very top left describes the situation where the correct autoinducer molecule has bound the corresponding regulator and this complex has then induced the correct promoter. The solid lines in the graphs show the model data whereas the data points indicated with standard deviation show experimental data.
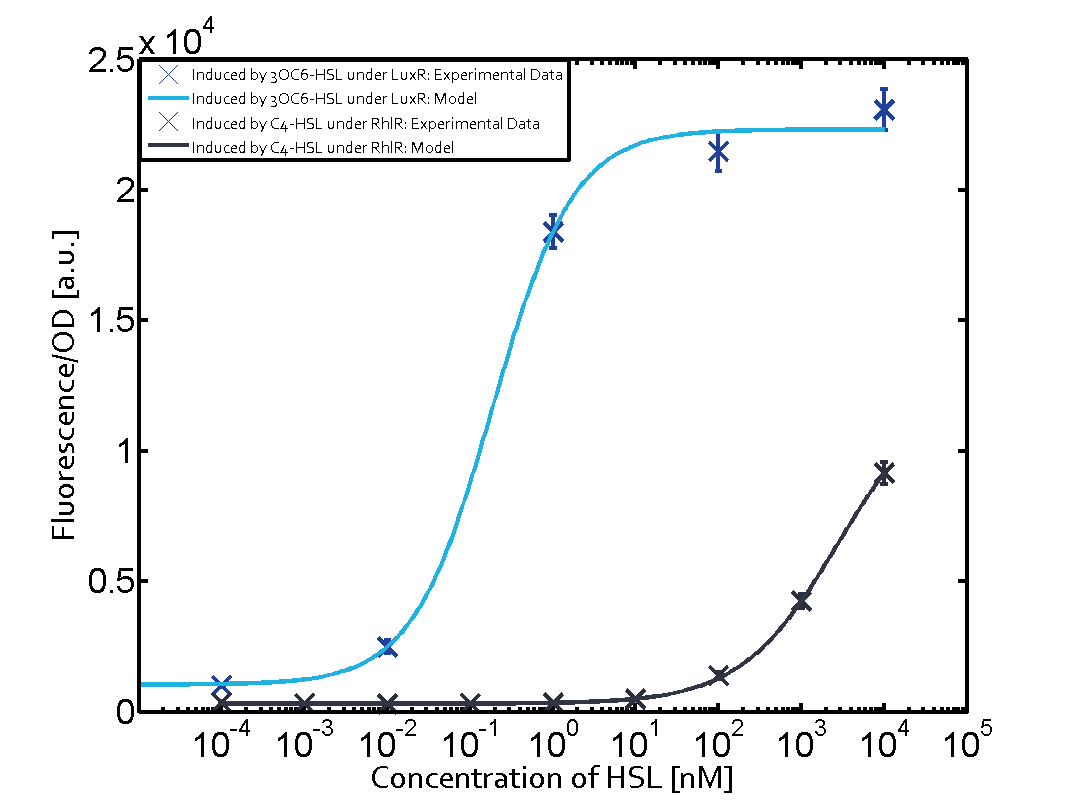
In all the measurements made for this matrix the promoter pLux was the basis. In this case the promoter was induced in six different variations shown.
The dark blue points in the graph top left show the activation of gene expression when pLux is induced by 3OC6-HSL (Lux-AHL) binding to the corresponding LuxR regulator. The observed transition occurs at a concentration of approximately 1nM 3OC6-HSL. The light-blue curve plotted shows the latter but not experimental but the model.
This curve from the model and the dark blue data point gained in experiments were plotted as a reference in all the other graphs describing pLux.
