Team:Nagahama project
From 2014.igem.org
| ||||||||||||||
Contents |
Our Project
We make various systems by interaction of cell-cell communication. We keep one function in one E.coli. This means to make simple plasmid. The following is one example. We’d like to collect cadmium in water. Therefore we use two kinds of E.coli. One catches Cadmium. The other attracts all E.coli by using chemoattractant. Catches E.coli displays metallothionein a protein combines a heavy metal. Cadmium is a kind of heavy metal. The other synthesizes aspartic acid (Asp) one kind of chemoattractant. All E.coli gather in the E.coli synthesizes Asp. To use these E.coli, finally cadmium will be caught.
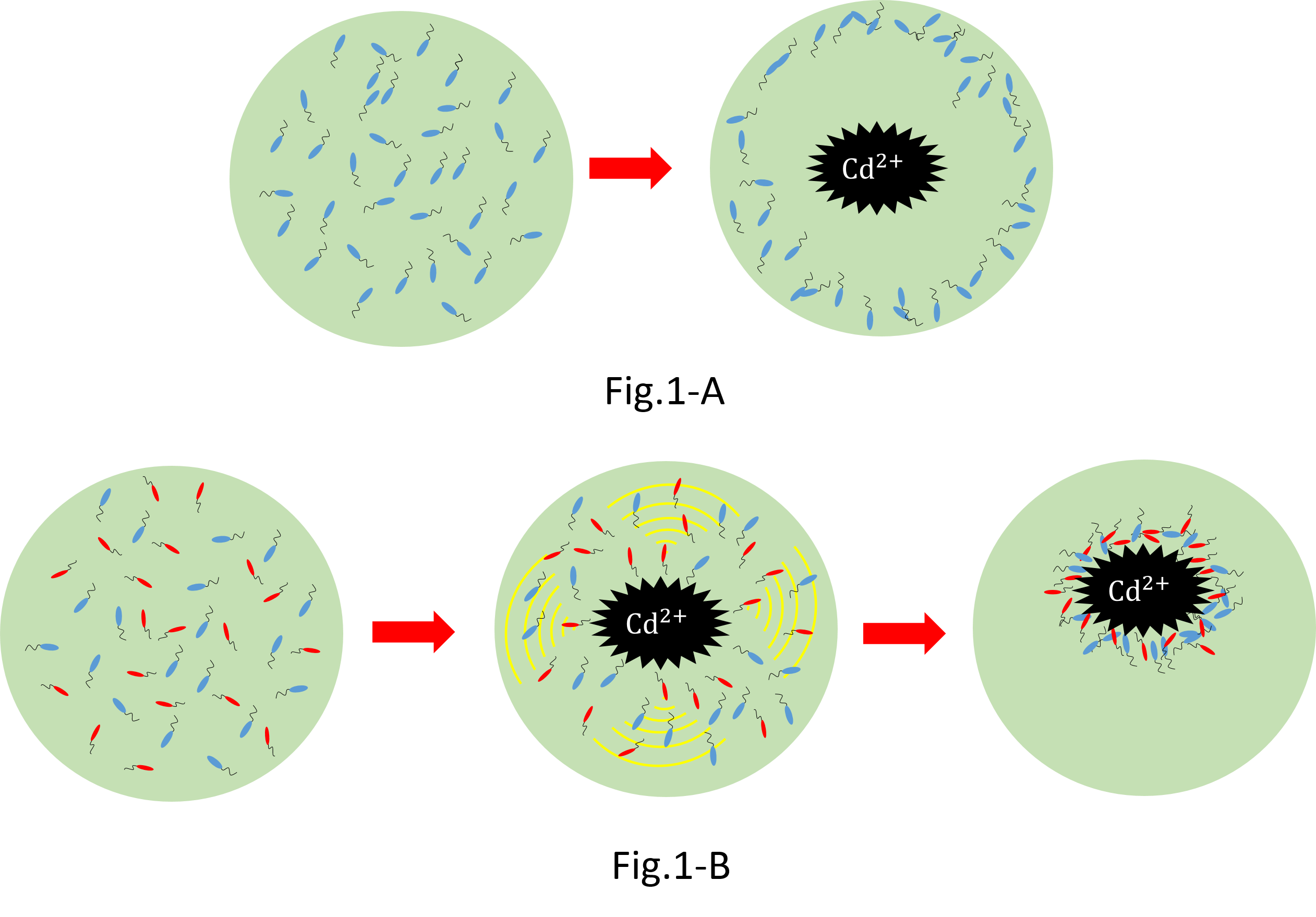
When collect cadmium in the water, if use only catching E.coli,they go away from cadmium. Because they have negative chemotaxisin contrast with cadmium. Consequently they</br>
Modeling
We consigned modeling of our project to
UT-Tokyo.They readily compiled with our requests. Their model is ideal.We really appreciate their jobs We wish a friendly relationship with UT-Tokyo.Thank you so much!! The detail of their jobs are lists below!!
