Team:ETH Zurich/lab/biobrick/used1
From 2014.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
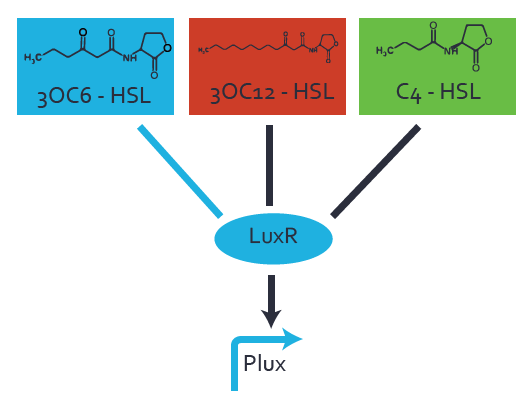
=== First Level crosstalk: LuxR binds to different HSL and activates the promoter === | === First Level crosstalk: LuxR binds to different HSL and activates the promoter === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ETH Zurich 1crosstalkPlux.png|400px|center]] | ||
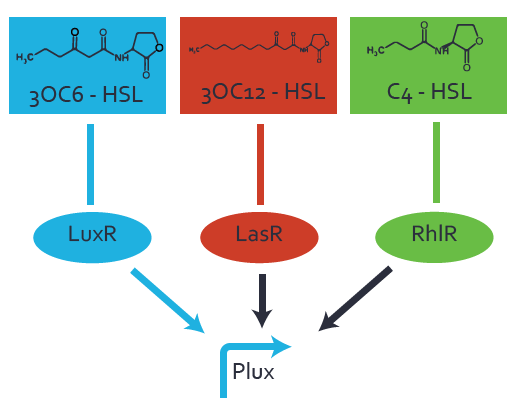
=== Second Level crosstalk: other regulatory proteins, like LasR, bind to their natural HSL substrate and activates the promoter === | === Second Level crosstalk: other regulatory proteins, like LasR, bind to their natural HSL substrate and activates the promoter === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ETH Zurich 2crosstalkPlux.png|400px|center]] | ||
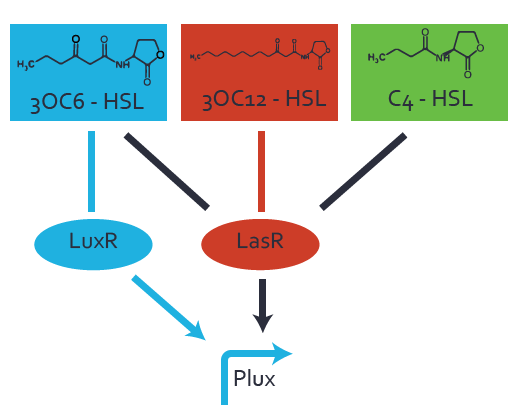
== Second order crosstalk: Combination of both cross-talk levels == | == Second order crosstalk: Combination of both cross-talk levels == | ||
Other regulatory proteins, like LasR, bind to different HSL and activates the promoter | Other regulatory proteins, like LasR, bind to different HSL and activates the promoter | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ETH Zurich 3crosstalkPlux.png|400px|center]] | ||
== Results == | == Results == | ||
Revision as of 12:10, 16 October 2014
|
<partinfo>BBa_R0062 AddReview 4</partinfo> ETH Zurich 2014 |
Characterization of the promoter's basal leakiness to LuxR in the absence of 3OC6-HSLBackground informationSystems consideredModeling leakinessResultsCharacterization of two-level crosstalk on the promoterBackground informationSystem consideredModeling crosstalkFirst-order crosstalkFirst Level crosstalk: LuxR binds to different HSL and activates the promoterSecond Level crosstalk: other regulatory proteins, like LasR, bind to their natural HSL substrate and activates the promoterSecond order crosstalk: Combination of both cross-talk levelsOther regulatory proteins, like LasR, bind to different HSL and activates the promoter ResultsCharacterization of the promoter's sensitivity to 3OC6-HSL depending on LuxR concentrationBackground informationSystems consideredModeling promoter's sensitivityResults |
 "
"