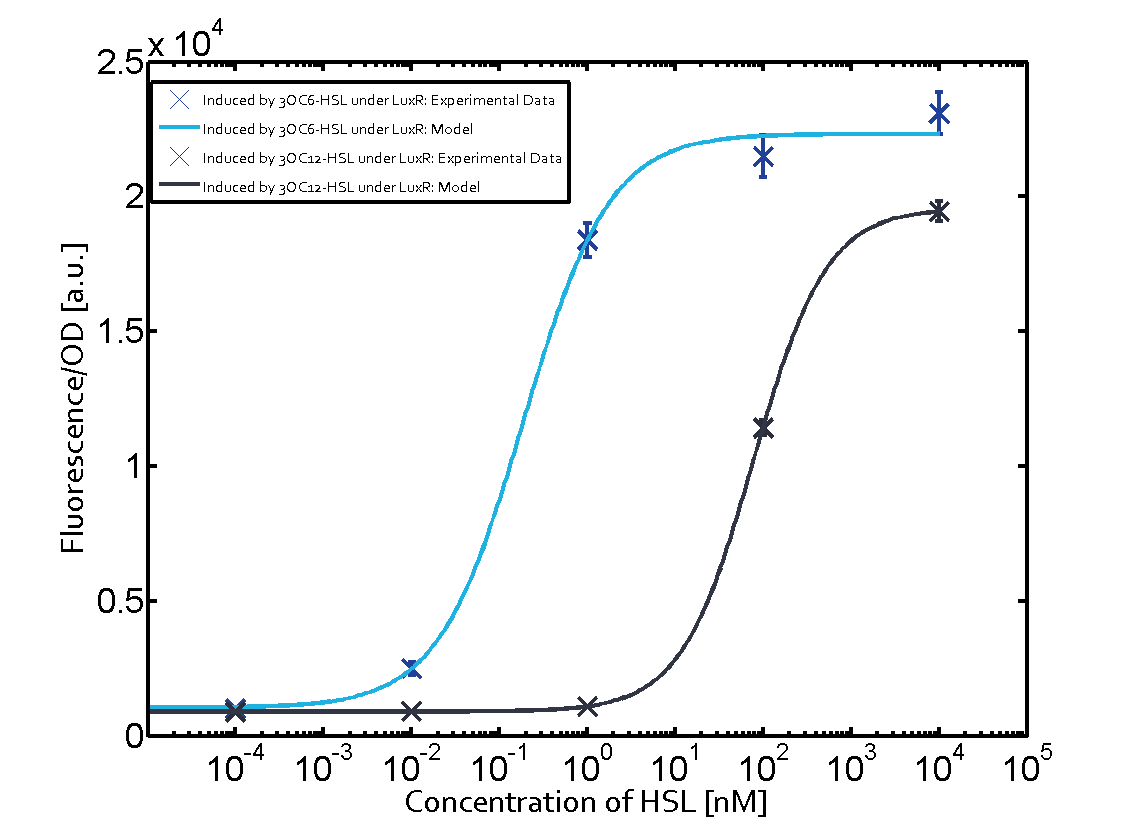
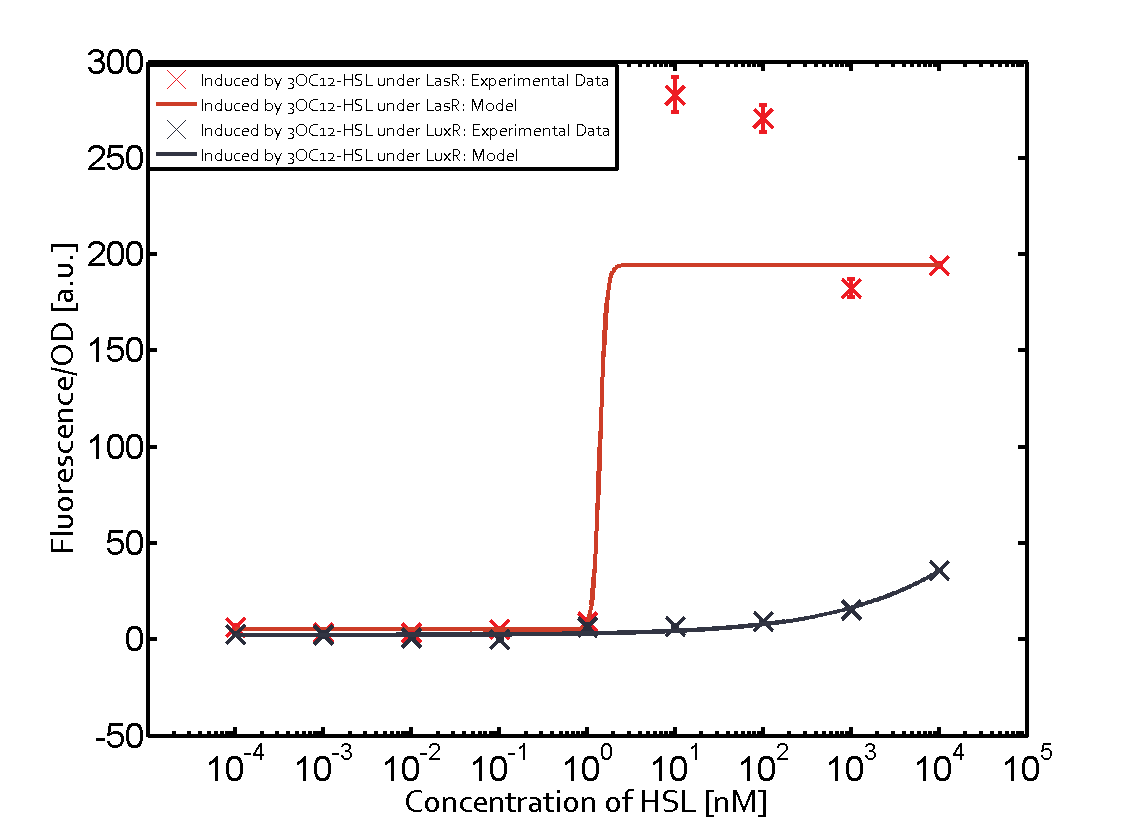
Cross-talk can be observed for the cases where the 3OC12-HSL (Las-AHL) binds the LuxR regulator or when 3OC12-HSL bind to its corresponding regulator LasR and then binding to the pLux as seen in top middle and center. For the case of Las-AHL binding the LasR and then pLux the transition occurs at 1nM and reaches 0.5 fold the fluorescence as pLux induced by 3OC6-HSL binding LuxR. In the case of 3OC12-HSL binding LuxR and inducing the promoter pLux, the transition is observed at approximately 100nM and severe cross-talk is observed. The promoter pLux was not tested in combination with the RhlR regulator and the C4-HSL.
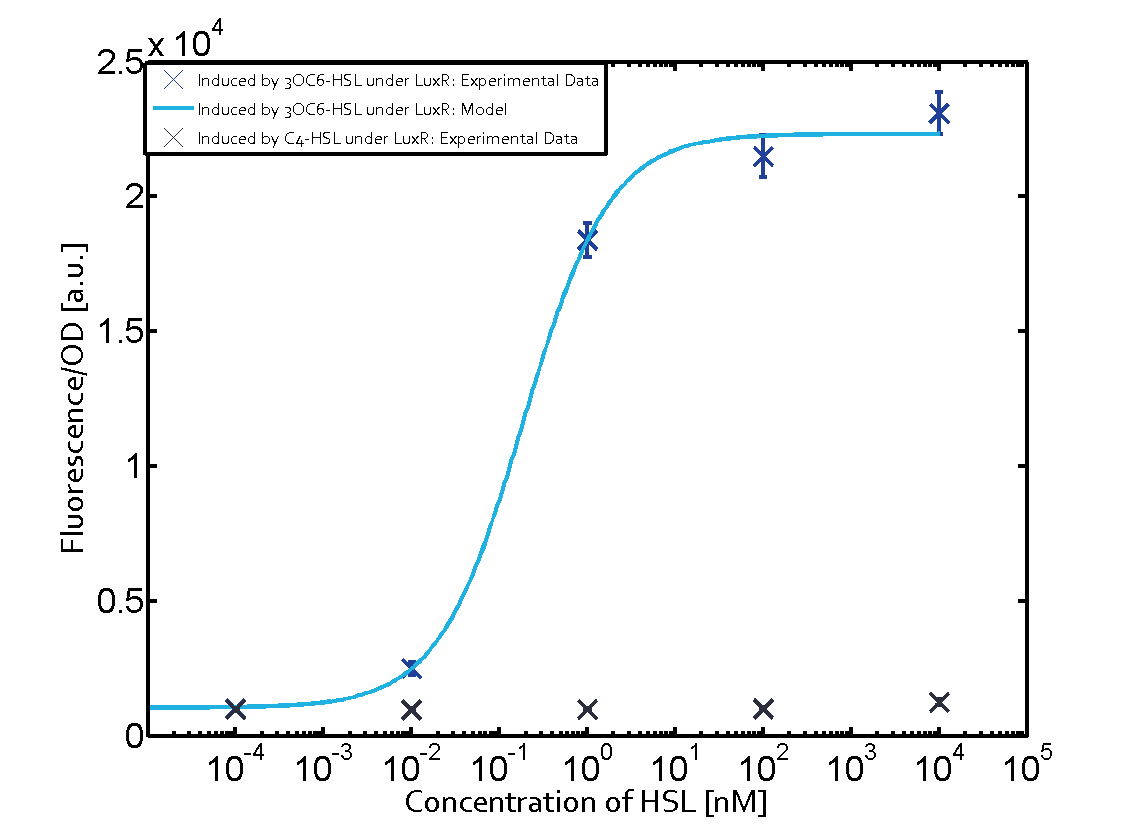
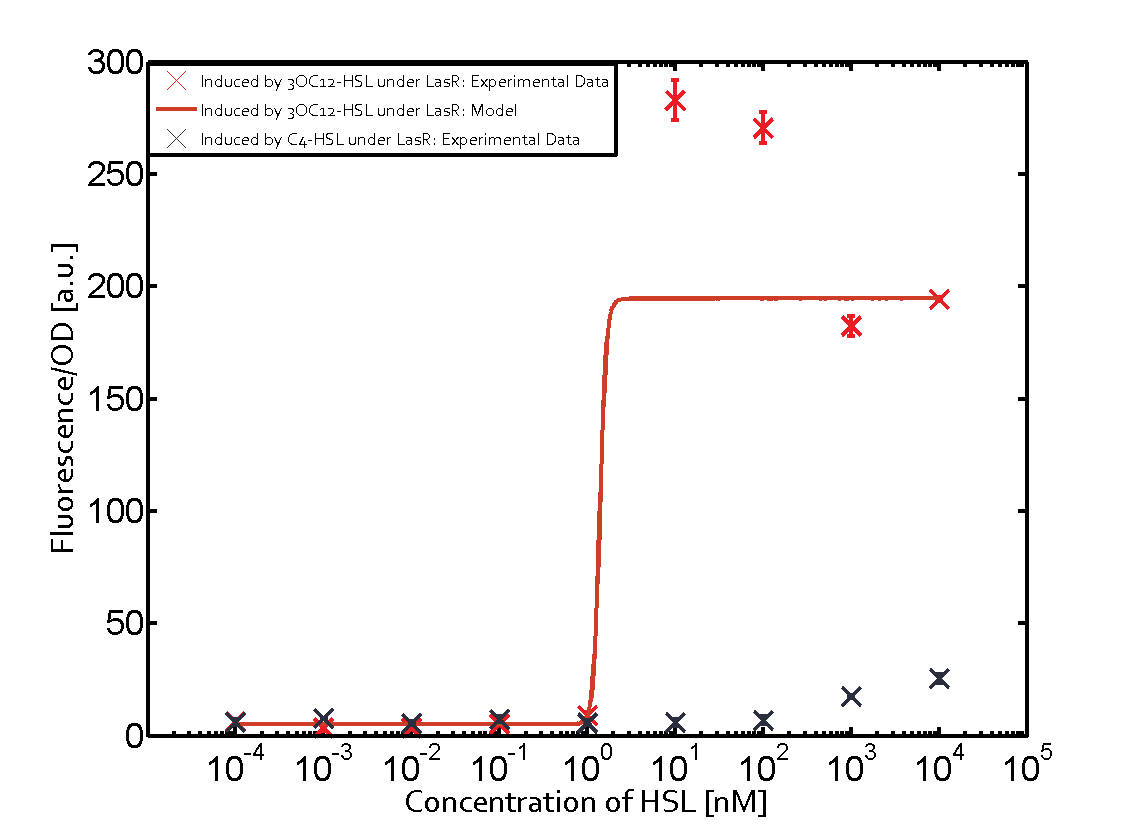
Observation of C4-HSL has shown that there is no significant cross-talk with the LuxR and LasR regulators binding C4-HSL and subsequently the pLux as indicated on top right and middle right graphs.