Method
Bold text
Medium
Trypton Broth
Trypton 10g/L
NaCl 10g/L
H2O 1L
Wash medium
Potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), 10⁻²M
MgSO₄, 10⁻³M
potassium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA), 10⁻⁴M
Chemotaxis medium
Synthesis medium
Sodium hydrogen fumarate 46g/L
Ammonium chloride 17.8g/L
Magnesium sulfate 7 hydrate 0.25g/L
H₂O 1L
Ph8.5with sodium hydrogen
LB medium
Tryptone 10g/L
Yeast extract 5g/L
NaCl 10g/L
(agar 15g/L)
H₂O 1L
2×YT medium
Tripton 16g/L
Yeast extract 10g/L
NaCl 5g/L
(agar 15g/L)
H₂O 1L
M9 swarming Agar
20 % (v/v) 5×M9 salt
1.25 % (v/v) glycerol
0.3 % (v/v) agar
0.1 % (v/v) 0.136M CaCl2 solution (after autoclave)
0.1 % (v/v) 1M MgSo4 solution (after autoclave)
0.03 % (w/v) 1mM thiamine (after autoclave)
stir until dissolved
5×M9 stock solution
6.4 % (w/v) Na2HPO4
1.5 % (w/v) KH2PO4
0.25 % (w/v) NaCl
0.5 % (w/v) NH4Cl
Aspartate synthesis
E.coli K12 transformed with CdP-R.B.S-AspA-d.Ter (BBa_K1342001) previous cultured with cadmium in LB medium (250μM) in 37℃ for 12hr at 120rpm. Adjust Cell mass (OD1.0) and therefor centrifuged 4000rpm for 20 min. Cell pellets ware activated in synthesis medium in 37℃ for 2hr at 120rpm/min.
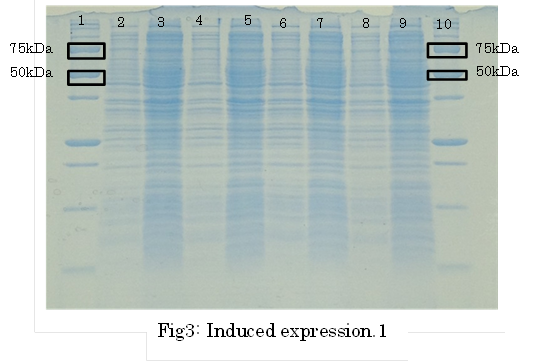
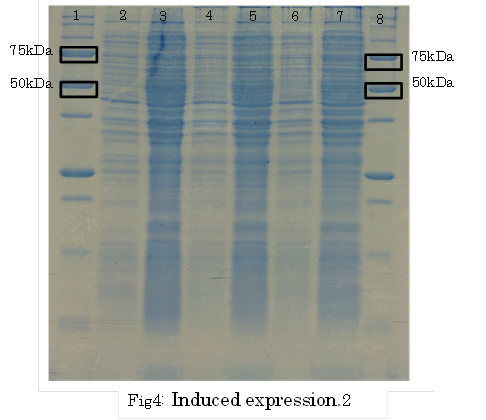
SDS PAGE
・Preculture E.coli holding a plasmid containing a target gene or nomal E.coli.
・Measure OD600 0.6-1.0
・the expression of fusion protein by isopropylthio-β-D-galactoside (IPTG) and Cd2+ soln.
・Transfer a sample a 200 µl in a microcentrifuge tube
・Centrifuge at 13,000rpm for a minute at 4℃
・Discard supernatant quantitative
・Store pellet at -20 °C
・Thaw pellet and resupend in Sample Buffer (100 µL 1xSample Buffer per samples)
・Heat for 5 minutes at 98 °C
・Centrifuge at 13,000rpm for 10 minutes at 4℃
・Transfer supernatant to a new microcentrifuge tube
・Analyze samples by SDS-PAGE.(Use 20 µL per samples)
TLC assay
We analyzed L-aspartate by thin-layer chromatography (TLC). The equal volume of the supernatant of synthesis medium was added with 7 mg/mL 5-Dimethylamino naphthalene-1-sulfonyl Chloride (dissolved in acetone) and was incubated for more than 30 min at room temperature. Two microliters of the reactant was spotted on a TLC silica plate, and was developed in a mixture of ethyl acetate, pyridine, water, and acetic acid(162:21:11:6 v/v).
Chemotaxis Assay
Introduction
Chemotaxis by E.coli was assay by some methods. We assay the chemotaxis of E.coli against aspartate using two methods. One was swarming assay. We have used sawaming plate. swarming plate is medium that contained a low concentration by agar. E.coli can swim to aspartate on the swarming plate. The other was capillary assay. We have used capillary that including aspartate. We set capillary in chemotaxis medium including motile E.coli We have determined the number of E.coli attracted to capillary by colony formation on LB plate.
Swarmming Assay
E. coli JM109 cultured at 30℃ with 50 rpm was need.
1. A inoculate of the culture was spotted on the center of agar plate.
2. 10mM L-Aspartate (40μl) or 100mM Cd solution (4μl) was spotted on 25mm distant from the center of 0.3 % agar plate.
3. The plate was standed 5 min at RT.
4. The plate was incubated at 30℃.
Capillary Assay
Object
To assay chemotaxis by E.coli against aspartarte using capillary.
