Team:Austin Texas/kit
From 2014.igem.org
(→Background) |
(→Background) |
||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
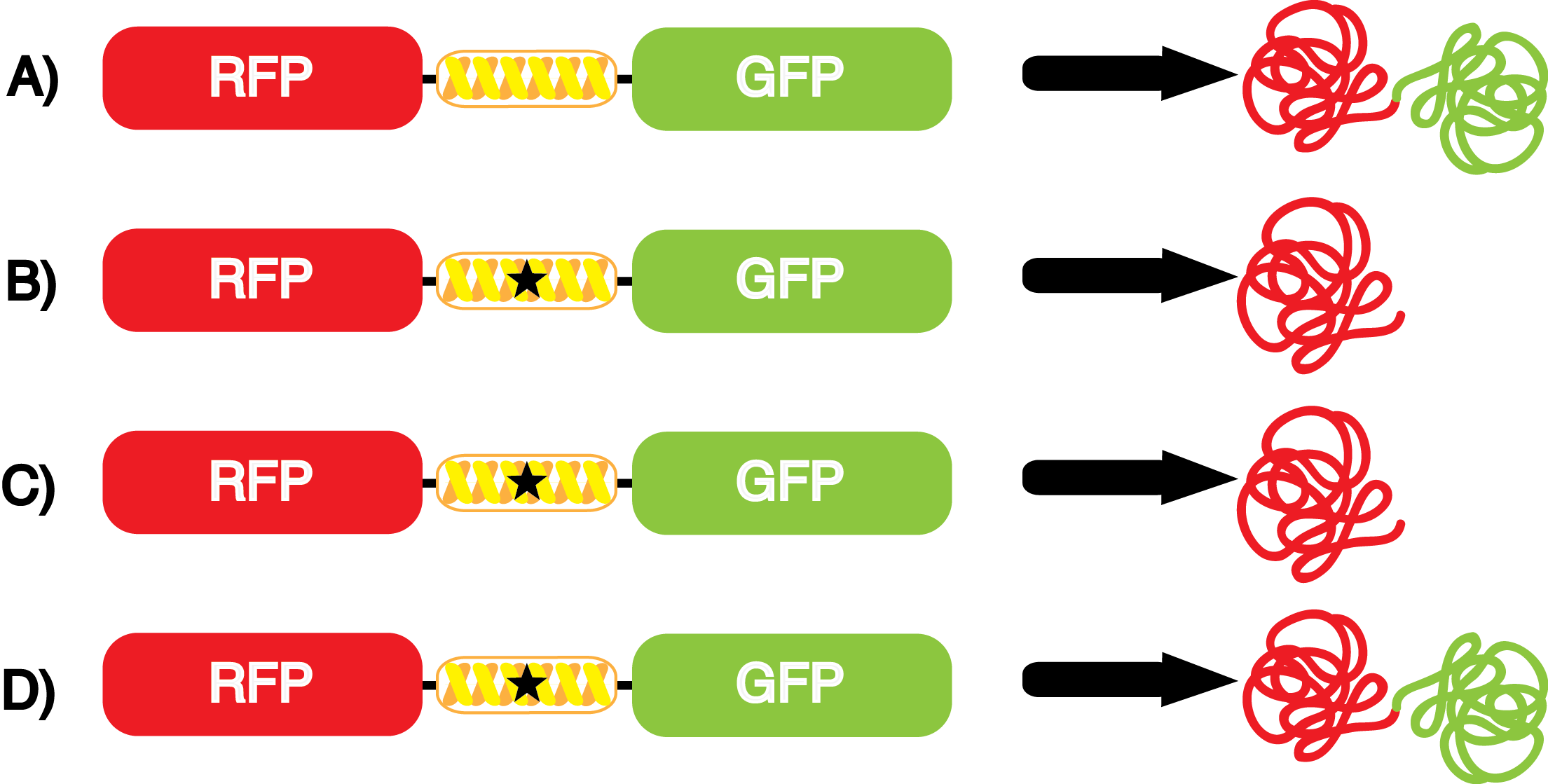
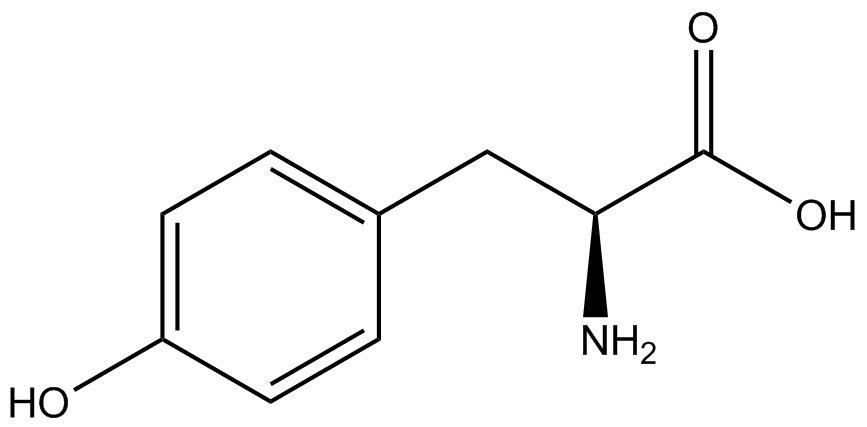
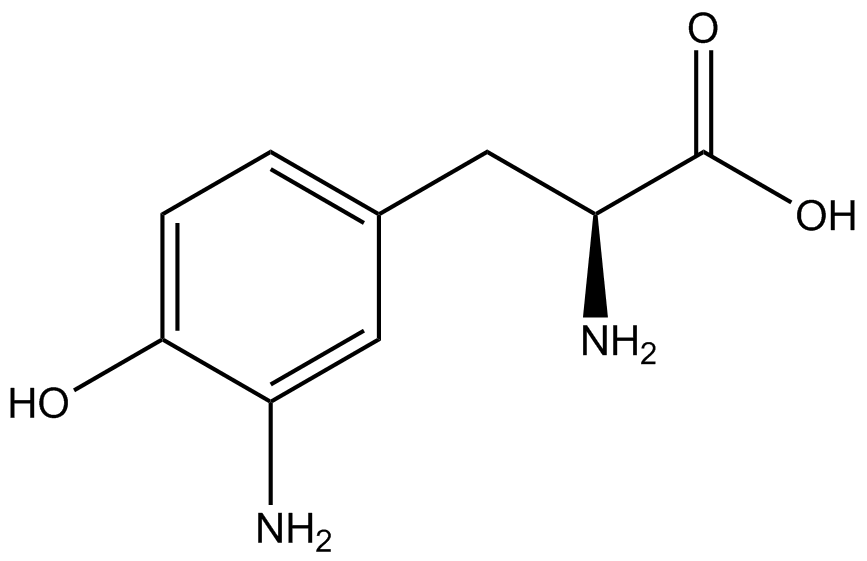
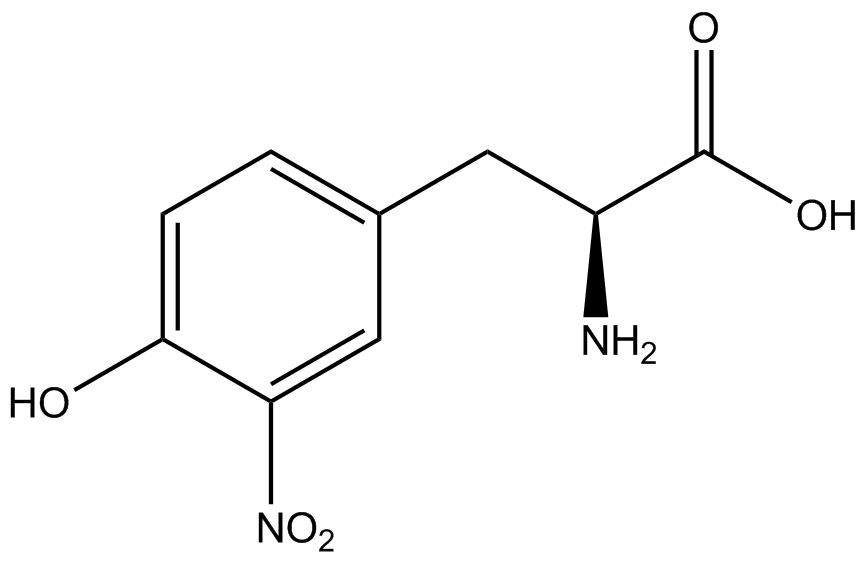
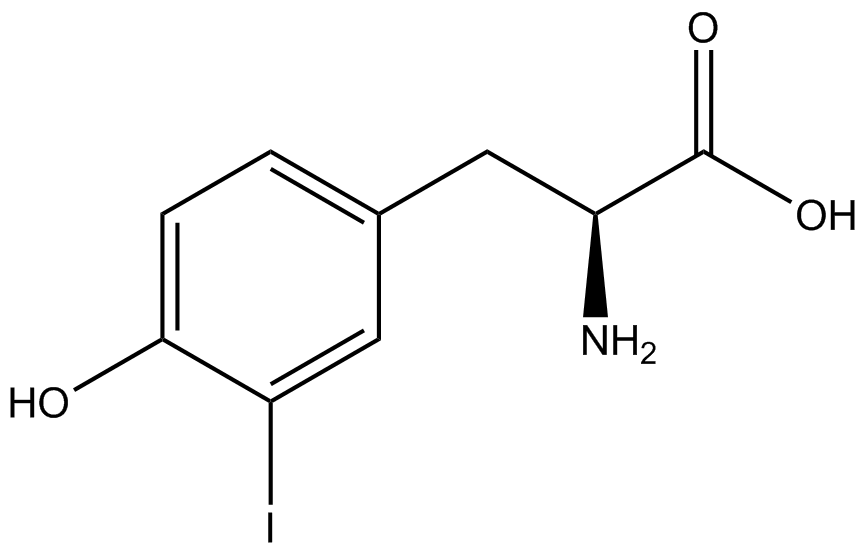
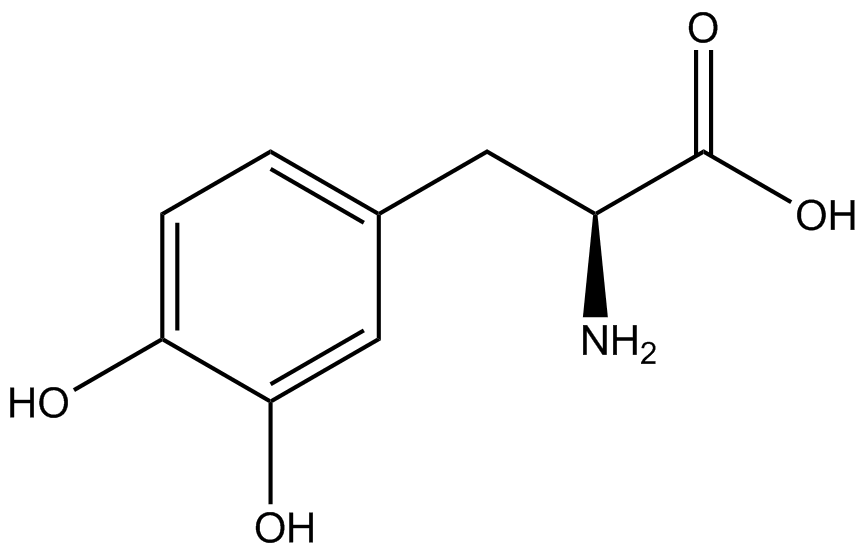
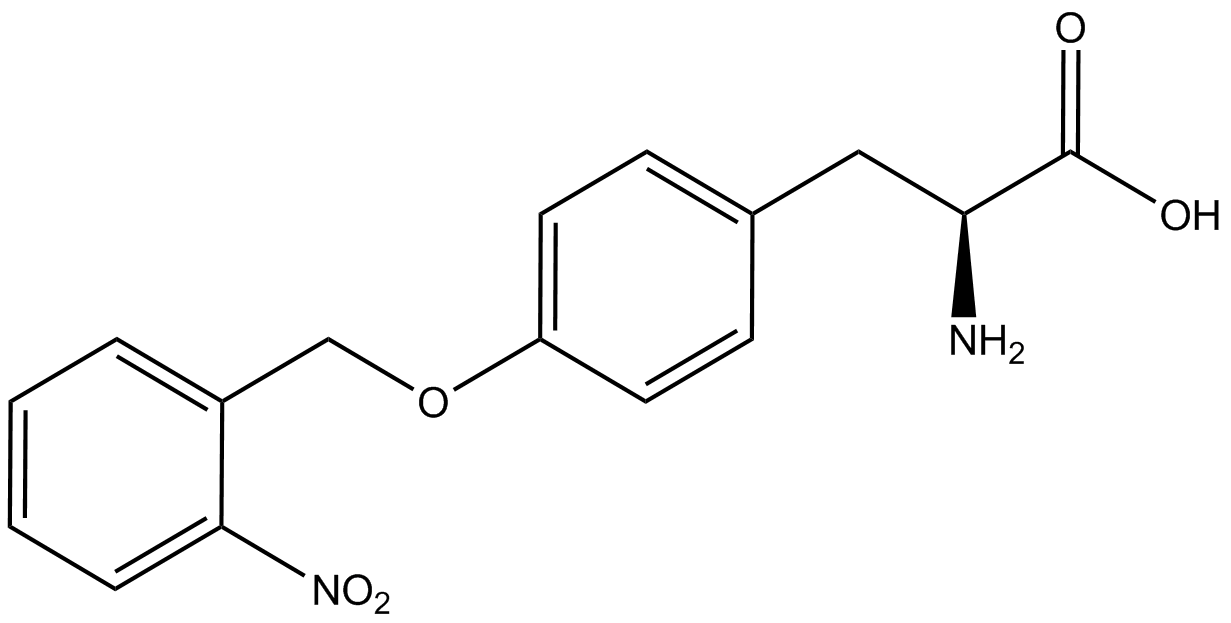
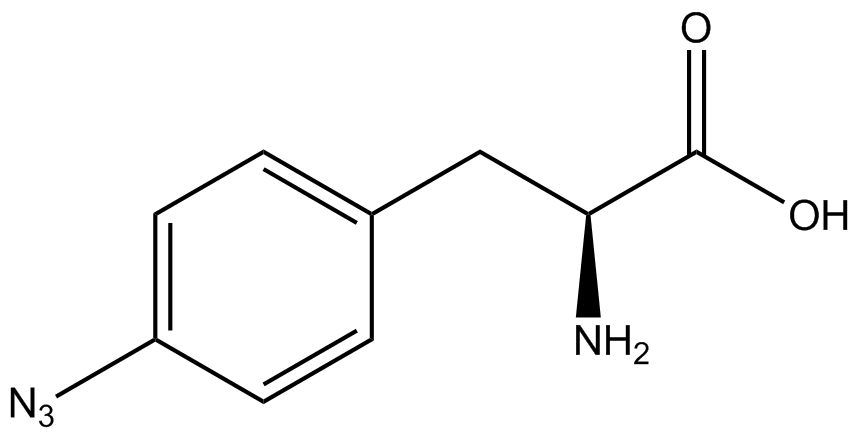
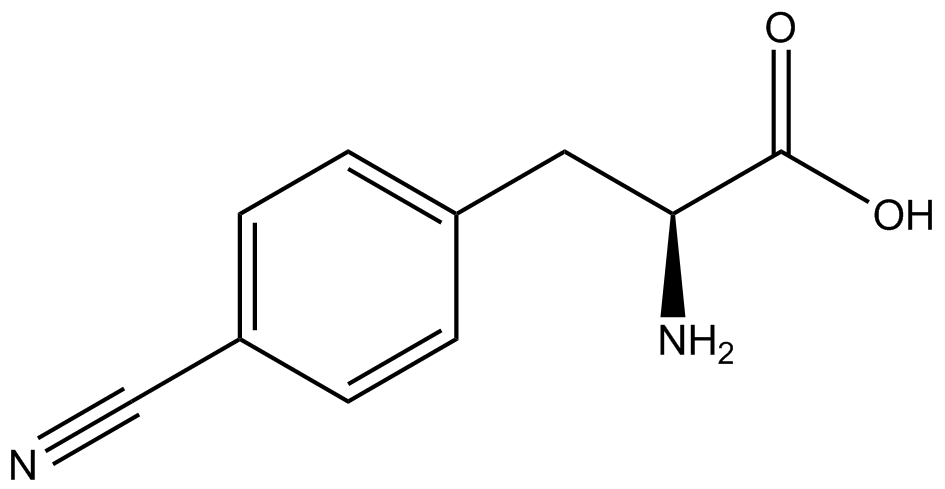
| - | Complications arise when the genetic code is recoded. In a normal bacterium, release factor RF1 is responsible for terminating translation when the ribosome reaches the amber stop codon. To avoid termination at a UAG amber codon, a strain of ''E. coli'' was engineered by the Church and Isaacs groups using MAGE and CAGE to remove all of the amber codons from the genome and knock out the RF1 gene (Isaacs et al. 2011). The resulting strain, called "amberless" ''E. coli'', has all amber codons free to code for any ncAA. | + | Complications arise when the genetic code is recoded. In a normal bacterium, release factor RF1 is responsible for terminating translation when the ribosome reaches the amber stop codon. To avoid termination at a UAG amber codon, a strain of ''E. coli'' was engineered by the Church and Isaacs groups using MAGE and CAGE to remove all of the amber codons from the genome and knock out the RF1 gene (Isaacs et al. 2011). The resulting strain, called "amberless" ''E. coli'', has all amber codons free to code for any ncAA. When both are present during translation, a synthetase with mutations that allow the acceptance of an ncAA, charges that ncAA onto its orthogonal tRNA with the amber codon's anticodon, CUA. |
=Experimental Design and Method= | =Experimental Design and Method= | ||
Revision as of 01:50, 17 October 2014
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"