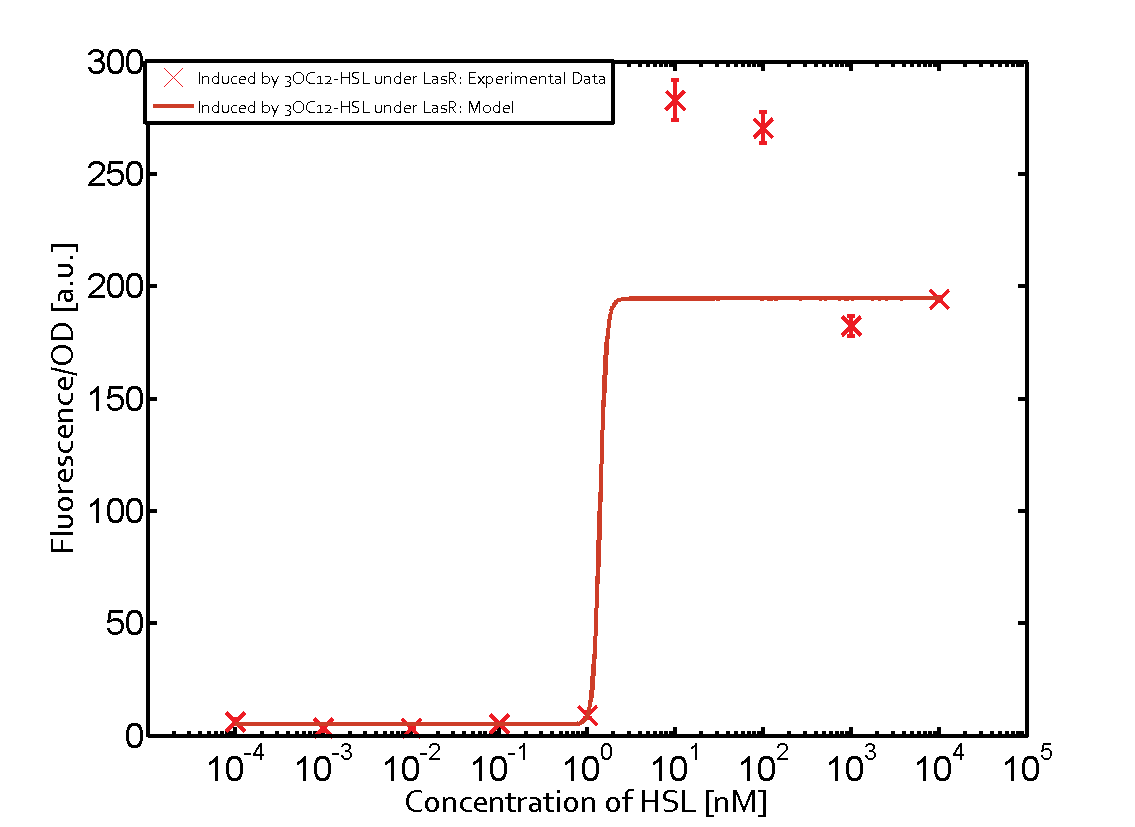
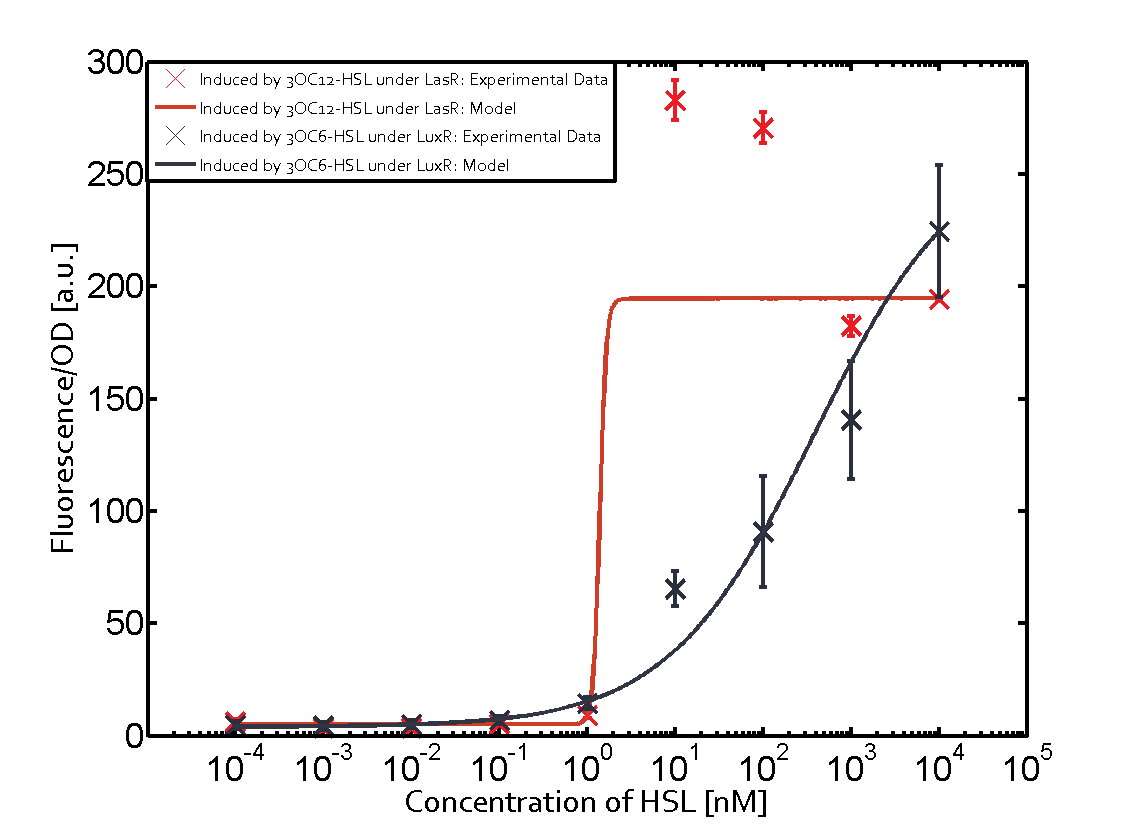
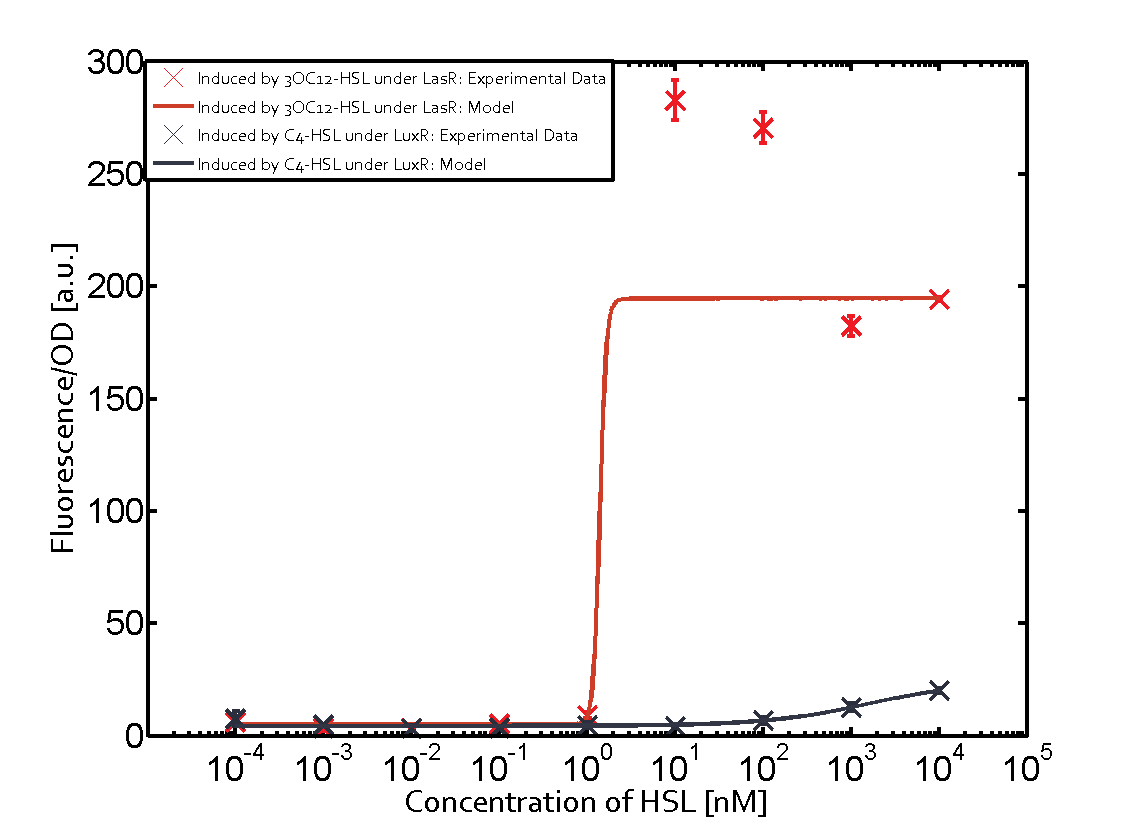
The promoter of interest of the experiments summarized in this matrix is pLas.
The graph on top left corner shows the induction of pLux by 3OC12-HSL binding the corresponding LasR. The red line shows the model whereas the cross shown in red represent the experimental data. The transition can be observed at a concentration of Las-AHL of about 5nM.