Plotocol
1. Preculture E.coli with tripton broth at 30℃ 12 hr 50 rpm
2. Check motility under the microscope(×800).
3. Diluting the E.coli culture 100 times. (tripton broth:E.coli culture=20mL : 200μL)
4. Incubate 50rpm 30℃ until log phase (OD600 = ~ 0.2)
5. 500㎕ into micro tubes.
6. Centrifuge (25℃ 10min in 3400G)
7. Dicand the supernatant.
8. Add wash medium(50μL)
9. Resuspending pellets gently.
10. Do 5~9 step repeat.
11. Add chemotaxis medium(500μL)
12. Resuspending pellets gently.
13. Check motility under the microscope(×800).
14. E.coli chemotaxis medium into chamber apparatus.(100μL)
15. Prepare the positive and negative control capillary.(1μL of 10mM aspartate chemotaxis medium and chemotaxis medium into capillary)
16. Two capillary into chamber preparation.
17. 90mim 30℃ incubation.
18. Dilute the chemotaxis buffer in capillary`s liquid 100 times.
19. Prating to LBplate.
20. 37℃ 12h incubation.
21. Counting the colony.
Result & Discussion
TLC Assay

SDS PAGE
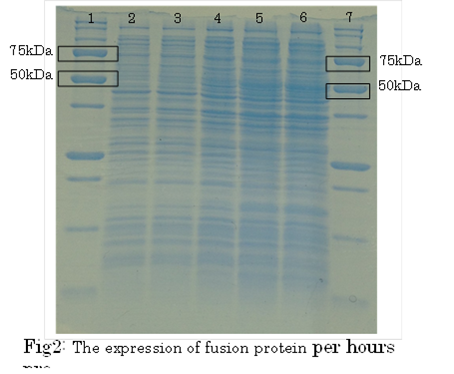 1. marker 2. 0hr 3. 0.5hr 4. 2hr 5. 6hr 6. 24hr 7. Marker
marker:Precision Plus Protein Standards (BIO-RAD)
1. marker 2. 0hr 3. 0.5hr 4. 2hr 5. 6hr 6. 24hr 7. Marker
marker:Precision Plus Protein Standards (BIO-RAD)
OD600=0.74
CdCl2 100μM/IPTG 1mM
Swarming Assay
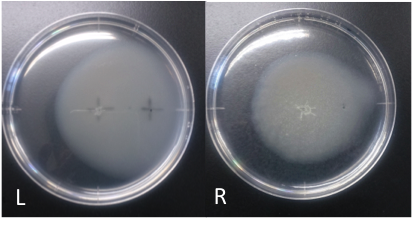
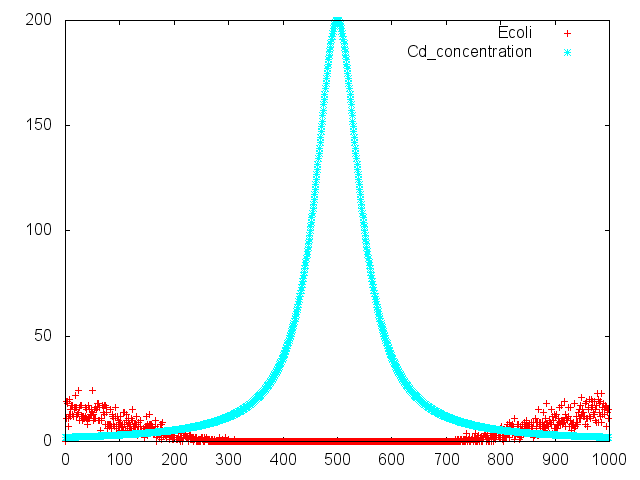
Culture time: 108 hours 30 minutes (4days and 12 hours 30 minutes) Circle is larger the Aspartate which I spotted Cdim into than the medium which I spotted ddH20 into. It is that Escherichia coli swims for Aspartate to understand from photographs of L and R. E. coli swim the side where I put aspartic acid in. I think that Escherichia coli may have positive chemotaxis for Aspartate than these two (Aspartate and ddH2O) control experiment.
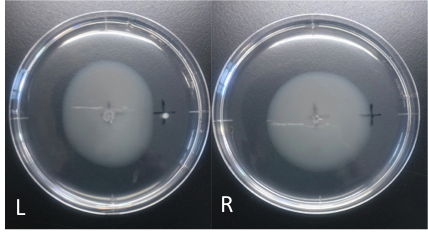
Culture time: 109 hours 50 minutes (4days and 13 hours 50 minutes) Circle is smaller the medium which I spotted Cdim into than the medium which I spotted ddH20 into. It is that Escherichia coli swims against Cdim to understand from photographs of L and R. I compare the Cd with the medium which I spotted ddH2O into in the medium which I put. In the side where I put Cd in, circle becomes dented. I think that Escherichia coli may have negative chemotaxis for Cd than these two (Cd and ddH2O) control experiment.
Capillary Assay
This assay didn`t check chemotaxis by E.coli. We did eleven assays. But all results weren`t authenticity.
 "
"