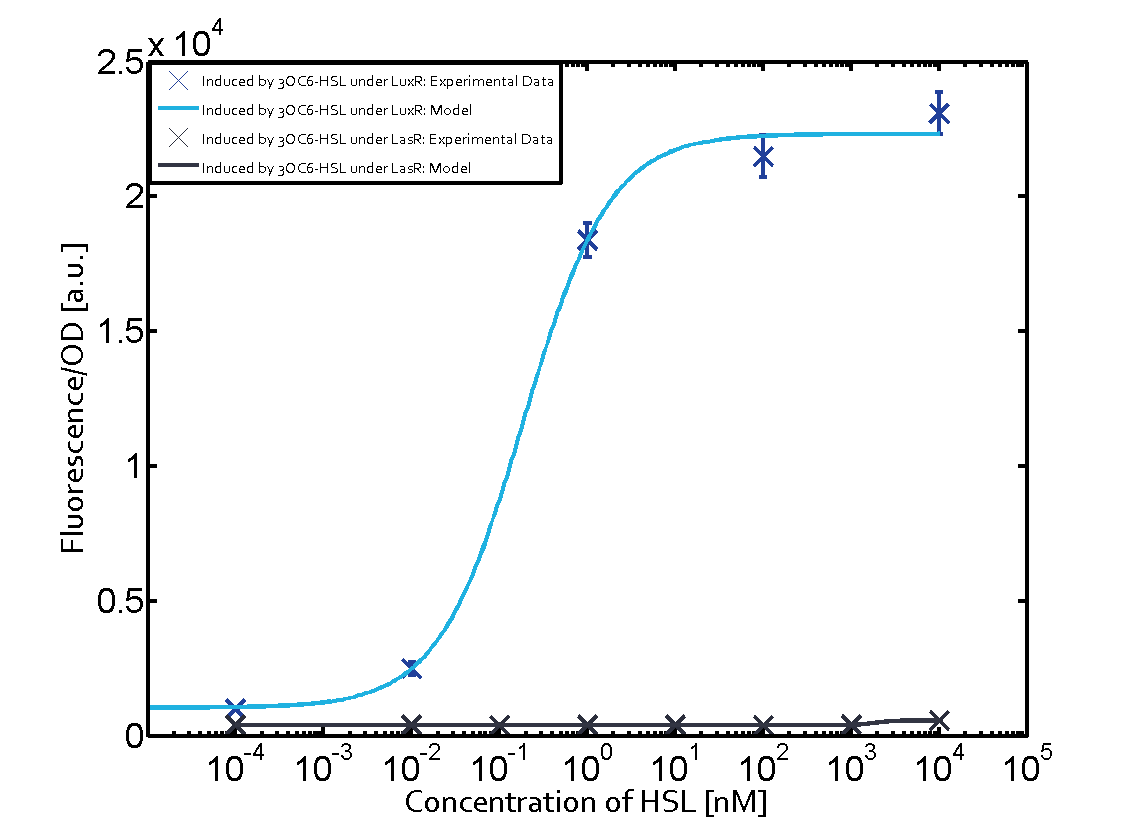
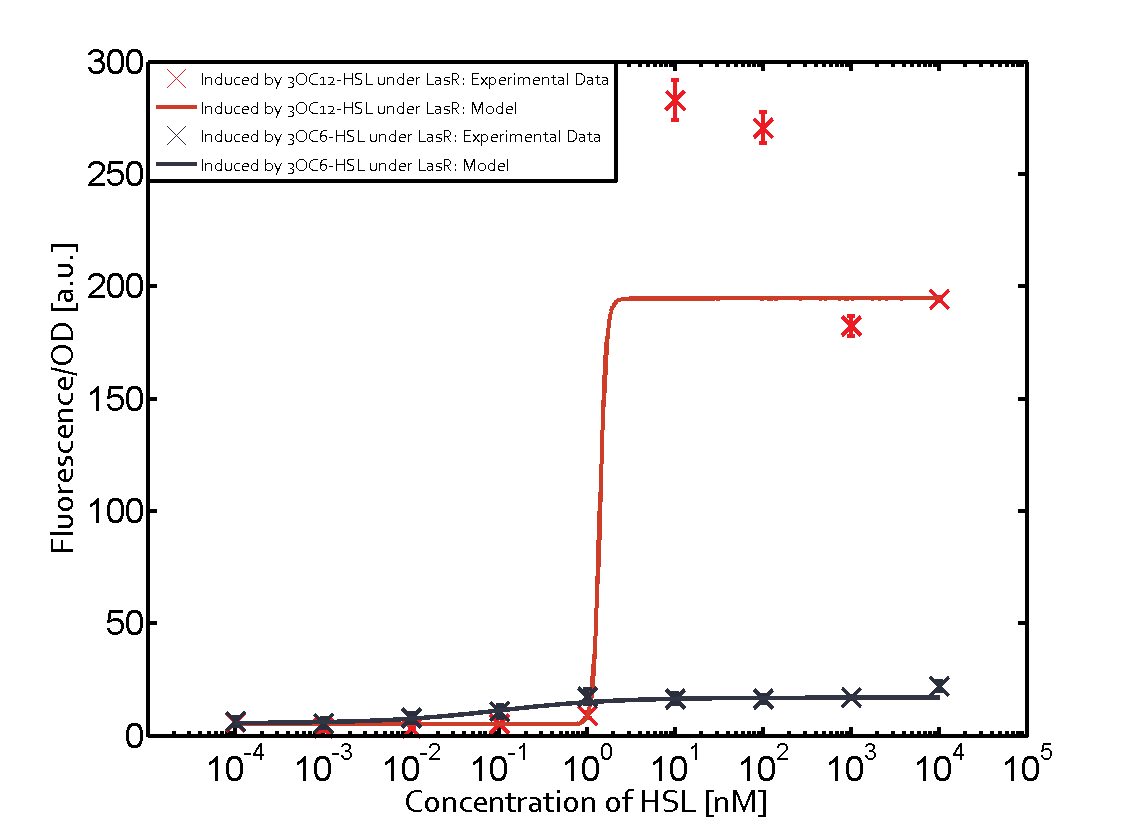
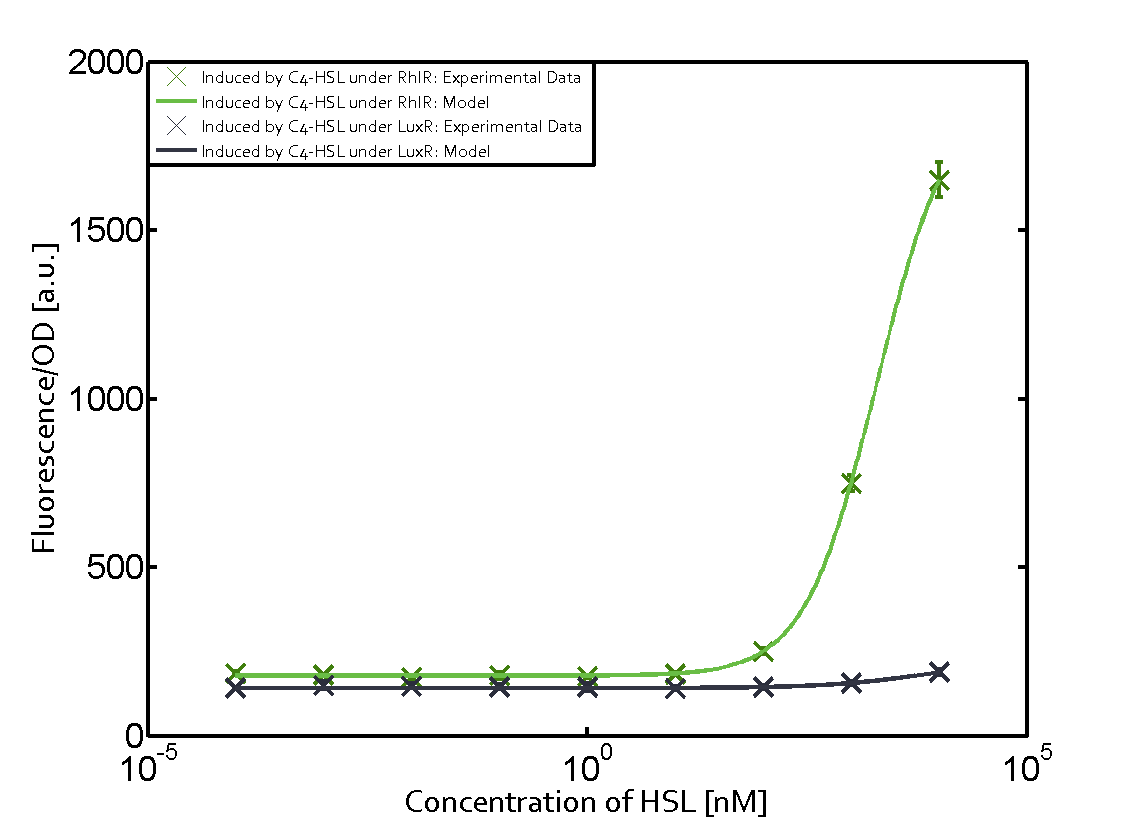
For C4-HSL binding the three regulators LasR, LuxR and RhlR and then the pLas no crosstalk can be observed. Also 3OC6-HSL binding RhlR does not induce the pLas. For the binding of 3OC12-HSL to RhlR a negligible increase of fluorescence can be observed. The same can be observed for 3OC12-HSL binding to the LuxR as this combination is to a small degree inducing pLas.
The interesting case of crosstalk when observing pLas is shown in the graph in the center of the matrix. It is clearly shown that 3OC6-HSL (Lux-AHL) binding to the corresponding LuxR regulator is able to induce pLas to fluorescence values of about 250. This is the phenomenon of severe crosstalk as the induction of pLas by the corresponding inducer and regulator molecule is nearly on the same level measured by fluorescence as induction by Lux-AHL binding the LuxR and subsequently pLas.
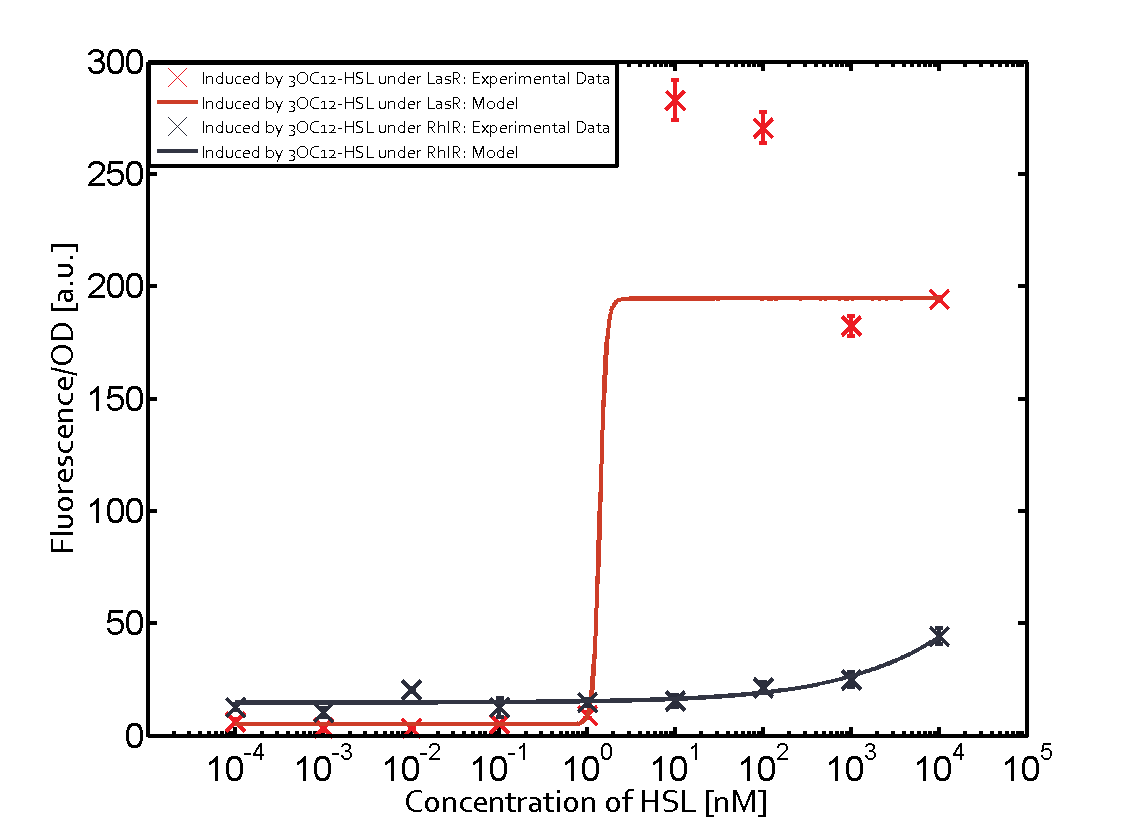
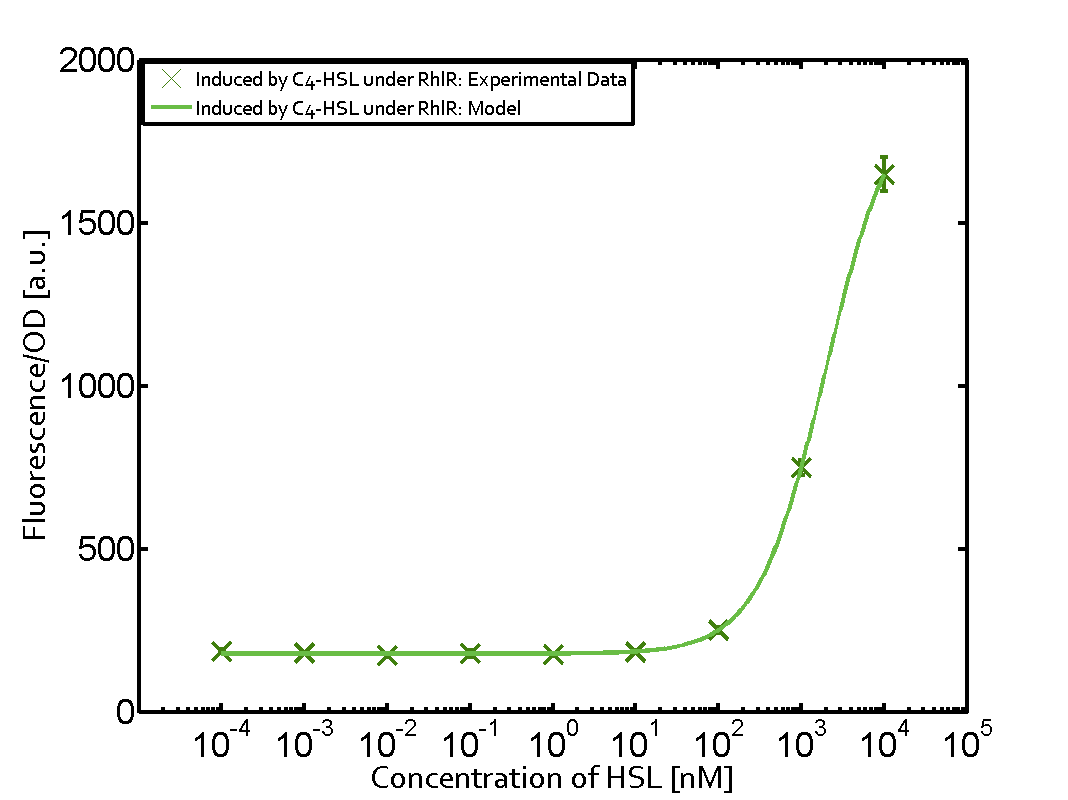
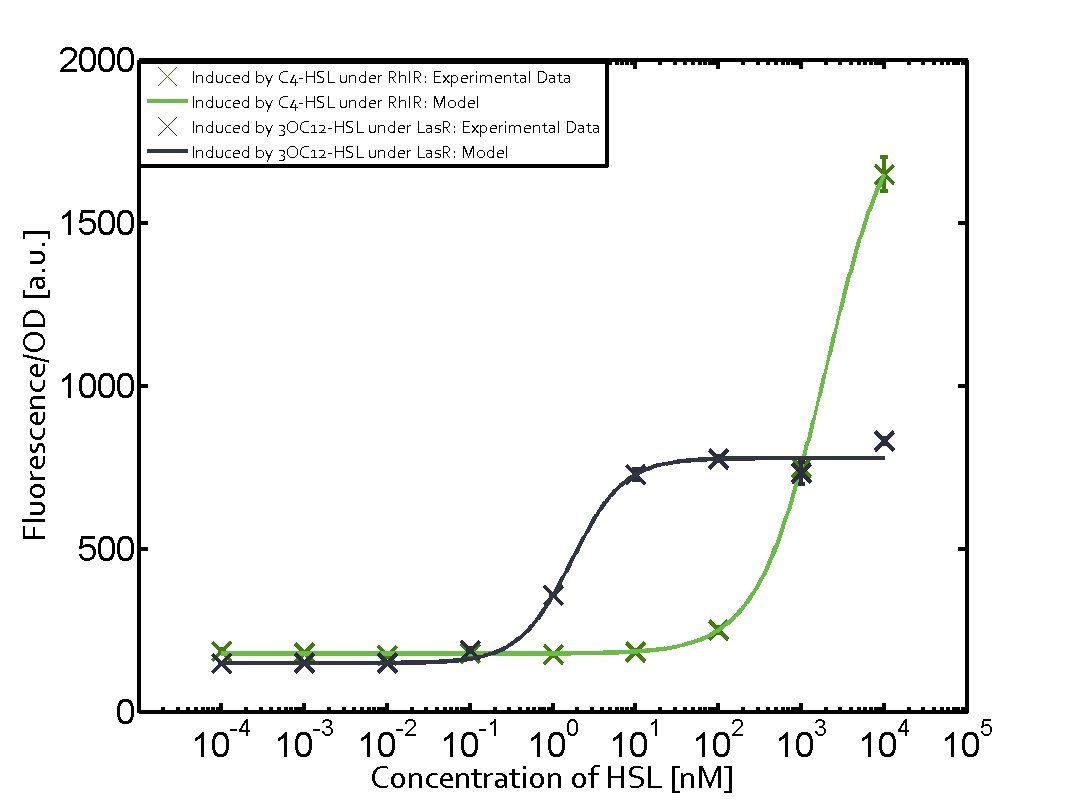
In this matrix the results of experiments with the promoter pRhl are summarized. The solid green line shows the modeling data whereas the cross represent experimental data.
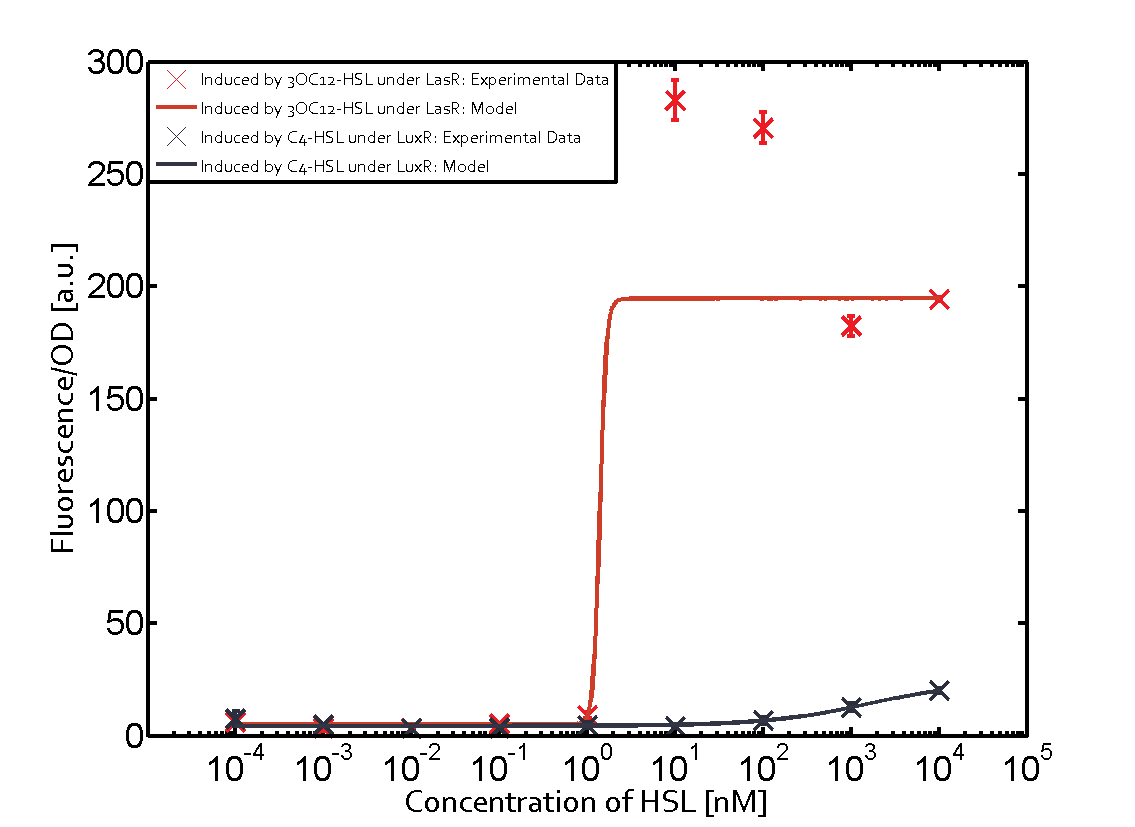
In the top left corner we see the pRhl induced by the corresponding C4-HSL bound to RhlR. Transition occurs at a concentration of 1 micromolar of CS4-HSL.
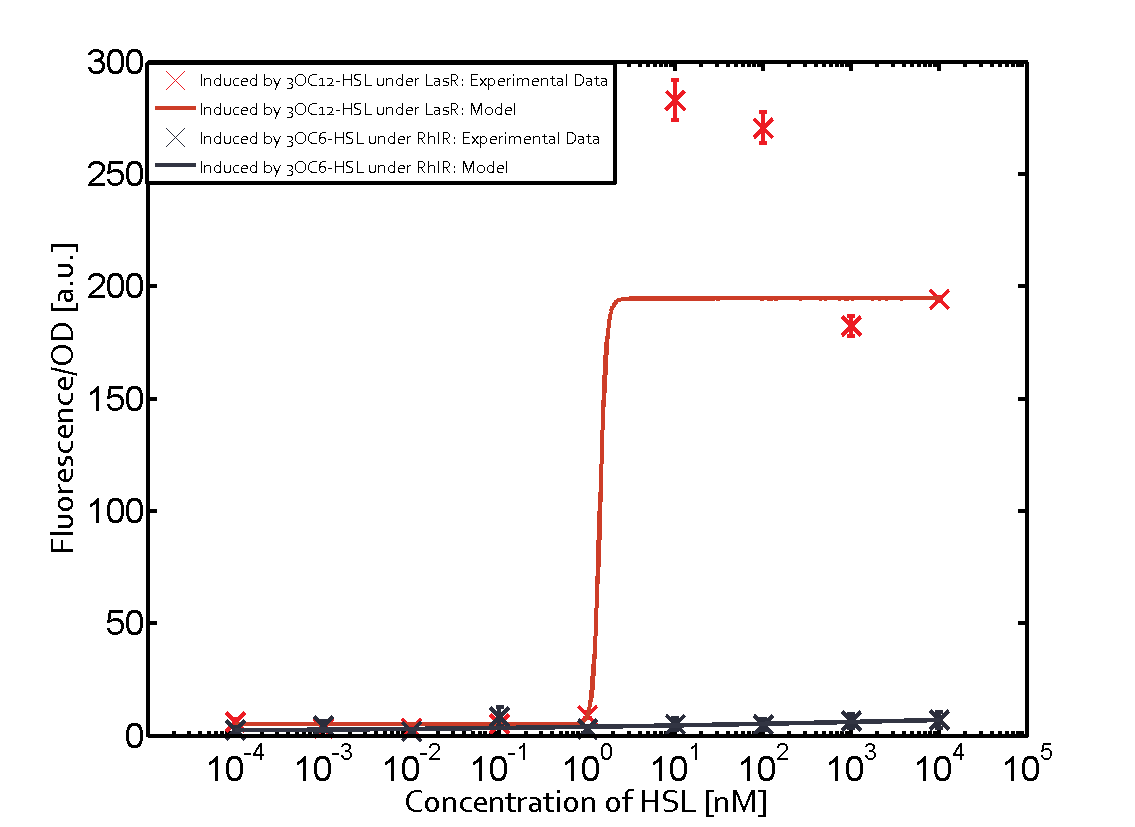
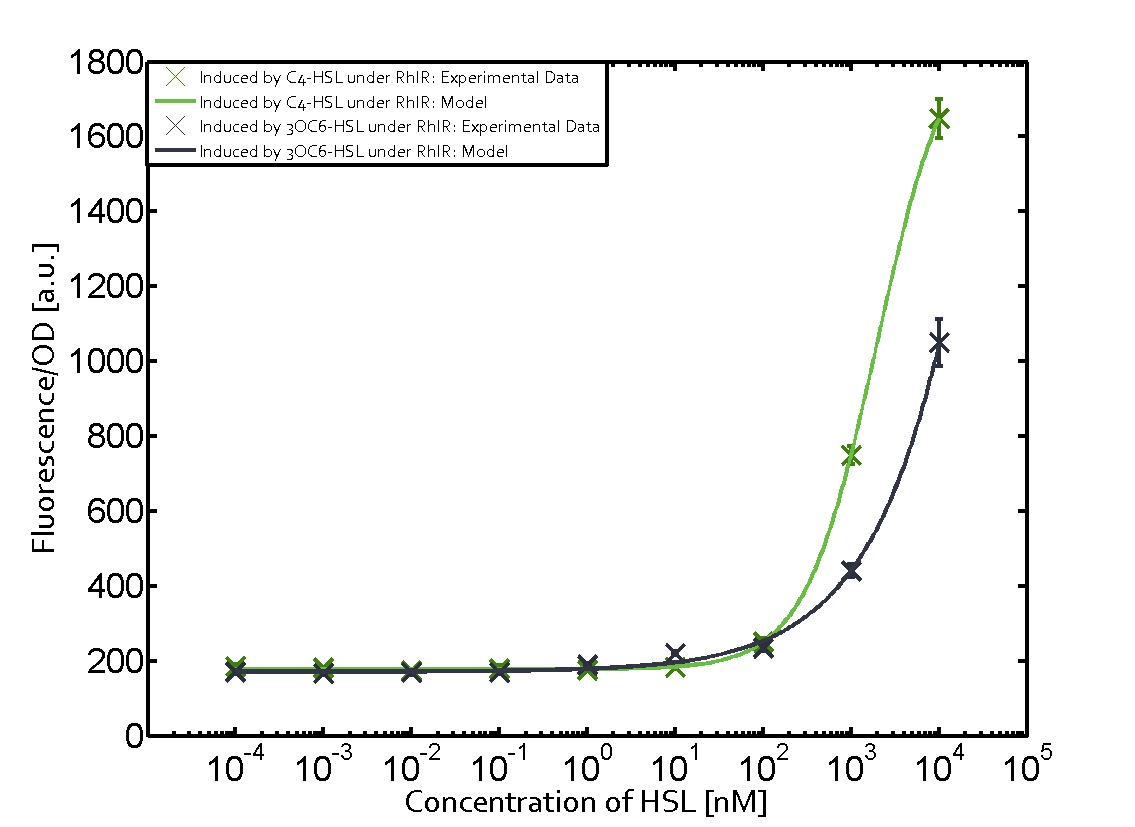
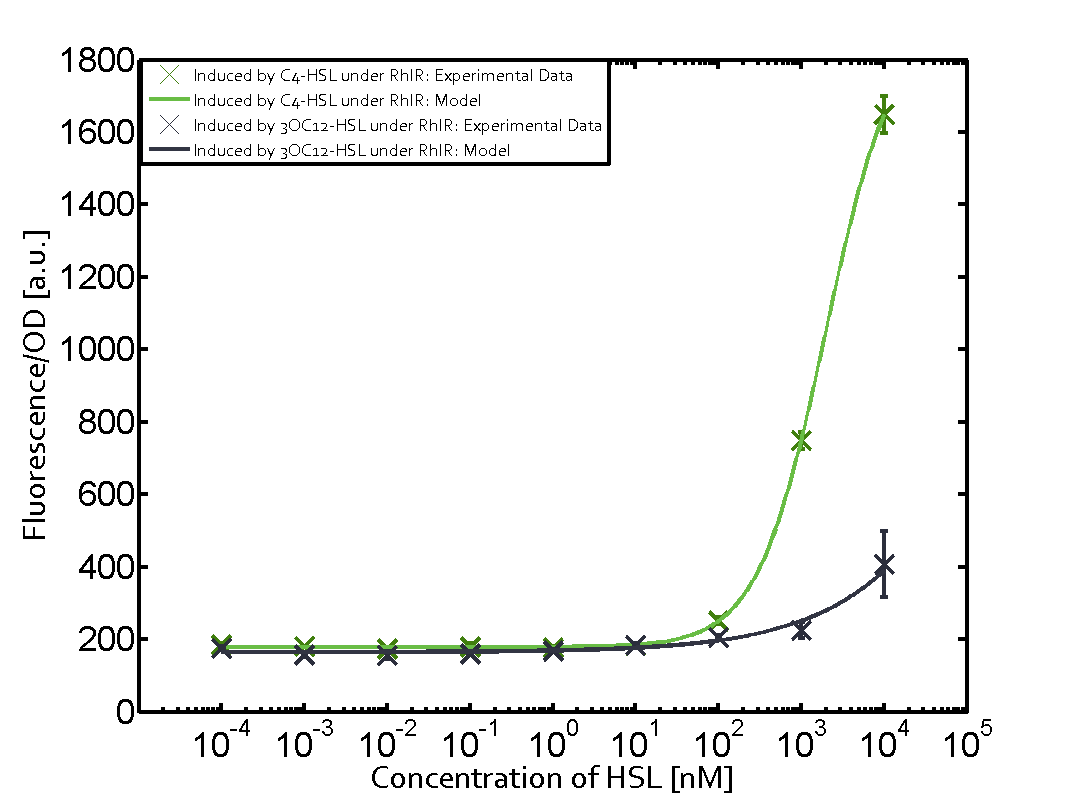
When observing pRhl we see cross-talk when inducing the promoter with 3OC6-HSL binding to RhlR for induction of pRhl. In this case the switching behaviour is observable at a concentration of 1 micro molar of 3OC6-HSL. The other observed cross-talk is the binding of 3OC12-HSL to LasR with subsequent induction of the promoter pRhl with a transition at 1nM of 3OC12-HSL.
Conclusion of cross-talk experiments
As shown in the graphs in the matrices above, we found and quantitatively characterized all three levels of cross-talk described previously. Unspecific inducer binding to the regulators as well as unspecific binding of the regulator to the promoter occurred in almost all possible combinations. To conclude, we were not able to find an orthogonal quorum-sensing pair due to inevitable cross-talk between the systems employing LuxI/LuxR, LasI/LasR, or RhlI/RhlR.
 "
"